Breadcrumb

Improving the Performance of Semantic Text Similarity Tasks on Short Text Pairs
Training semantic similarity model to detect duplicate text pairs is a challenging task as almost all of datasets are imbalanced, by data nature positive samples are fewer than negative samples, this issue can easily lead to model bias. Using traditional pairwise loss functions like pairwise binary cross entropy or Contrastive loss on imbalanced data may lead to model bias, however triplet loss showed improved performance compared to other loss functions. In triplet loss-based models data is fed to the model as follow: Anchor sentence, positive sentence and negative sentence. The original data
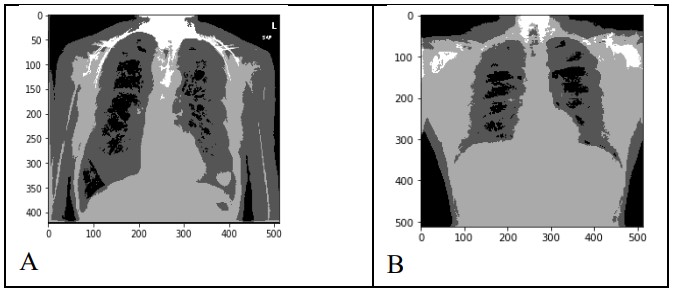
Using X-ray Image Processing Techniques to Improve Pneumonia Diagnosis based on Machine Learning Algorithms
the diagnosis of chest disease depends in most cases on the complex grouping of clinical data and images. According to this complexity, the debate is increased between researchers and doctors about the efficient and accurate method for chest disease prediction. The purpose of this research is to enhance the first handling of the patient data to get a prior diagnosis of the disease. The main problem in such diagnosis is the quality and quantity of the images.In this paper such problem is solved by utilizing some methods of preprocessing such as augmentation and segmentation. In addition are

Comparative Analysis of a Generalized Heart Localization Model: Assessing Its Efficacy Against Specialized Models
