Breadcrumb
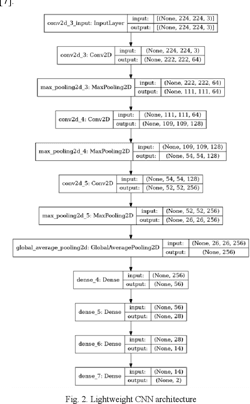
Light-Weight Food/Non-Food Classifier for Real-Time Applications
Today, automatic food/non-food classification became extremely important for many real-time applications, specifically since the pandemic of the COVID-19 virus. Such that the 'no food policy' now became applied more than ever to help decrease the spread of the COVID-19 virus. Consequently, many studies used deep neural networks for the food/non-food classification task, yet these deep neural networks were computationally expensive. As a result, in this paper, a lightweight Convolution Neural Network (CNN) is proposed and put into use for classifying foods and non-foods. Compared to prior
Analytical Methods for the Determination of Quercetin and Quercetin Glycosides in Pharmaceuticals and Biological Samples
Flavonoids are plant-derived compounds that have several health benefits, including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-mutagenic, and anti-carcinogenic effects. Quercetin is a flavonoid that is widely present in various fruits, vegetables, and drinks. Accurate determination of quercetin in different samples is of great importance for its potential health benefits. This review, is an overview of sample preparation and determination methods for quercetin in diverse matrices. Previous research on sample preparation and determination methods for quercetin are summarized, highlighting the
Comprehensive machine learning models for predicting therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes utilizing molecular and biochemical features in rats
Introduction: With the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), there is an urgent need to discover effective therapeutic targets for this complex condition. Coding and non-coding RNAs, with traditional biochemical parameters, have shown promise as viable targets for therapy. Machine learning (ML) techniques have emerged as powerful tools for predicting drug responses. Method: In this study, we developed an ML-based model to identify the most influential features for drug response in the treatment of type 2 diabetes using three medicinal plant-based drugs (Rosavin, Caffeic
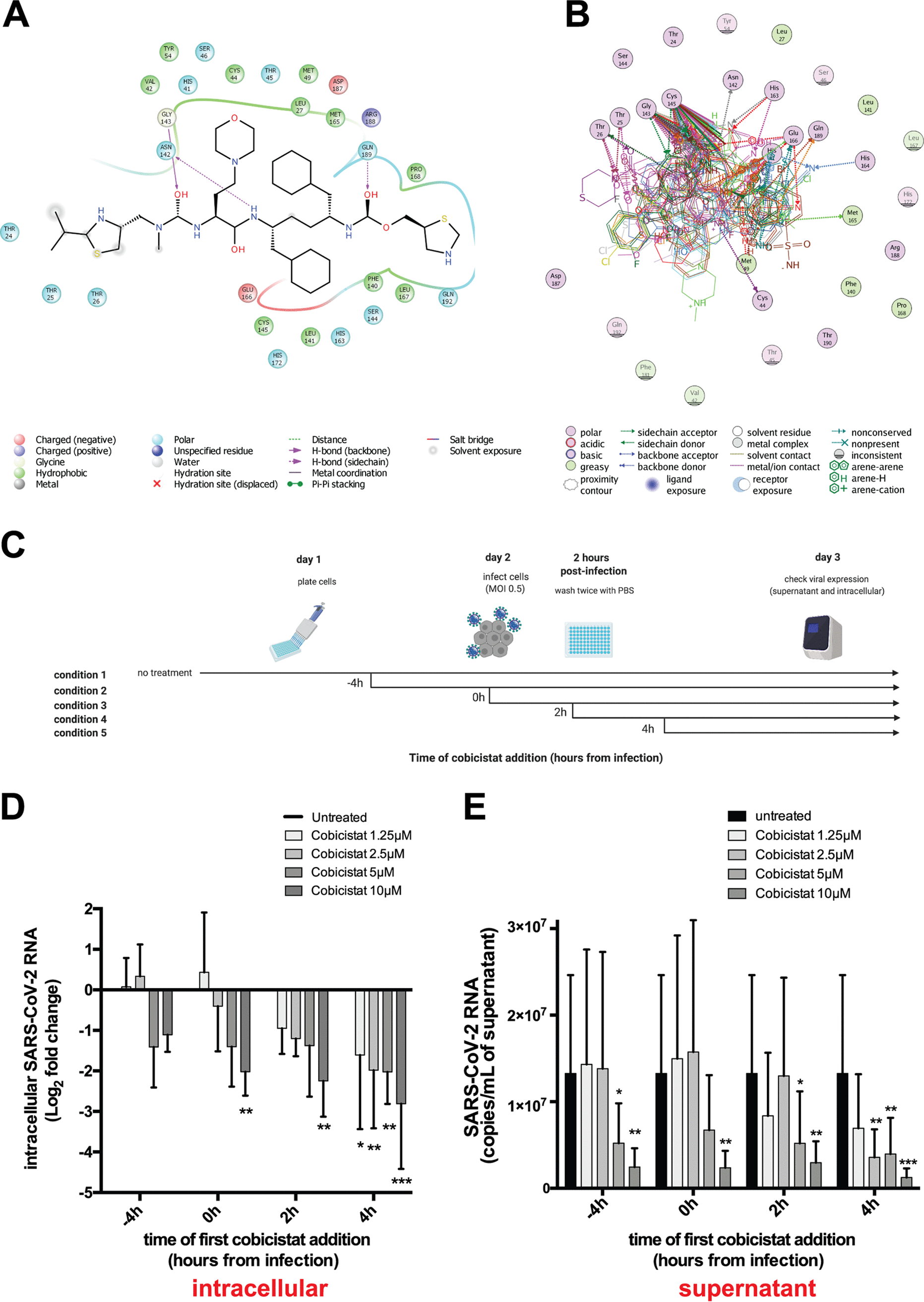
