Smart Agricultural Clinic: Egyptian Farmer Electronic Platform for the Future
Objective/Contributions:
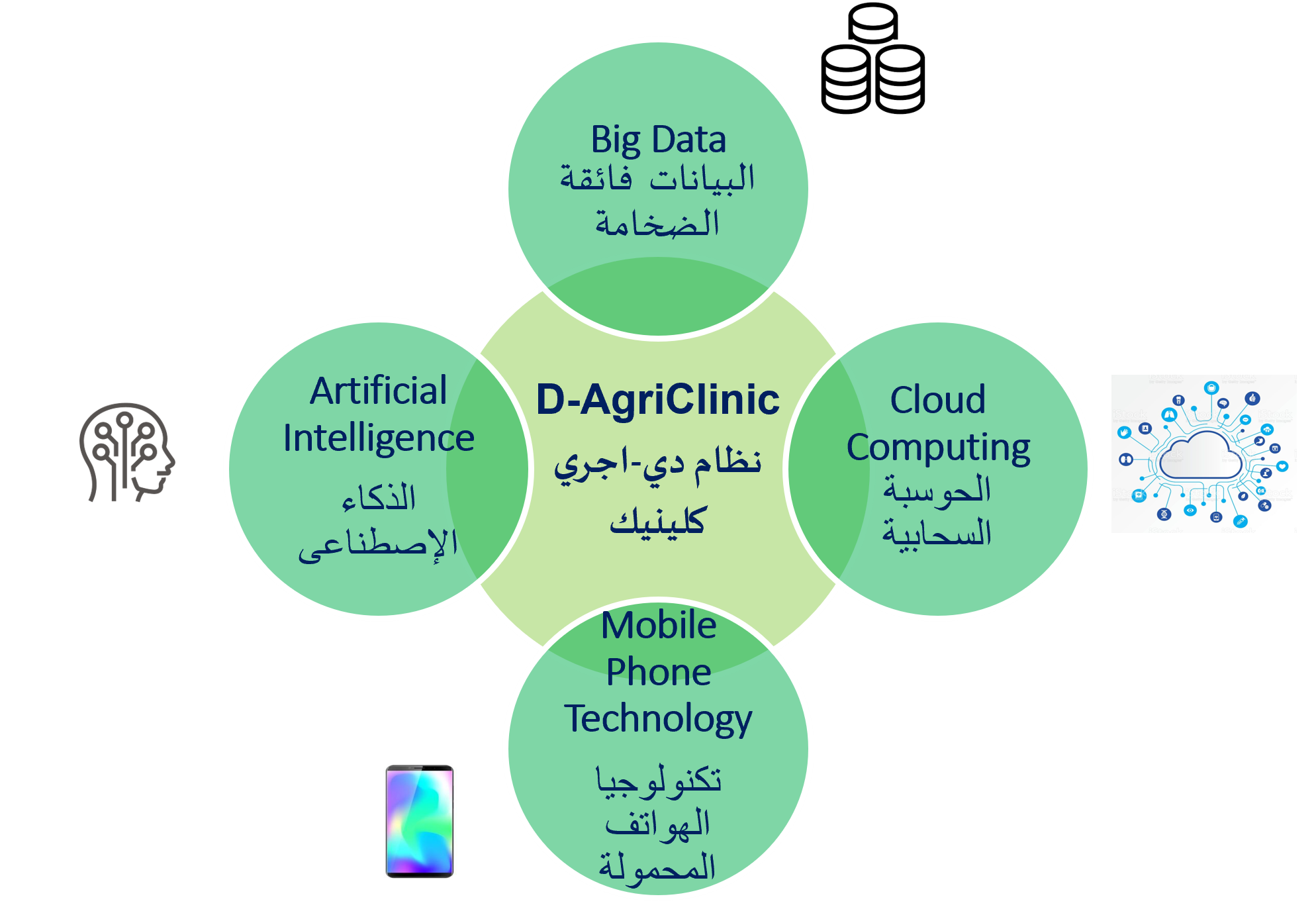
Smart agricultural clinic (SAC) aims to:
1) Provide an integrated end-to-end digital system to effectively deliver personalized agriculture extension and veterinary services, including best cultivation, fertilization and breeding practices, to farmers and animal producers through the use of mobile/handheld devices.