Heart localization holds significant importance in the process of the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases. Additionally, it plays an important role in planning the cardiac scanning protocol. This research focuses on heart localization by employing the multi-label classification task with the utilization of RES-Net50. The primary objective is to predict the slices containing the heart and determine its endpoint. To ensure high-quality data, we implement filtering techniques and perform up-sampling during the pre-processing stage. Two experiments were conducted to assess different
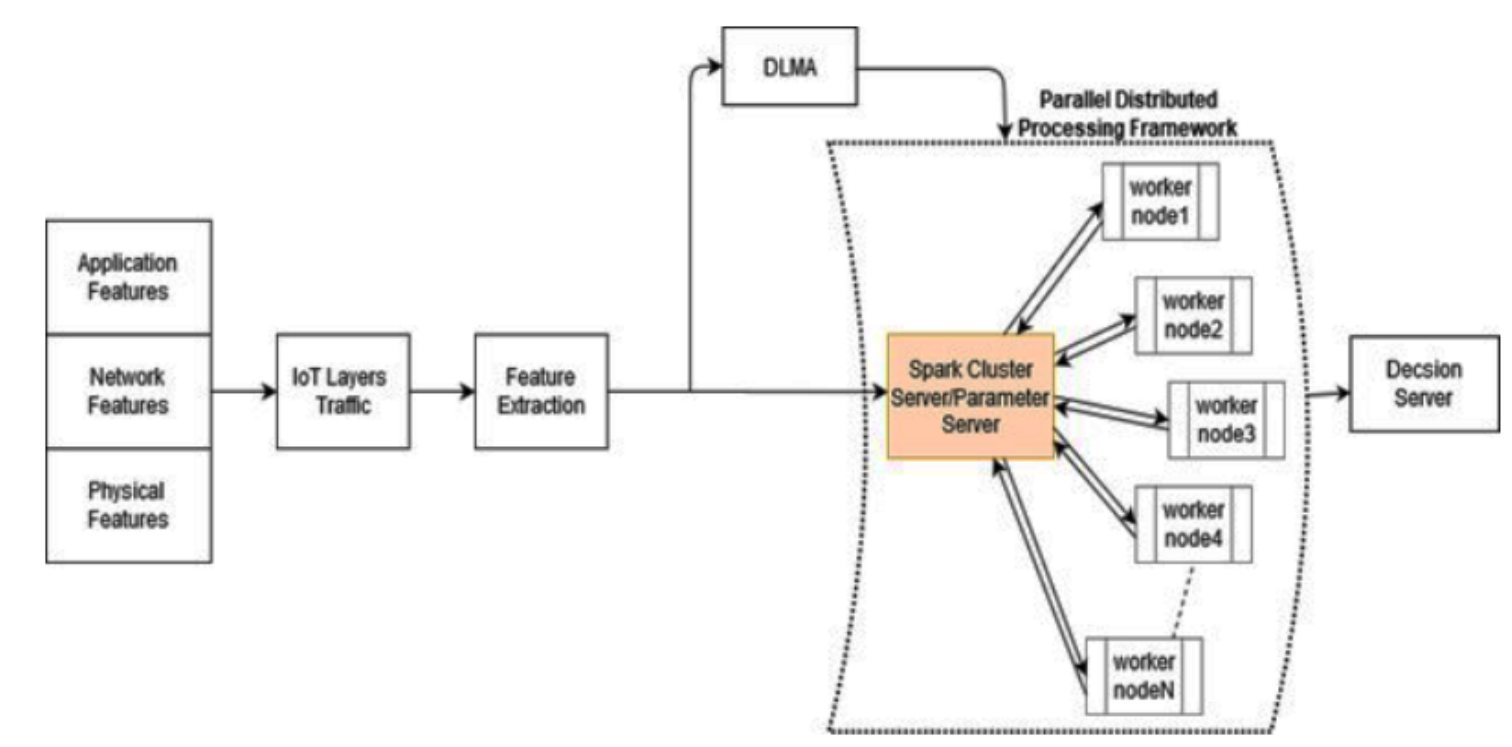
Cross-Layer Distributed Attack Detection Model for the IoT
The security of IoT that is based on layered approaches has shortcomings such as the redundancy, inflexibility, and inefficiently of security solutions. There are many harmful attacks in IoT networks such as DoS and DDoS attacks, which can compromise the IoT architecture in all layers. Consequently, cross layer approach is proposed as an effective and practical security defending mechanism. Cross-layer distributed attack detection model (CLDAD) is proposed to enhance security solutions for IoT environments. CLDAD presents a general detection method of DDoS in sensing layer, network layer, and

A distributed real-time recommender system for big data streams
Recommender Systems (RS) play a crucial role in our lives. As users become continuously connected to the internet, they are less tolerant of obsolete recommendations made by an RS. Online RS has to address three requirements: continuous training and recommendation, handling concept drifts, and the ability to scale. Streaming RS proposed in the literature address the first two requirements only. That is because they run the training process on a single machine. To tackle the third challenge, we propose a Splitting and Replication mechanism for distributed streaming RS. Our mechanism is inspired
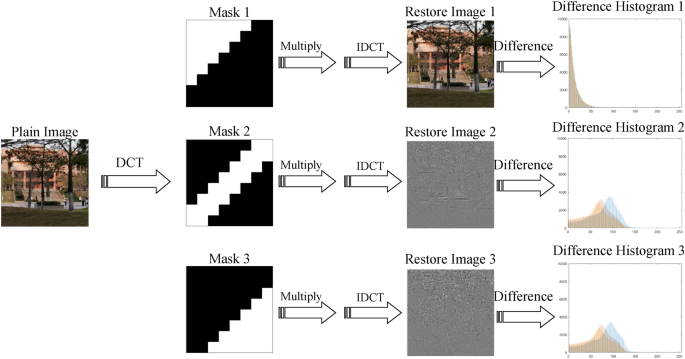
