Breadcrumb
Smart Automotive Diagnostic and Performance Analysis Using Blockchain Technology
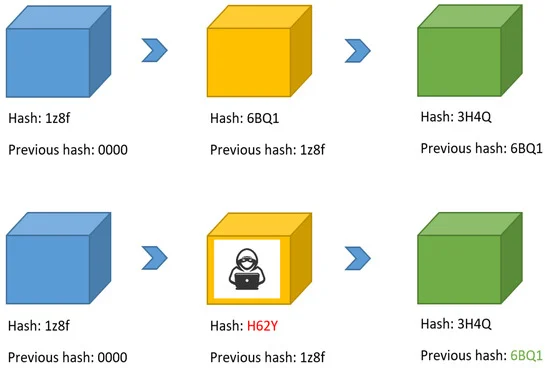
The automotive industry currently is seeking to increase remote connectivity to a vehicle, which creates a high demand to implement a secure way of connecting vehicles, as well as verifying and storing their data in a trusted way. Furthermore, much information must be leaked in order to correctly diagnose the vehicle and determine when or how to remotely update it. In this context, we propose a Blockchain-based, fully automated remote vehicle diagnosis system. The proposed system provides a secure and trusted way of storing and verifying vehicle data and analyzing their performance in
Industrial Practitioner Perspective of Mobile Applications Programming Languages and Systems
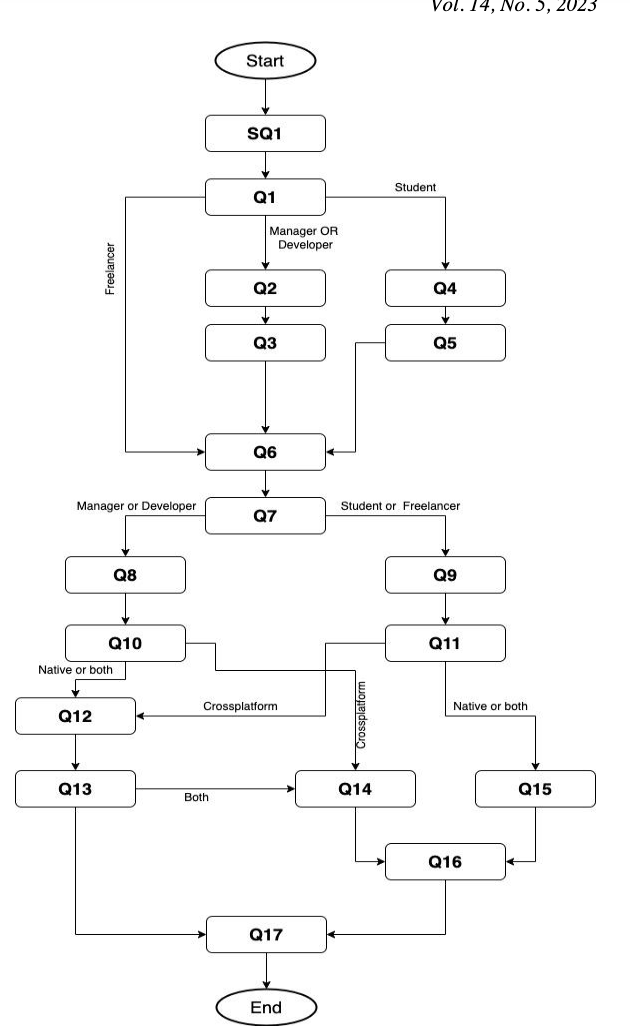
The growth of mobile application development industry made it crucial for researchers to study the industry practices of choosing mobile applications programming languages, systems, and tools. With the increased attention of cross-platform mobile applications development from both researchers and industry, this paper aims at answering the question of whether most of the industries are using cross-platform development or native development. The paper collects feedback about industry’s most used mobile development systems. In addition, it provides a map of the different technologies used by
Smart Customer Care: Scraping Social Media to Predict Customer Satisfaction in Egypt Using Machine Learning Models
This paper proposes the utilization of posts from social media to extract and analyze customer opinions and sentiments towards any specified topic in Egypt. Summarized statistics and sentiment values are then displayed to the consumer (companies such as Vodafone, WE etc.) through both an attractive and functional user interface. Text, location, and time of thous and s of posts are scrapped, stored, preprocessed, then managed through topic modelling to infer all the hidden themes and delivered to a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) to output whether the topic was positive or negative. Topic
Predicting non-synonymous single nucleotide variants pathogenic effects in human diseases
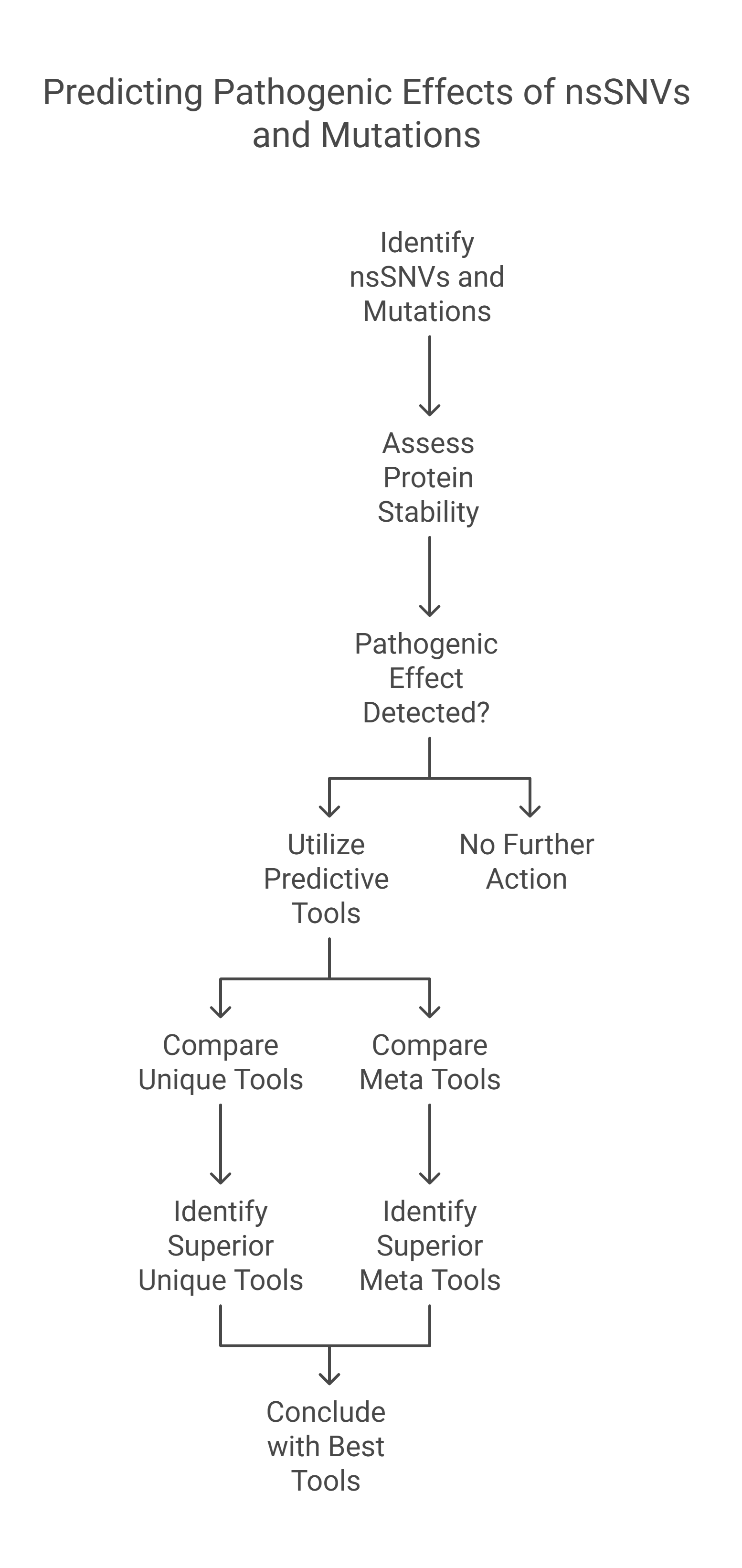
