Breadcrumb
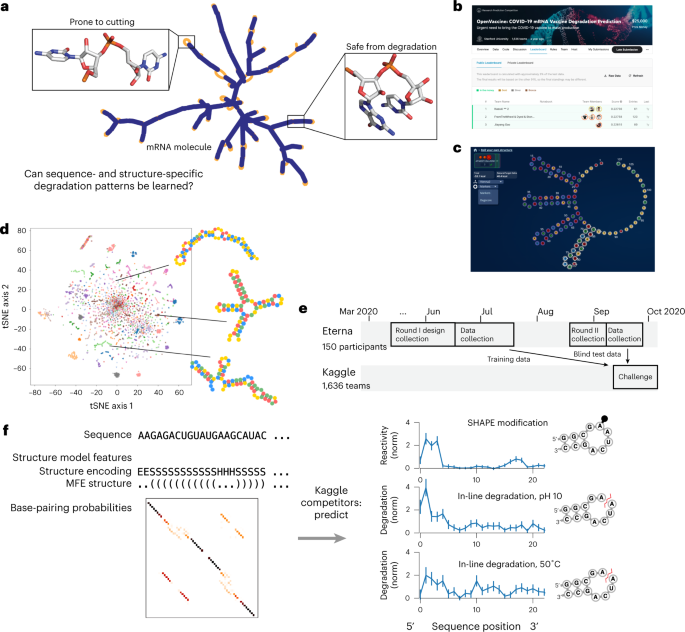
Deep learning models for predicting RNA degradation via dual crowdsourcing
Medicines based on messenger RNA (mRNA) hold immense potential, as evidenced by their rapid deployment as COVID-19 vaccines. However, worldwide distribution of mRNA molecules has been limited by their thermostability, which is fundamentally limited by the intrinsic instability of RNA molecules to a chemical degradation reaction called in-line hydrolysis. Predicting the degradation of an RNA molecule is a key task in designing more stable RNA-based therapeutics. Here, we describe a crowdsourced machine learning competition (‘Stanford OpenVaccine’) on Kaggle, involving single-nucleotide
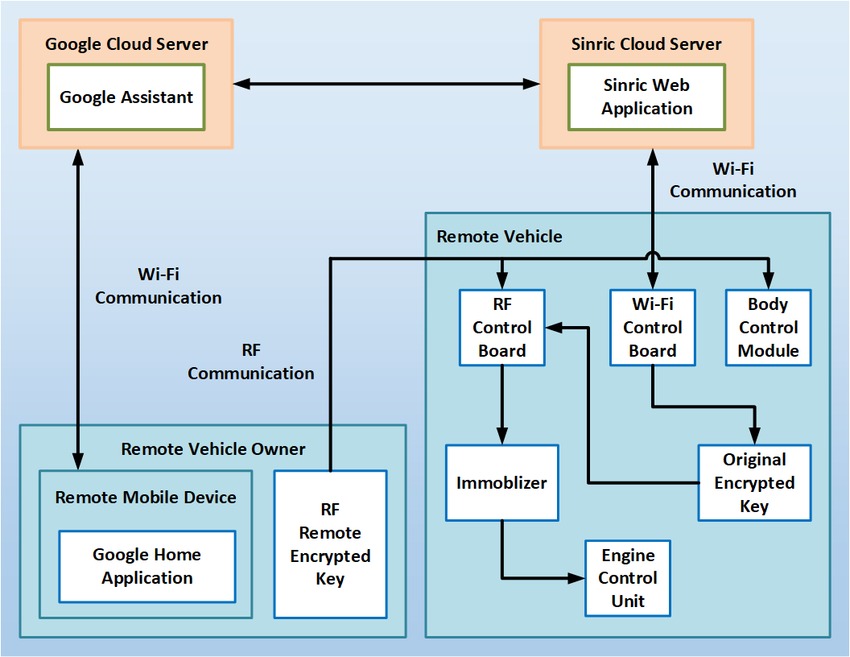
A Reliable Secure Architecture for Remote Wireless Controlling of Vehicle's Internal Systems based on Internet of Vehicles using RF and Wi-Fi
Internet of Vehicles is considered one of the most unprecedented outputs of the Internet of Things. No one has realized or even expected the rapidly-growing revolution regarding autonomous connected vehicles. Nowadays, Internet of Vehicles is massively progressing from Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks as a huge futuristic research and