Breadcrumb
Does Deep Learning Require Image Registration for Early Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease? A Comparative Study Using ADNI Database
Image registration is the process of using a reference image to map the input images to match the corresponding images based on certain features. It has the ability to assist the physicians in the diagnosis and following up on the patient’s condition. One of the main challenges of the registration is that it takes a huge time to be computationally efficient, accurate, and robust as it can be framed as an optimization problem. In this paper, we introduce a comparative study to investigate the influence of the registration step exclusion from the preprocessing pipeline and study the counter
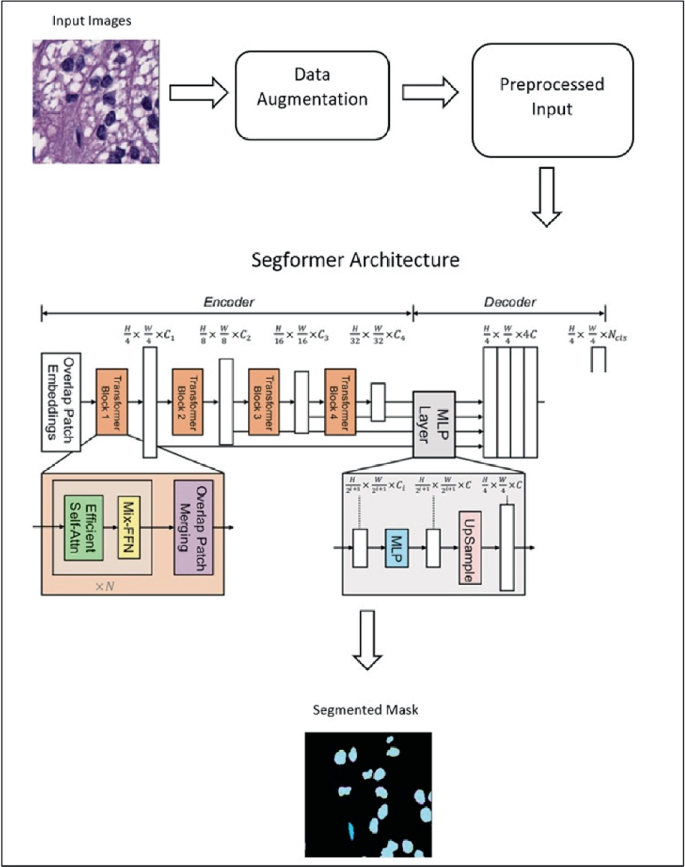
Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Nuclei in Histopathology Images Using Segformer
Segmentation of nuclei in histopathology images with high accuracy is crucial for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer and other diseases. Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the segmentation process enables pathologists to identify and study the unique properties of individual cells, which can reveal important information about the disease, its stage, and the best treatment approach. By using AI-powered automatic segmentation, this process can be significantly improved in terms of efficiency and accuracy, resulting in faster and more precise diagnoses. Ultimately, this can potentially lead
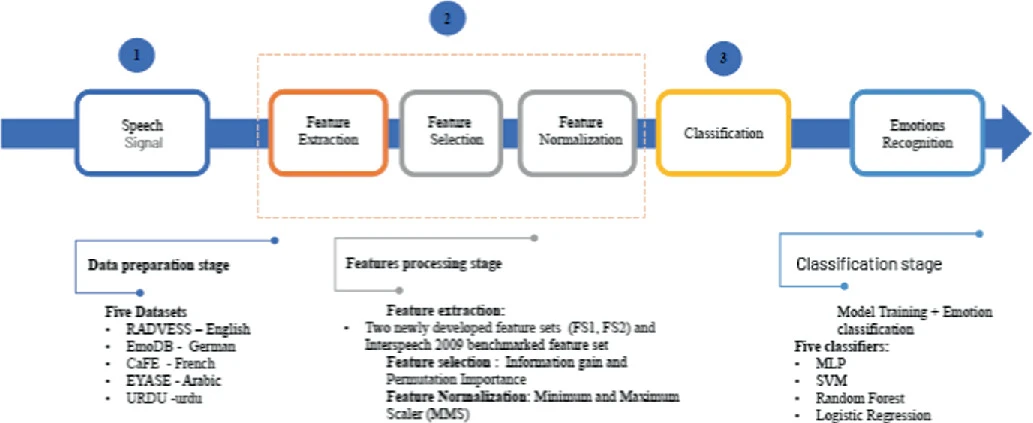
Emotion Recognition System for Arabic Speech: Case Study Egyptian Accent
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) systems are widely regarded as essential human-computer interface applications. Extracting emotional content from voice signals enhances the communication between humans and machines. Despite the rapid advancement of Speech Emotion Recognition systems for several languages, there is still a gap in SER research for the Arabic language. The goal of this research is to build an Arabic-based SER system using a feature set that has both high performance and low computational cost. Two novel feature sets were created using a mix of spectral and prosodic features

Ambulance Routing Optimization for CT-Ready Hospitals
This paper aims to enhance emergency medical services by optimizing ambulance routes towards hospitals equipped for spiral CT scans with minimal wait times. It integrates real-time data on hospital availability and traffic conditions, utilizing machine learning and smart routing algorithms to predict traffic jams and determine the fastest routes. Additionally, a machine learning model is used to detect the risk level of patients based on reported symptoms, helping prioritize critical cases. It aims to reduce emergency response times, ensuring quicker patient treatment. Preliminary results show