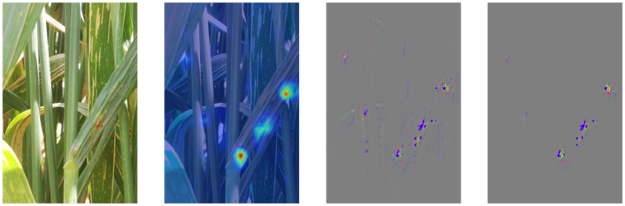
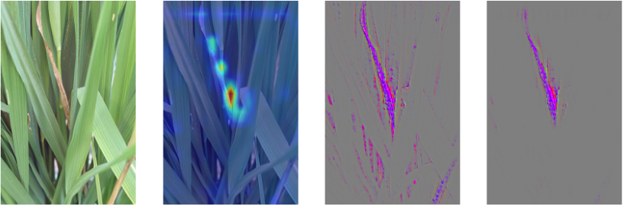
2) Use advanced computer vision and deep learning algorithms and RGB and hyperspectral imaging to detect and diagnose crop and animal diseases, suggest treatments and automatically point out access to solution resources.
3) Utilize Arabic Speech Recognition and Text to Speech audio technologies to facilitate communications between farmers/breeders and the SAC system.
4) Create an intelligent scalable cloud-based system that automatically manages the interaction between the SAC system components with a large number of farmers using advanced big data technologies/architectures.
5) Demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed system through an actual field deployment in a specific agriculture area to deliver extension services for a strategic crop (e.g. wheat and wheat rust) and veterinary services for a common type of animal disease (e.g. foot and mouth disease), study and analyze the results, and devise recommendations. The SAC system leverages existing hardware and physical infrastructures, whereas its beneficiaries cover a wide spectrum of user categories including small-scale farmers and animal breeders and government agencies, researchers and agro-technology solution providers. The expected results of the project include raising the efficiency of the agriculture and livestock production sectors, increasing farmer/breeder income, managing plant and animal disease, and contributing to the improvement of the overall national economy and the development of society as a whole.
Outcome:
- The Smart Agricultural Clinic team collected more than 50,000 recorded voices for 180 different sentences summarizing 115 hours and after applying data augmentation algorithms, the total recording length reached 805 hours as 160 farmers participated in the process of collecting the audio data.
- An Android-powered mobile application for voice data collection has been developed and tested to suit project-specific needs and be used by Extension Service Officers.
- The team researched and evaluated different algorithms for voice recognition and text-to-speech and evaluated their performance.
- The Smart Agricultural Clinic team developed protocols for image data collection and annotations to be used during the machine learning algorithms training phase of the project.
- The Smart Agricultural Clinic team has developed an image annotation web application for ARC experts to use to label the collected images.
- Two workshops were organized to collect image data to train ARC staff on how to obtain digital image data.
- The fields subject to research experiments were planned by the ARC team and the experiments were designed to show specific diseases of wheat, rice and barley during the imaging period.
- A WhatsApp support group was established to support more than 30 ARC scientists during the image collection process to discuss the quality of the data acquired on a daily basis.
- About one and a half million images were collected that proved their high quality through automatic and manual evaluation.
- A technical survey was conducted to evaluate artificial intelligence prediction algorithms that recognize diseases and determine their prevalence in wheat and rice crops.
- Preliminary results for disease identification using deep convolutional neural networks show a great performance, as the developed model scores 0.94 degrees F1 when tested.
- The Smart Agricultural Clinic team has digitized the guidelines for wheat cultivation and created videos for guidance and providing the best information to farmers.
- The Smart Agricultural Clinic team developed image data collection and annotation protocols for use throughout the project.