development discipline. This paper proposes a novel reliable and secure architecture for ubiquitously controlling remote connected cars' internal systems, such as engine, doors' locks, sunroof, horn, windows' and lights' control systems. The main contribution is that
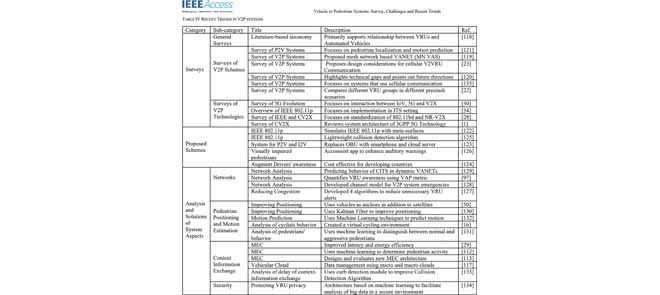
Vehicle to Pedestrian Systems: Survey, Challenges and Recent Trends
The accelerated rise of new technologies has reshaped the manufacturing industry of contemporary vehicles. Numerous technologies and applications have completely revolutionized the driving experience in terms of both safety and convenience. Although vehicles are now connected and equipped with a multitude of sensors and radars for collision avoidance, millions of people suffer serious accidents on the road, and unfortunately, the death rate is still on the rise. Collisions are still a dire reality for vehicles and pedestrians alike, which is why the improvement of collision prevention
Immunoinformatics approach of epitope prediction for SARS-CoV-2
Background: The novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) caused lethal infections worldwide during an unprecedented pandemic. Identification of the candidate viral epitopes is the first step in the design of vaccines against