Breadcrumb
A Comparative Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Brain Tumor Segmentation
A brain tumor is an extremely hazardous illness that can affect people of any age. Less than 50% of individuals with brain cancer have a chance of surviving. As a result, precise segmentation of brain tumors is crucial for the diagnosis, planning of the course of treatment, and tracking of the tumor growth. Deep Learning (DL) models can increase the precision and speed of brain tumor diagnosis by precisely segmenting and identifying tumor locations in medical pictures. In this study, we compare four DL models for segmenting brain tumors, the 3D U-Net, the Attention Res U-Net, the U-Net++, and
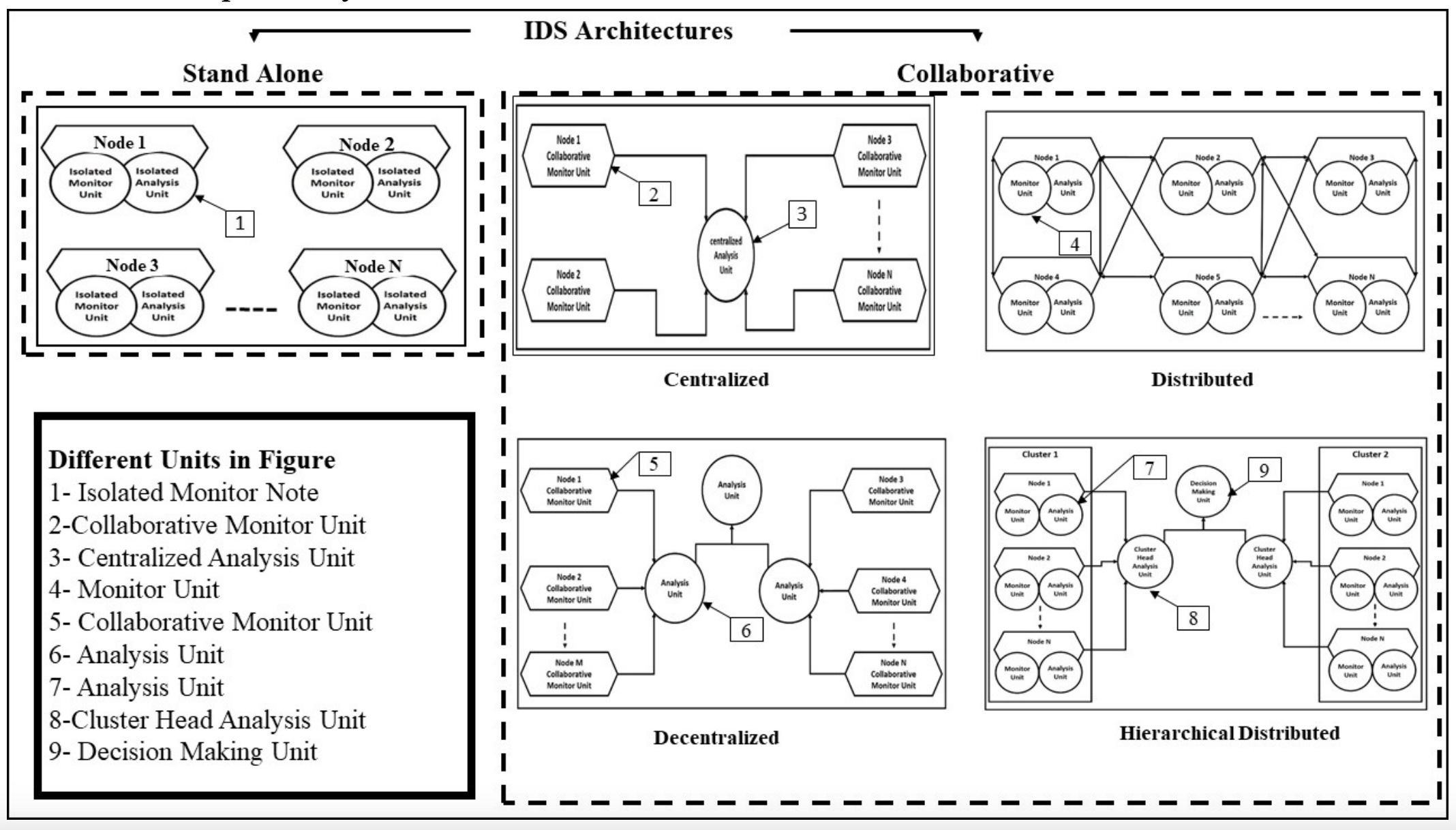
MSDAR: Multi-Stage Dynamic Architecture Intrusion Detection System
Ad hoc networks have been through extensive research in the last decade. Even with their desirable characteristics, major issues related to their security need to be considered. Various security solutions have been proposed to reduce the risks of malicious actions. They mainly focus on key management, authentication, secure localization, and aggregation techniques. These techniques have been proposed to secure wireless communications but they can only deal with external threats. Therefore, they are considered the first line of defense. Intrusion detection systems are always required to
In-Silico targeting of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 for drug and natural products repurposing
Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) has a protecting role for SARS-CoV-2 replication by inhibiting the expansion of autophagosomes inside the cell. NSP6 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response by binding to Sigma receptor 1 (SR1). Nevertheless, NSP6 crystal structure is not solved yet. Therefore, NSP6 is considered a challenging target in Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Herein, we utilized the high quality NSP6 model built by AlphaFold in our study. Targeting a putative NSP6 binding site is believed to inhibit the SR1-NSP6 protein-protein interactions. Three databases were

Anomaly Detection Based on CNN and Regularization Techniques Against Zero-Day Attacks in IoT Networks