A Run-Length and Discrete Cosine Transform Based Technique for Image Splicing Detection
Digital images have emerged as the most popular means for sharing information in articles, newspapers, and even courtrooms. However, the widespread use of advanced digital imaging tools has made it easier to forge images. One such technique is image splicing, where multiple source images are merged into a single destination image to conceal or alter its content. Image splicing is an effective forgery technique, as it is difficult to detect by the naked eye. Detection of image splicing is a pattern recognition problem, based on finding image features that are sensitive to splicing. In this
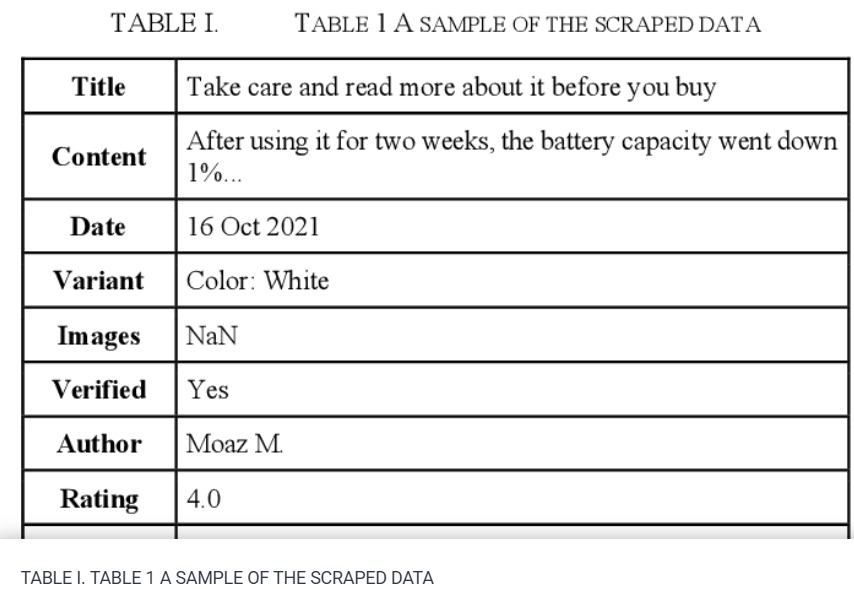
Sentiment Analysis: Amazon Electronics Reviews Using BERT and Textblob
The market needs a deeper and more comprehensive grasp of its insight, where the analytics world and methodologies such as 'Sentiment Analysis' come in. These methods can assist people especially 'business owners' in gaining live insights into their businesses and determining wheatear customers are satisfied or not. This paper plans to provide indicators by gathering real world Amazon reviews from Egyptian customers. By applying both Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers 'Bert' and 'Text Blob' sentiment analysis methods. The processes shall determine the overall satisfaction
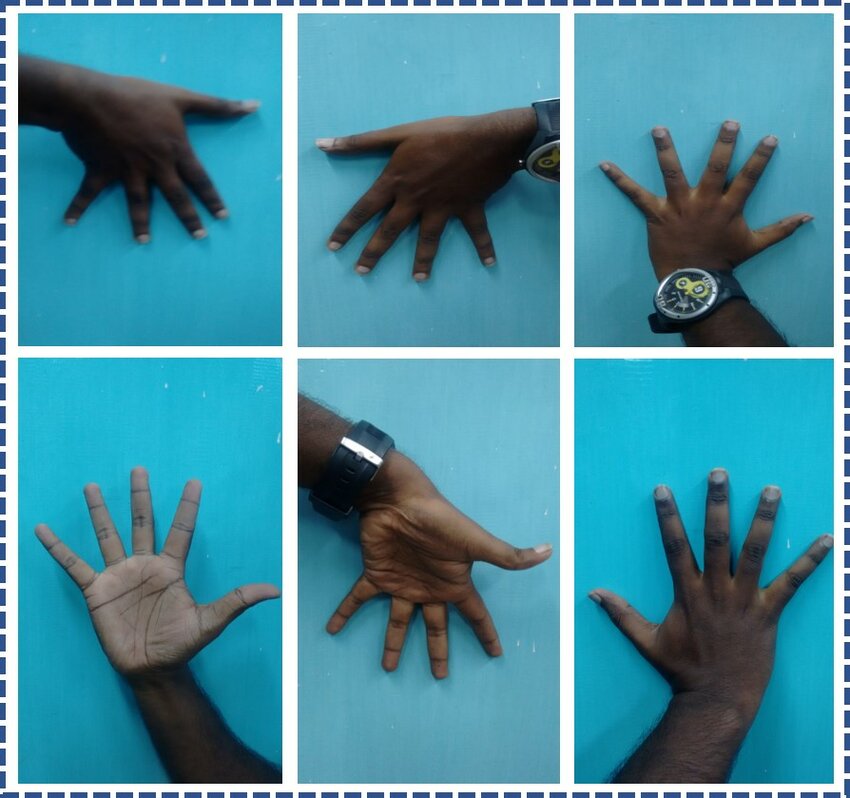

Gender Detection from Hand Palm Images: A PySpark-Driven Approach with VGG19 Feature Extraction and MLP Classification
