Breadcrumb

Scale-adaptive object tracking with diverse ensembles
Tracking by detection techniques have recently been gaining increased attention in visual object tracking due to their promising results in applications such as robotics, surveillance, traffic monitoring, to name a few. These techniques often employ semi-supervised appearance model where a set of samples are continuously extracted around the object to train a discriminant classifier between the object and the background whereas real-time performance is attained by using reduced object representations as in the case of the compressive tracking algorithm. However, because they rely on self
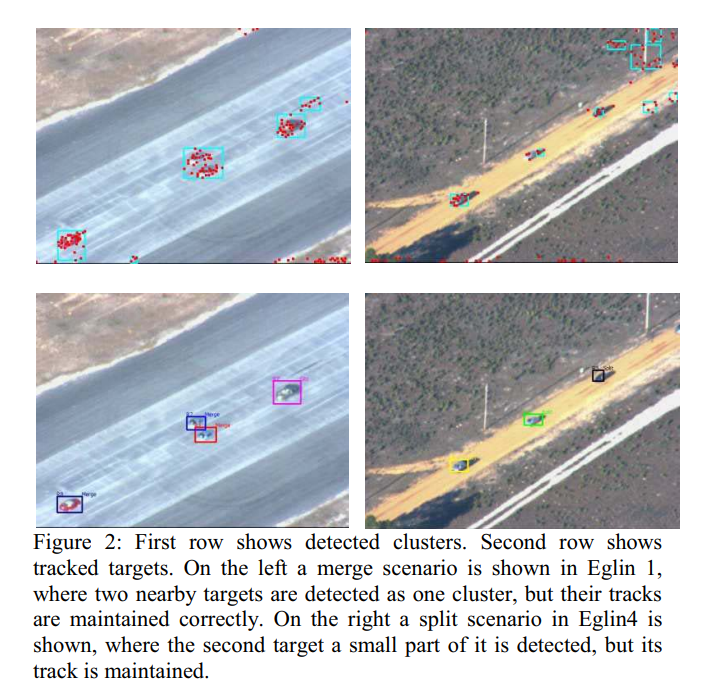

Robust autonomous visual detection and tracking of moving targets in UAV imagery
The use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for reconnaissance and surveillance applications has been steadily growing over the past few years. The operations of such largely autonomous systems rely primarily on the automatic detection and tracking of targets of interest. This paper presents a novel automatic multiple moving target detection and tracking framework that executes in real-time and is suitable for UAV imagery. The framework is based on image feature processing and projective geometry and is carried out on the following stages. First, outlier image features are computed with least
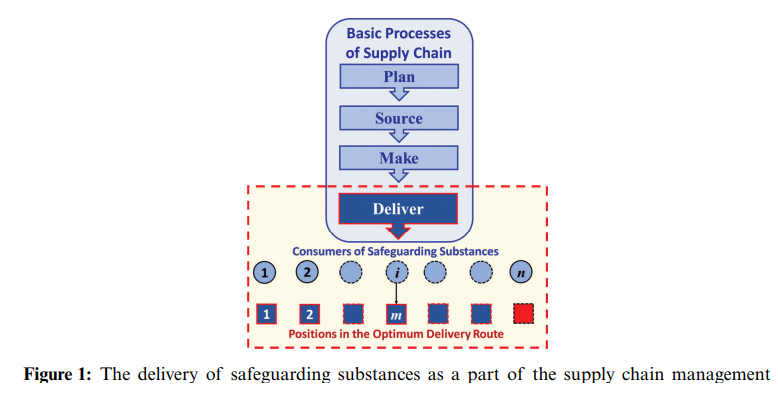
Managing Delivery of Safeguarding Substances as a Mitigation against Outbreaks of Pandemics
The optimum delivery of safeguarding substances is a major part of supply chain management and a crucial issue in the mitigation against the outbreak of pandemics. A problem arises for a decision maker who wants to optimally choose a subset of candidate consumers to maximize the distributed quantities of the needed safeguarding substances within a specic time period. A nonlinear binary mathematical programming model for the problem is formulated. The decision variables are binary ones that represent whether to choose a specic consumer, and design constraints are formulated to keep track of the

The overexpression of DNA repair genes in invasive ductal and lobular breast carcinomas: Insights on individual variations and precision medicine