The fast expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the technology and communication industries necessitates a continuously updated cyber-security mechanism to keep protecting the systems' users from any possible attack that might target their data and privacy. Botnets pose a severe risk to the IoT, they use malicious nodes in order to compromise other nodes inside the network to launch several types of attacks causing service disruption. Examples of these attacks are Denial of Service (DoS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Service Scan, and OS Fingerprint. DoS and DDoS attacks are the
ArabicQuest: Enhancing Arabic Visual Question Answering with LLM Fine-Tuning
In an attempt to bridge the semantic gap between language understanding and visuals, Visual Question Answering (VQA) offers a challenging intersection of computer vision and natural language processing. Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable ability in natural language understanding; however, their use in VQA, particularly for Arabic, is still largely unexplored. This study aims to bridge this gap by examining how well LLMs can improve VQA models. We use state-of-the-art AI algorithms on datasets from multiple fields, including electric devices, Visual Genome, RSVQA, and ChartsQA
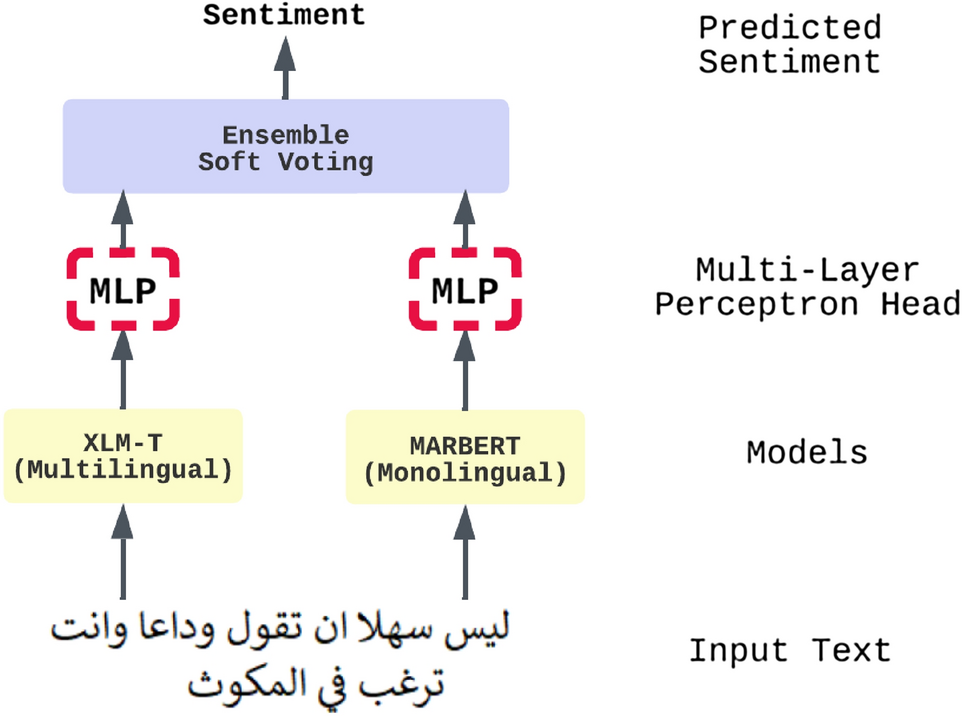
An ensemble transformer-based model for Arabic sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis is a common and challenging task in natural language processing (NLP). It is a widely studied area of research; it facilitates capturing public opinions about a topic, product, or service. There is much research that tackles English sentiment analysis. However, the research in the Arabic language is behind other high-resource languages. Recently, models such as bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) and generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) have been widely used in many NLP tasks; it significantly improved performance in NLP tasks, especially
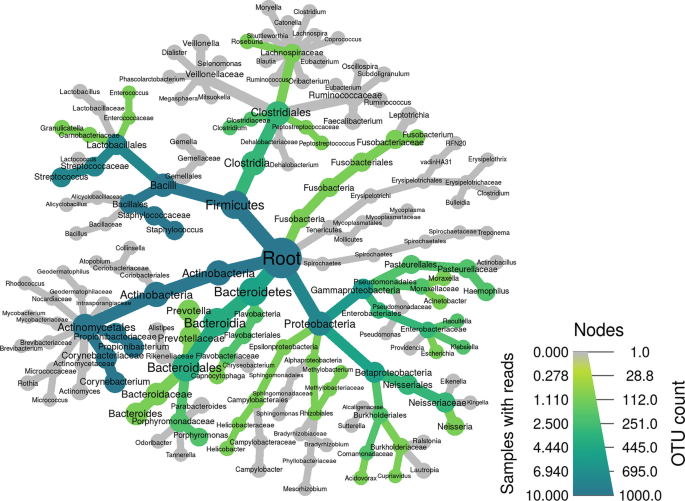
Comprehensive Guideline for Microbiome Analysis Using R
The need for a comprehensive consolidated guide for R packages and tools that are used in microbiome data analysis is significant; thus, we aim to provide a detailed step-by-step dissection of the most used R packages and tools in the field of microbiome data integration and analysis. The guideline aims to be a user-friendly simplification and tutorial on five main packages, namely phyloseq, MegaR, DADA2, Metacoder, and microbiomeExplorer due to their high efficiency and benefit in microbiome data analysis. © 2023, The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