Non-synonymous Single - Nucleotide Variants (nsSNVs) and mutations can create a diversity of the contrary influence of proteins like varying genotype and phenotype of any protein which affects its stability. The alterations in the protein stability may cause diseases. Detecting of nsSNVs and mutations can be a helpful tool in diagnosing diseases at an early stage. The study of singular and consensus tools for predicting pathogenic effects is very essential. Many studies utilized various predicting servers based on distinct Machine Learning Techniques (MLTs). In this research, we conduct a

A (k,n)-Secret Image Sharing With Steganography Using Generalized Tent Map
Secret Image Sharing (SIS) transfers an image to mutually suspicious receivers as n meaningless shares, where k or more shares must be present to recover the secret. This paper proposes a (k, n)-SIS system for any image type using polynomial interpolation based on Lagrange polynomials, where the generated shares are of size 1/k of the secret image size. A full encryption system, consisting of substitution and permutation stages, is employed by using the generalized Tent map as a source of randomness. In addition to using a long and sensitive system key, steganography using the Least
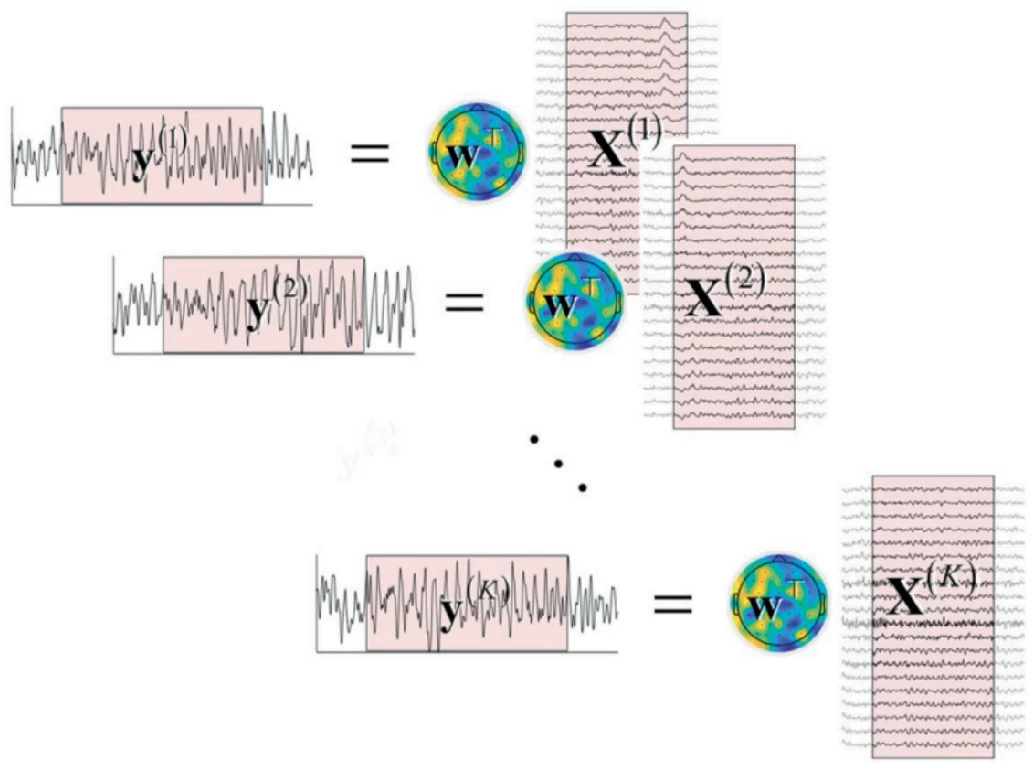
A Comparative Analysis of Time Series Transformers and Alternative Deep Learning Models for SSVEP Classification
Steady State Visually Evoked Potentials (SSVEPs) are intrinsic responses to specific visual stimulus frequencies. When the retina is activated by a frequency ranging from 3.5 to 75 Hz, the brain produces electrical activity at the same frequency as the visual signal, or its multiples. Identifying the preferred frequencies of neurocortical dynamic processes is a benefit of SSVEPs. However, the time consumed during calibration sessions limits the number of training trials and gives rise to visual fatigue since there is significant human variation across and within individuals over time, which

Semi-Fragile Watermark for the Authentication and Recovery of Tampered Images
In order to strengthen the safety of corporate multimedia assets, a semi-fragile watermarking method is developed, which makes use of the integer wavelet transform (IWT) and the discrete cosine transform (DCT) for tamper detection and recovery. In this paper, we produce two distinct kinds of watermarks: an authentication watermark and a recovery watermark. A tamper detection methodology is utilized at the receiving end to check the watermarked image for validity and detect any assaults. If the changes are determined to be malicious, the suggested tamper recovery method is used to restore the