the viral infection. Several immunoinformatic approaches were employed to identify the SARS-CoV-2 epitopes that bind specifically with the major histocompatibility molecules class I (MHC-I). We utilized immunoinformatic tools to analyze the whole viral protein sequences, to identify the SARS-CoV-2 epitopes responsible for binding to the most frequent human leukocyte antigen (HLA)
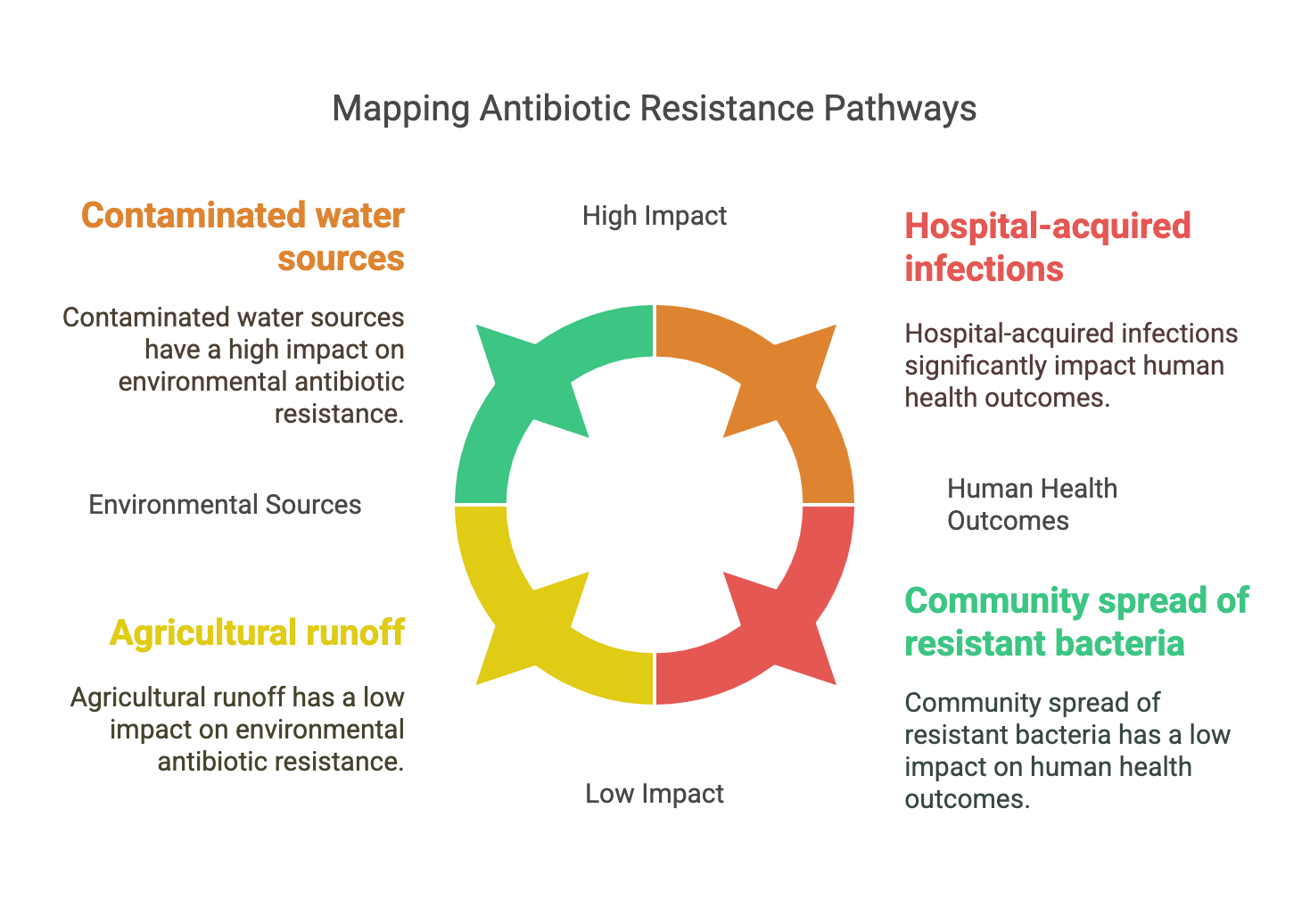
Tracking Antibiotic Resistance from the Environment to Human Health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the threats to our world according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Resistance is an evolutionary dynamic process where host-associated microbes have to adapt to their stressful environments. AMR could be classified according to the mechanism of resistance or the biome where resistance takes place. Antibiotics are one of the stresses that lead to resistance through antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). The resistome could be defined as the collection of all ARGs in an organism’s genome or metagenome. Currently, there is a growing body of evidence
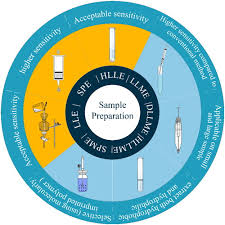
Analytical Methods for the Determination of Quercetin and Quercetin Glycosides in Pharmaceuticals and Biological Samples
