Breadcrumb
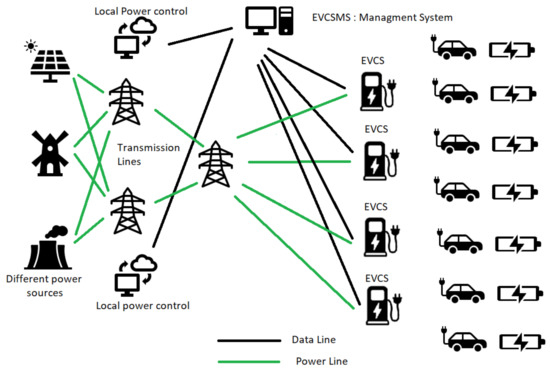
Intrusion Detection for Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS)
The market for Electric Vehicles (EVs) has expanded tremendously as seen in the recent Conference of the Parties 27 (COP27) held at Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt in November 2022. This needs the creation of an ecosystem that is user-friendly and secure. Internet-connected Electric Vehicle Charging Stations (EVCSs) provide a rich user experience and add-on services. Eventually, the EVCSs are connected to a management system, which is the Electric Vehicle Charging Station Management System (EVCSMS). Attacking the EVCS ecosystem remotely via cyberattacks is rising at the same rate as physical attacks
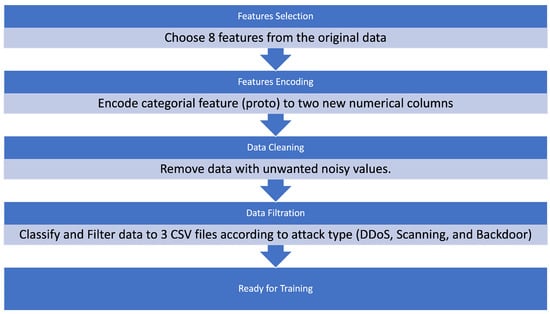
Anomaly Detection of Zero-Day Attacks Based on CNN and Regularization Techniques
The rapid development of cyberattacks in the field of the Internet of things (IoT) introduces new security challenges regarding zero-day attacks. Intrusion-detection systems (IDS) are usually trained on specific attacks to protect the IoT application, but the attacks that are yet unknown for IDS (i.e., zero-day attacks) still represent challenges and concerns regarding users’ data privacy and security in those applications. Anomaly-detection methods usually depend on machine learning (ML)-based methods. Under the ML umbrella are classical ML-based methods, which are known to have low
Study of LiDAR Segmentation and Model’s Uncertainty using Transformer for Different Pre-trainings∗
For the task of semantic segmentation of 2D or 3D inputs, Transformer architecture suffers limitation in the ability of localization because of lacking low-level details. Also for the Transformer to function well, it has to be pre-trained first. Still pre-training the Transformer is an open area of research. In this work, Transformer is integrated into the U-Net architecture as (Chen et al., 2021). The new architecture is trained to conduct semantic segmentation of 2D spherical images generated from projecting the 3D LiDAR point cloud. Such integration allows capturing the the local
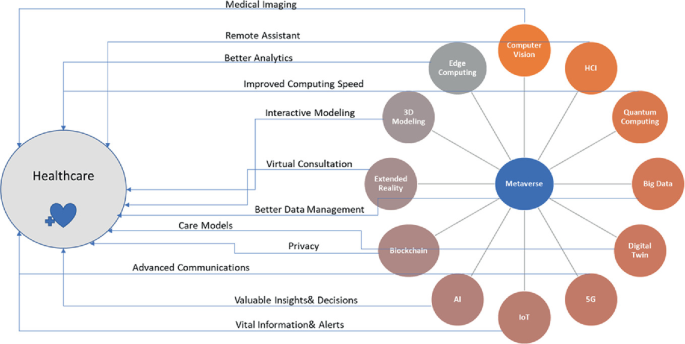
The Implication of Metaverse in the Traditional Medical Environment and Healthcare Sector: Applications and Challenges