The FDA-Approved Drug Cobicistat Synergizes with Remdesivir to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Vitro and Decreases Viral Titers and Disease Progression in Syrian Hamsters
Combinations of direct-acting antivirals are needed to minimize drug resistance mutations and stably suppress replication of RNA viruses. Currently, there are limited therapeutic options against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and testing of a number of drug regimens has led to conflicting results. Here, we show that cobicistat, which is an FDA-approved drug booster that blocks the activity of the drug-metabolizing proteins cytochrome P450-3As (CYP3As) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication. Two independent cell-to-cell membrane fusion
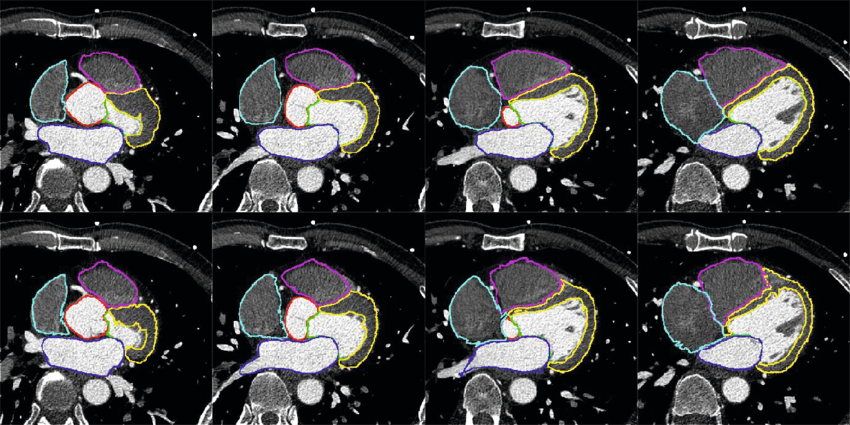
Myocardial segmentation using constrained multi-seeded region growing
Multi-slice short-axis acquisitions of the left ventricle are fundamental for estimating the volume and mass of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI scans. Manual segmentation of the myocardium in all time frames per each cross-section is a cumbersome task. Therefore, automatic myocardium segmentation methods are essential for cardiac functional analysis. Region growing has been proposed to segment the myocardium. Although the technique is simple and fast, non uniform intensity and low-contrast interfaces of the myocardium are major challenges of the technique that limit its use in myocardial
Improved Semantic Segmentation of Low-Resolution 3D Point Clouds Using Supervised Domain Adaptation
One of the key challenges in applying deep learning to solve real-life problems is the lack of large annotated datasets. Furthermore, for a deep learning model to perform well on the test set, all samples in the training and test sets should be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), which means that test samples should be similar to the samples that were used to train the model. In many cases, however, the underlying training and test set distributions are different. In such cases, it is common to adapt the test samples by transforming them to their equivalent counterparts in the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