Flavonoids are plant-derived compounds that have several health benefits, including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-mutagenic, and anti-carcinogenic effects. Quercetin is a flavonoid that is widely present in various fruits, vegetables, and drinks. Accurate determination of quercetin in different samples is of great importance for its potential health benefits. This review, is an overview of sample preparation and determination methods for quercetin in diverse matrices. Previous research on sample preparation and determination methods for quercetin are summarized, highlighting the
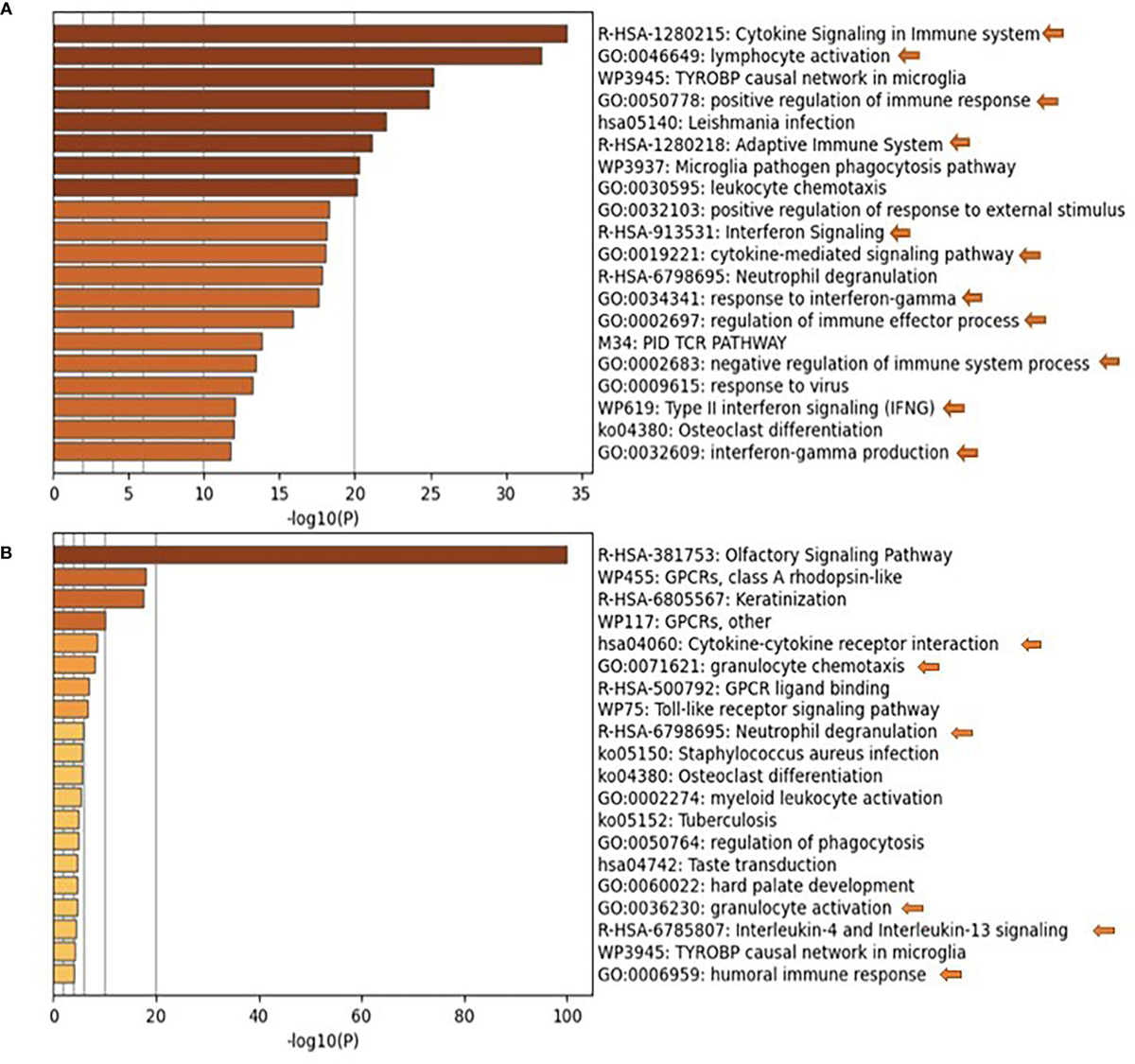
Identifying Immunological and Clinical Predictors of COVID-19 Severity and Sequelae by Mathematical Modeling
Since its emergence as a pandemic in March 2020, coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outcome has been explored via several predictive models, using specific clinical or biochemical parameters. In the current study, we developed an integrative non-linear predictive model of COVID-19 outcome, using clinical, biochemical, immunological, and radiological data of patients with different disease severities. Initially, the immunological signature of the disease was investigated through transcriptomics analysis of nasopharyngeal swab samples of patients with different COVID-19 severity versus control