There are a lot of studies that have been presenting the idea of the metaverse since 2021. It's the term for the next-generation mobile computing platform, which will be extensively utilized in the future and refers to the internet accessed through VR and AR glasses. The range of illnesses people face today is different from what it was decades ago. Cancer, COPD, diabetes, heart disease, and asthma are just few of the many non-communicable diseases that pose a serious risk to human health in the modern world. As a result, efforts toward chronic disease prevention and management need to be
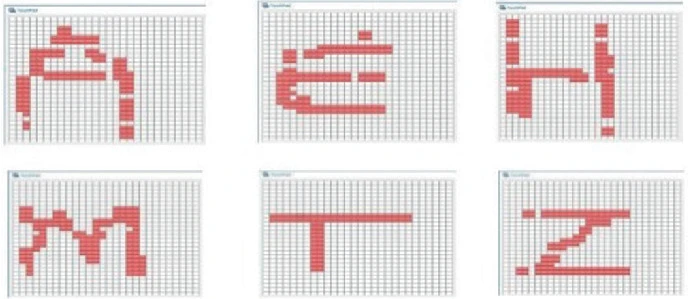
Handwriting Letter Recognition on the Steering Wheel Switches
Automotive steering wheel switches technologies are evolving to give easy access to the several interior or exterior functions. This is worth a deep analysis for the current trends in order not to become unintuitive for the driver due to the increasing number of buttons. Through different technologies particularly the capacitive ones, range of innovative solutions have been developed like reconfigurable buttons on the steering wheel to offer commanding several functions twice or triple the number of allocated push buttons. In this paper, we address the problem in a different freely way to
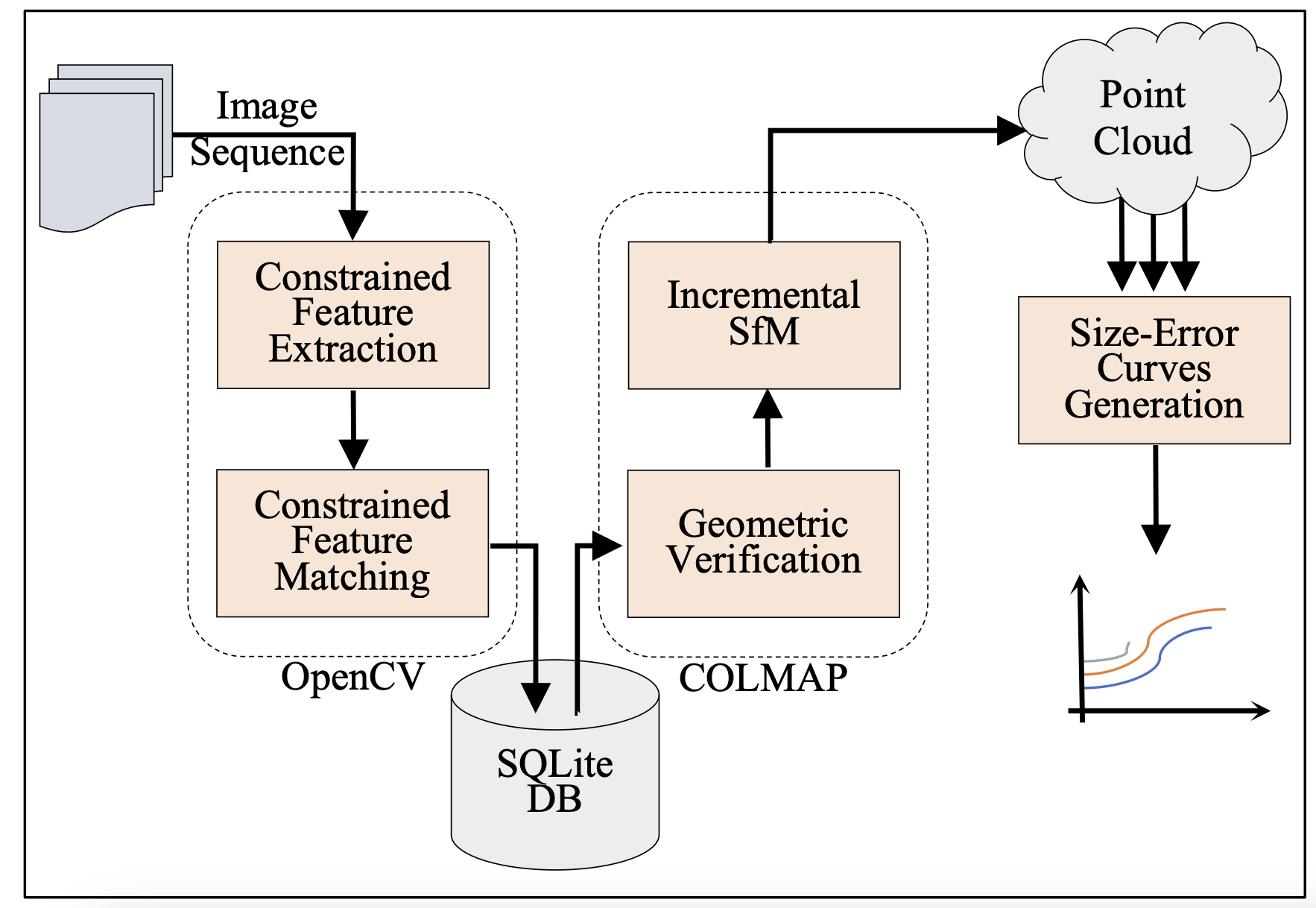
Towards a Fair Evaluation of Feature Extraction Algorithms Robustness in Structure from Motion
Structure from Motion is a pipeline for 3D reconstruction in which the true geometry of an object or a scene is inferred from a sequence of 2D images. As feature extraction is usually the first phase in the pipeline, the reconstruction quality depends on the accuracy of the feature extraction algorithm. Fairly evaluating the robustness of feature extraction algorithms in the absence of reconstruction ground truth is challenging due to the considerable number of parameters that affect the algorithms' sensitivity and the tradeoff between reconstruction size and error. The evaluation methodology

Integrated Analysis of Bulk and Single-Cell Transcriptomics in Cervical Cancer: Insights into BPGM, EGLN3, and SUN1
Cervical cancer (CC) is considered a significant global health threat to women therefore there is a need for personalized treatment strategy based on individual-specific gene expression patterns to enhance recovery and survival rates. Although a few studies have linked bisphosphoglycerate mutase (BPGM) expression with CC, its precise role in CC progression remains unclear. In this study, we conducted an integrated analysis for both bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing data to investigate the involvement of BPGM in CC. On the bulk RNA level, the Wilcoxon test result showed a significant