Computational Intelligence for Medical Internet of Things (MIoT) Applications
Computational Intelligence for Medical Internet of Things (MIoT) Applications: Machine Intelligence Applications for IoT in Healthcare explores machine intelligence techniques necessary for effective MIoT research and practice, taking a practical approach for practitioners and students entering the field. This book investigates advanced concepts and applications in the MIoT field, guiding readers through emerging developments and future trends. A wide range of international authors guide readers through advanced concepts, including deep learning, neural network, and big data analytic
Influence of increasing amount of attapulgite on the performance properties of Cu-free brake-pads
Copper is almost inevitable functional filler in the brake-material and efforts to replace it are continuing since it is now known as a hazard to the aquatic life. It is always desirable to search for ingredients for Cu-free brake-pads, which will be beneficial for friction-related properties and especially fade resistance. Attapulgite, is a mineral which was proven to be an excellent substitute for asbestos in brake-pads long back. However, hardly anything in details is reported on its exact role in controlling tribo-properties of friction materials (FMs). It was of interest, if it can be
NGU_CNLP at WANLP 2022 Shared Task: Propaganda Detection in Arabic
This paper presents the system developed by the NGU_CNLP team for addressing the shared task on Propaganda Detection in Arabic at WANLP 2022. The team participated in the shared tasks' two sub-tasks which are: 1) Propaganda technique identification in text and 2) Propaganda technique span identification. In the first sub-task the goal is to detect all employed propaganda techniques in some given piece of text out of a possible 17 different techniques, or to detect that no propaganda technique is being used in that piece of text. As such, this first sub task is a multi-label classification
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 13
- Next page ››