In the era of precision medicine, analyzing the transcriptomic profile of patients is essential to tailor the appropriate therapy. In this study, we explored transcriptional differences between two invasive breast cancer subtypes; infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) and lobular carcinoma (LC) using RNA-Seq data deposited in the TCGA-BRCA project. We revealed 3854 differentially expressed genes between normal ductal tissues and IDC. In addition, IDC to LC comparison resulted in 663 differentially expressed genes. We then focused on DNA repair genes because of their known effects on patients'
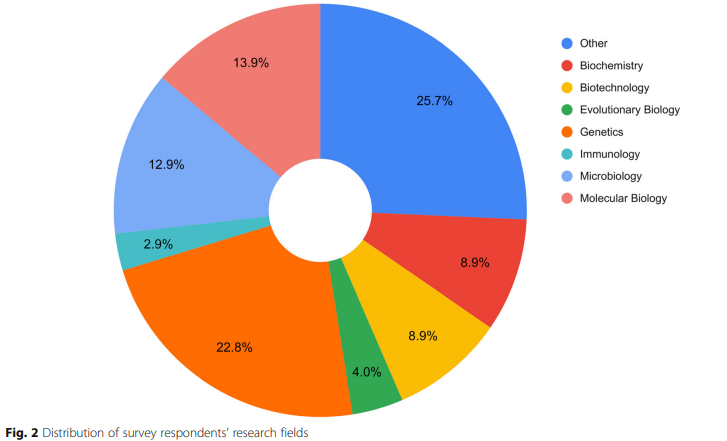
The H3ABioNet helpdesk: An online bioinformatics resource, enhancing Africa's capacity for genomics research
Background: Currently, formal mechanisms for bioinformatics support are limited. The H3Africa Bioinformatics Network has implemented a public and freely available Helpdesk (HD), which provides generic bioinformatics support to researchers through an online ticketing platform. The following article reports on the H3ABioNet HD (H3A-HD)'s development, outlining its design, management, usage and evaluation framework, as well as the lessons learned through implementation. Results: The H3A-HD evaluated using automatically generated usage logs, user feedback and qualitative ticket evaluation
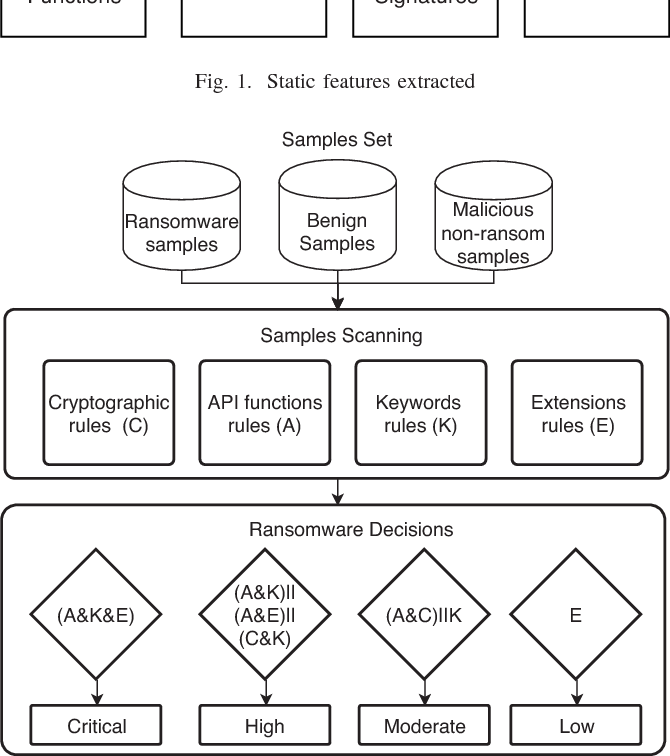
A new static-based framework for ransomware detection
Recently, ransomware attacks are on the rise hitting critical infrastructures and organizations globally. Ransomware uses advanced encryption techniques to encrypt important files on the targeted computer, then it requests payment to decrypt the encrypted files again. Therefore, the detection and prevention of ransomware attacks represent major challenges for security researchers. This research proposes a novel static-based rules ransomware detection framework. The decision rules of the proposed framework are based on static features extracted from the ransomware files. When scanned file
Decoding arm kinematics from EMG signals using Kalman filter
Myoelectric control of prosthetic arms provides a new hope for providing naturalistic movements to amputees. Extensive work has been made in recent years to use Electromyography (EMG) signals to enhance the operation of prosthetic arms. In this paper, we propose an EMG Kalman filter-based model, where we identify the relationship between the joint angles and recorded EMG signals. EMG signals were recorded from biceps and triceps muscles and used to train a Kalman filter decoder. We assessed the performance of the decoder by computing the correlation and the normalized root mean-square error