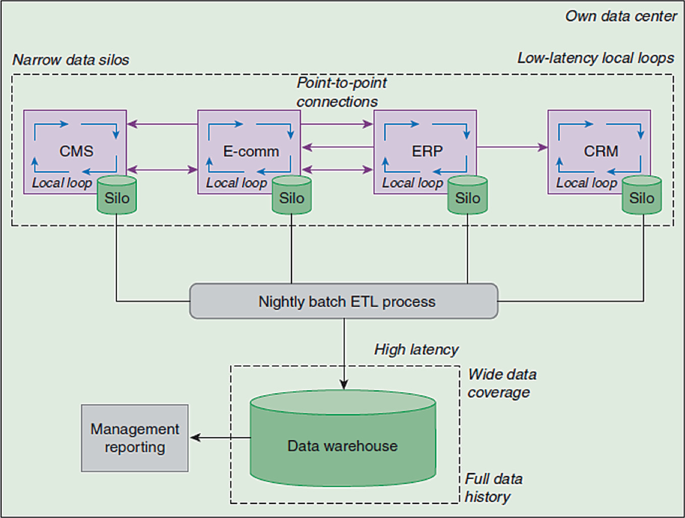
Walk Through Event Stream Processing Architecture, Use Cases and Frameworks Survey
Nowadays events stream processing is one of the top demanding field(s) because of the business urgent need for ongoing real time analytics & decisions. Most business domains avail huge amount of data aiming to make use of each data point efficiently. Corporate(s) have a cloud of events vary from internal business transactions, social media feeds, IoT devices logs,.. etc. In this paper we would discuss state of the art event stream processing technologies using cloud of events by summarizing event stream processing definition, data flow architectures, common use cases, frameworks and
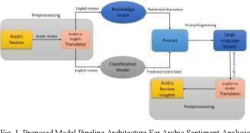
Sentiment Analysis for Arabic Product Reviews using LLMs and Knowledge Graphs
The exploration of sentiment analysis in multilingual contexts, particularly through the integration of deep learning techniques and knowledge graphs, represents a significant advance in language processing research. This study specifically concentrates on the Arabic language, addressing the challenges presented by its morphological complexity. While the primary focus is Arabic, the research also includes a comprehensive review of related work in other languages such as Bangla and Chinese. This contextualizes the challenges and solutions found in Arabic sentiment analysis within a broader

Automated multi-class skin cancer classification through concatenated deep learning models
Skin cancer is the most annoying type of cancer diagnosis according to its fast spread to various body areas, so it was necessary to establish computer-assisted diagnostic support systems. State-of-the-art classifiers based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are used to classify images of skin cancer. This paper tries to get the most accurate model to classify and detect skin cancer types from seven different classes using deep learning techniques; ResNet-50, VGG-16, and the merged model of these two techniques through the concatenate function. The performance of the proposed model was
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