On The Arabic Dialects' Identification: Overcoming Challenges of Geographical Similarities Between Arabic dialects and Imbalanced Datasets
Arabic is one of the world's richest languages, with a diverse range of dialects based on geographical origin. In this paper, we present a solution to tackle subtask 1 (Country-level dialect identification) of the Nuanced Arabic Dialect Identification (NADI) shared task 2022 achieving third place with an average macro F1 score between the two test sets of 26.44%. In the preprocessing stage, we removed the most common frequent terms from all sentences across all dialects, and in the modeling step, we employed a hybrid loss function approach that includes Weighted cross entropy loss and Vector
Ad-hoc Networks Performance based on Routing Protocol Type
There are many situations where there is a need for certain devices to be connected in a network independently without having a heavy infrastructure or human interventions to configure and connect them. This type of network is called ad-hoc networks. The key concern with such networks is how nodes communicate with each other and exchange information efficiently and securely. The issue with ad hoc networks is that traditional routing protocols are not suitable for such networks. In this paper, the performance of specific routing protocols for ad hoc networks will be evaluated. © 2022 IEEE.
Keyed Watermarks: A Fine-grained Tracking of Event-time in Apache Flink
Big Data Stream processing engines such as Apache Flink use windowing techniques to handle unbounded streams of events. Gathering all pertinent input within a window is crucial for event-time windowing since it affects how accurate results are. A significant part of this process is played by watermarks, which are unique timestamps that show the passage of events in time. However, the current watermark generation method in Apache Flink, which works at the level of the input stream, tends to favor faster sub-streams, resulting in dropped events from slower sub-streams. In our analysis, we found
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