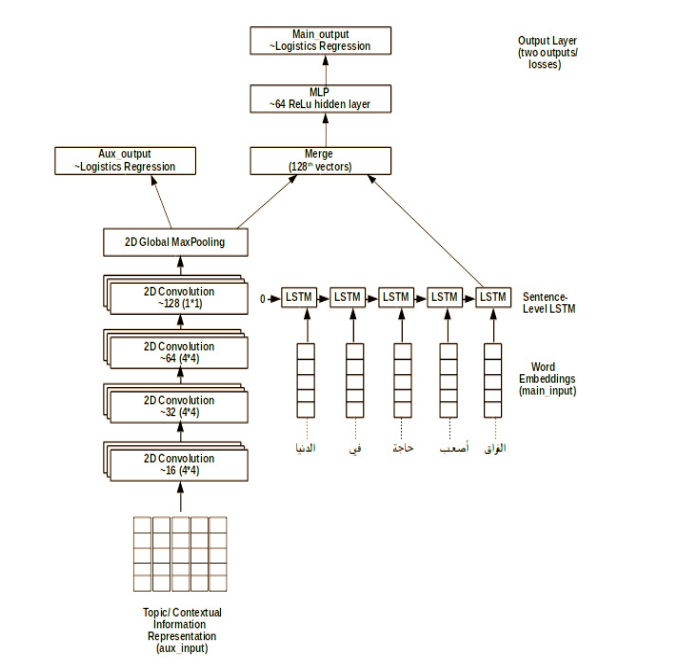
A Context Integrated Model for Multi-label Emotion Detection
This paper explores the impact of taking the environment within which a tweet is made, on the task of analyzing sentiment orientations of tweets produced by people in the same community. The paper proposes C-GRU (Context-aware Gated Recurrent Units), which extracts the contextual information (topics) from tweets and uses them as an extra layer to determine sentiments conveyed by the tweet. The proposed architecture learns direct co-relations between such information and the task's predication. The multi-modal model combines both outputs learnt (from topics and sentences) by learning the
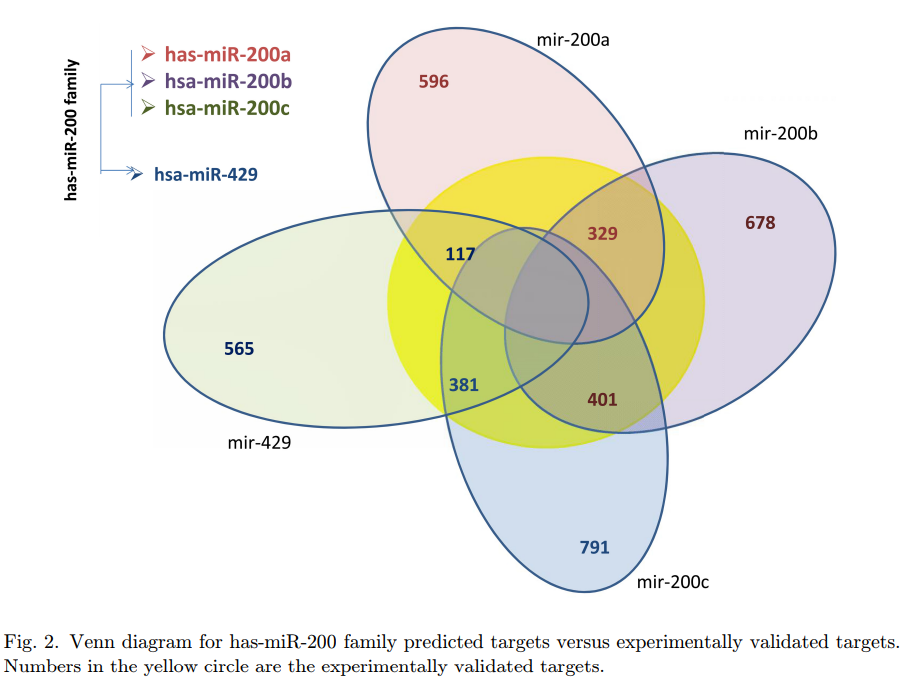
MicroTarget: MicroRNA target gene prediction approach with application to breast cancer
MicroRNAs are known to play an essential role in gene regulation in plants and animals. The standard method for understanding microRNA-gene interactions is randomized controlled perturbation experiments. These experiments are costly and time consuming. Therefore, use of computational methods is essential. Currently, several computational methods have been developed to discover microRNA target genes. However, these methods have limitations based on the features that are used for prediction. The commonly used features are complementarity to the seed region of the microRNA, site accessibility
Dyadchurn: Customer churn prediction using strong social ties
The increase in mobile phone subscriptions in recent years, has led to near market saturation in the telecom industry. As a result, it has become harder for telecom providers to acquire new customers, and the need for retaining existing ones has become of paramount importance. Because of fierce competition between different telecom providers and because the ease of which customers can move from one provider to another, all telecom service providers suffer from customer churn. In this paper, we propose a dyadic based churn prediction model, DyadChurn, where customer churn is modeled through
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 29
- Next page ››