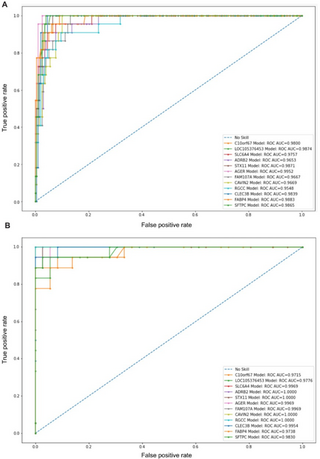
A feature selection-based framework to identify biomarkers for cancer diagnosis: A focus on lung adenocarcinoma
Lung cancer (LC) represents most of the cancer incidences in the world. There are many types of LC, but Lung Adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common type. Although RNA-seq and microarray data provide a vast amount of gene expression data, most of the genes are insignificant to clinical diagnosis. Feature selection (FS) techniques overcome the high dimensionality and sparsity issues of the large-scale data. We propose a framework that applies an ensemble of feature selection techniques to identify genes highly correlated to LUAD. Utilizing LUAD RNA-seq data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)
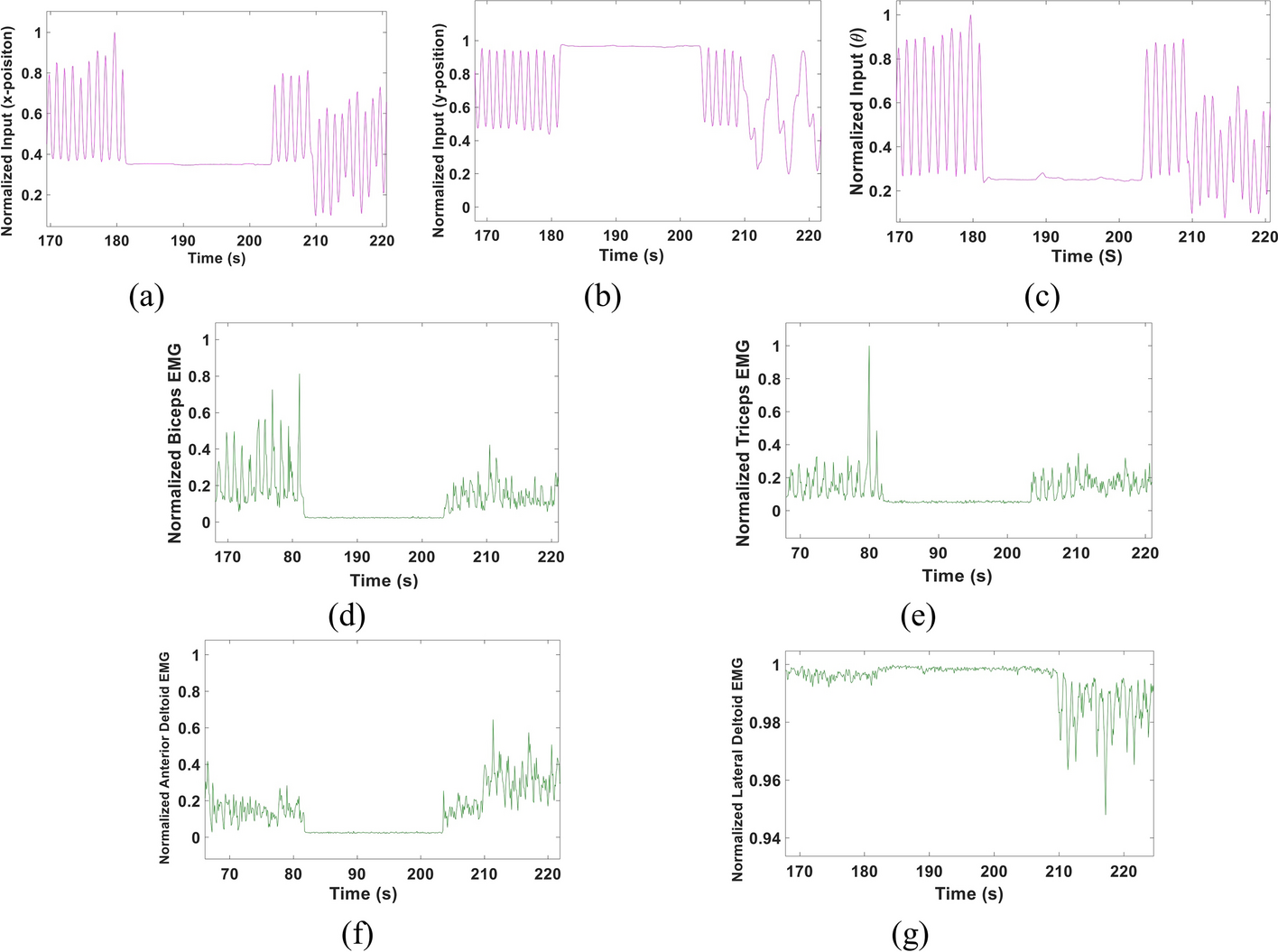
A multi-Kalman filter-based approach for decoding arm kinematics from EMG recordings
Background: Remarkable work has been recently introduced to enhance the usage of Electromyography (EMG) signals in operating prosthetic arms. Despite the rapid advancements in this field, providing a