This paper presents a comprehensive methodology for gender detection using hand palm images, leveraging image processing techniques and PySpark for scalable and efficient processing. The approach encompasses a meticulous image preprocessing pipeline, incorporating essential stages like grayscale conversion, the application ofthe Difference of Gaussians (DoG) filter, and adaptive histogram equalization. This approach not only refmes image features but also ensures scalability, accommodating large datasets seamlessly. After preprocessing of hand images, the VGG19 model is employed as a powerful
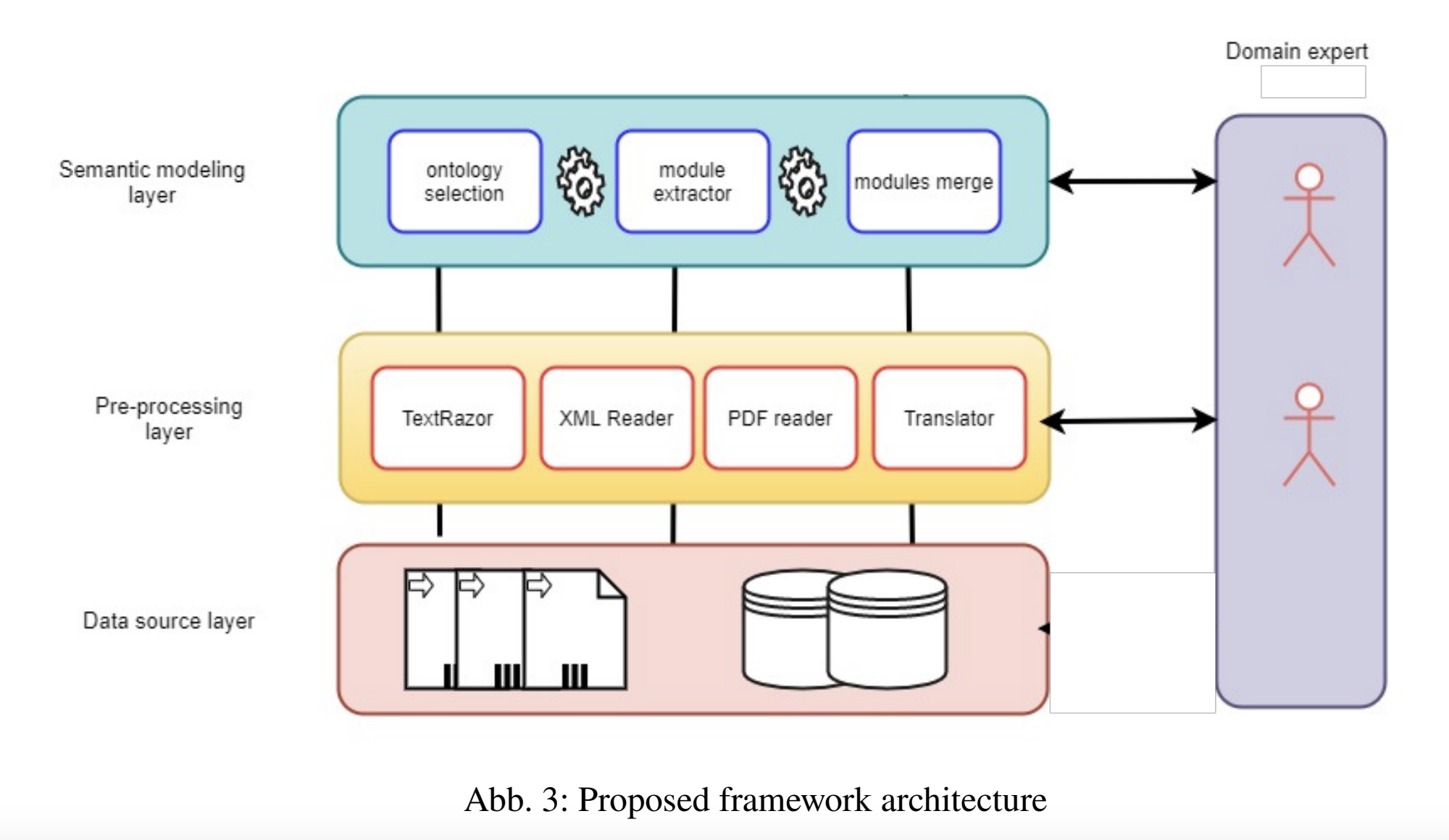
A Core Ontology to Support Agricultural Data Interoperability
The amount and variety of raw data generated in the agriculture sector from numerous sources, including soil sensors and local weather stations, are proliferating. However, these raw data in themselves are meaningless and isolated and, therefore, may offer little value to the farmer. Data usefulness is determined by its context and meaning and by how it is interoperable with data from other sources. Semantic web technology can provide context and meaning to data and its aggregation by providing standard data interchange formats and description languages. In this paper, we introduce the design

Database Security: Current Challenges and Effective Protection Strategies
Database security has grown to a necessary level of importance today, characterized by the escalating demand for data storage. The surge in data storage requirements, propelled by technological advancements, has led to increased attacks targeting database security vulnerabilities. While multiple storage and protection methods have emerged in tandem with evolving technologies, the discovery of security vulnerabilities has led to new attack vectors. This study aims to repair this gap by securing and fortifying the security of stored data within databases. Fundamental to information security, the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