reliable, naturalistic myoelectric prosthesis remains a significant challenge. Other challenges include the limited number of allowed movements, lack of simultaneous, continuous control and the high computational power that could be needed for accurate decoding. In this study, we propose an EMG-based multi-Kalman filter approach to decode arm kinematics; specifically, the elbow angle (θ), wrist
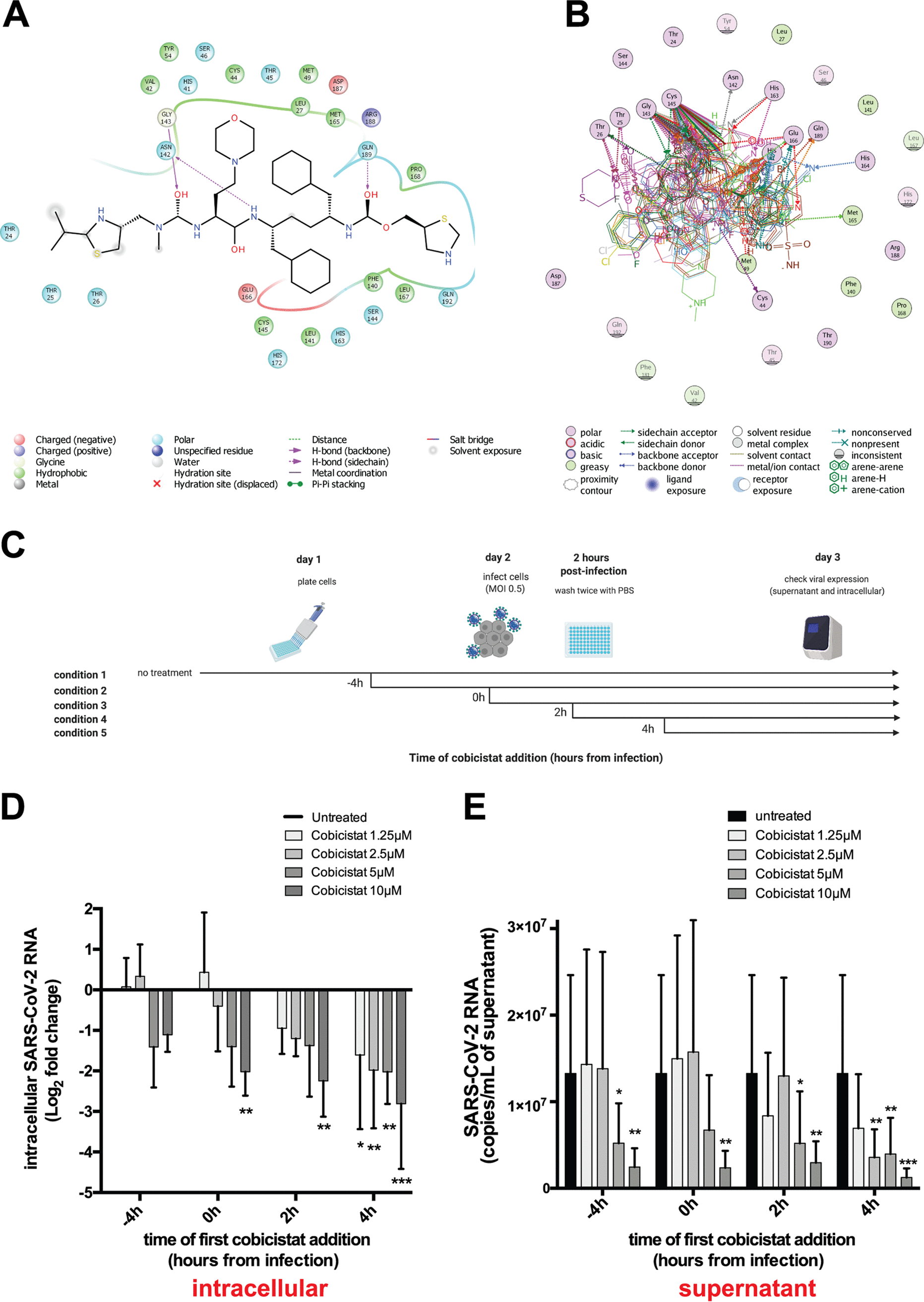
The FDA-Approved Drug Cobicistat Synergizes with Remdesivir to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Vitro and Decreases Viral Titers and Disease Progression in Syrian Hamsters
Combinations of direct-acting antivirals are needed to minimize drug resistance mutations and stably suppress replication of RNA viruses. Currently, there are limited therapeutic options against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and testing of a number of drug regimens has led to conflicting results. Here, we show that cobicistat, which is an FDA-approved drug booster that blocks the activity of the drug-metabolizing proteins cytochrome P450-3As (CYP3As) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication. Two independent cell-to-cell membrane fusion
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