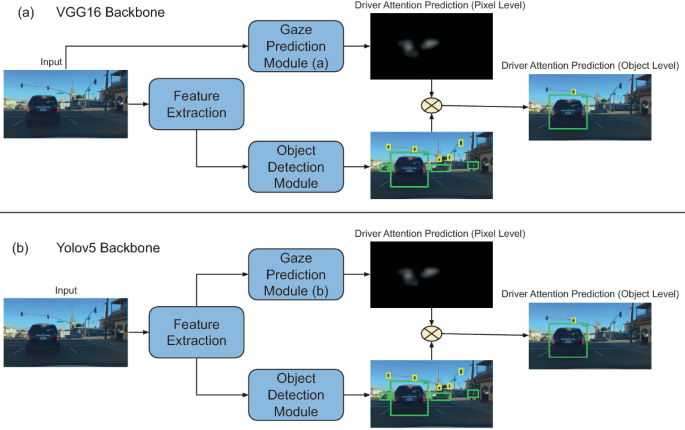
DAP: A Framework for Driver Attention Prediction
Human drivers employ their attentional systems during driving to focus on critical items and make judgments. Because gaze data can indicate human attention, collecting and analyzing gaze data has emerged in recent years to improve autonomous driving technologies. In safety-critical situations, it is important to predict not only where the driver focuses his attention but also on which objects. In this work, we propose DAP, a novel framework for driver attention prediction that bridges the attention prediction gap between pixels and objects. The DAP Framework is evaluated on the Berkeley
Speech Emotion Recognition System for Arabic Speakers
The Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) system is one of the essential human-computer interface applications. Despite the rapid advancement of technology, there is still a gap in SER research in the Arabic language corpus. The goal of this research is to build an Arabic-based SER based on a feature set that has both high performance and low computational cost. Two novel feature sets were implemented using a mix of spectral and prosodic features. An Arabic semi-natural corpus 'EYASE' was adopted for testing the proposed system. Five machine learning classifiers using the different feature sets
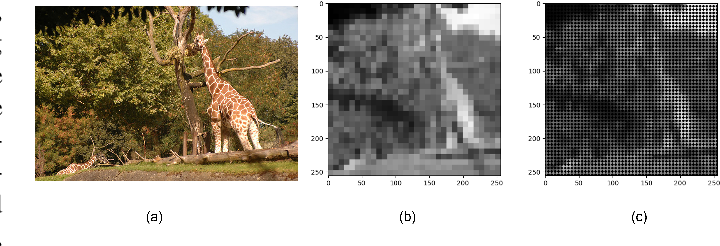
Enhancing Scene Simplification and Optimization for Retinal Prosthesis Platform
Retinal prostheses are designed to aid individuals with retinal degenerative conditions such as Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) and Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD). These prostheses seek to restore vision and improve the perceived scene by stimulating degenerated retinal cells using retinal stimulating electrodes. While these electrodes allow more efficient interaction with the surroundings, they offer limited resolution.This paper presents an innovative approach to revolutionize the visual perception of retinal prosthesis users. The key idea behind the proposed approach is to fuse
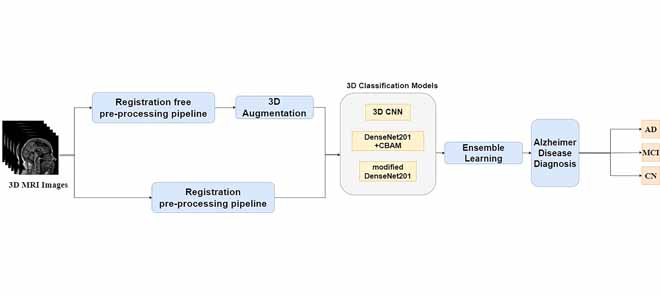
Automatic Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Using 3D Deep Ensemble Approach
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is considered the 6 th leading cause of death worldwide. Early diagnosis of AD is not an easy task, and no preventive cures have been discovered yet. Having an accurate computer-aided system for the early detection of AD is important to help patients with AD. This study proposes a new approach for classifying disease stages. First, we worked on the MRI images and split them into an appropriate format to avoid data leakage. Subsequently, a simple and fast registration-free preprocessing pipeline was applied to the dataset. Numerous experiments were conducted to analyze
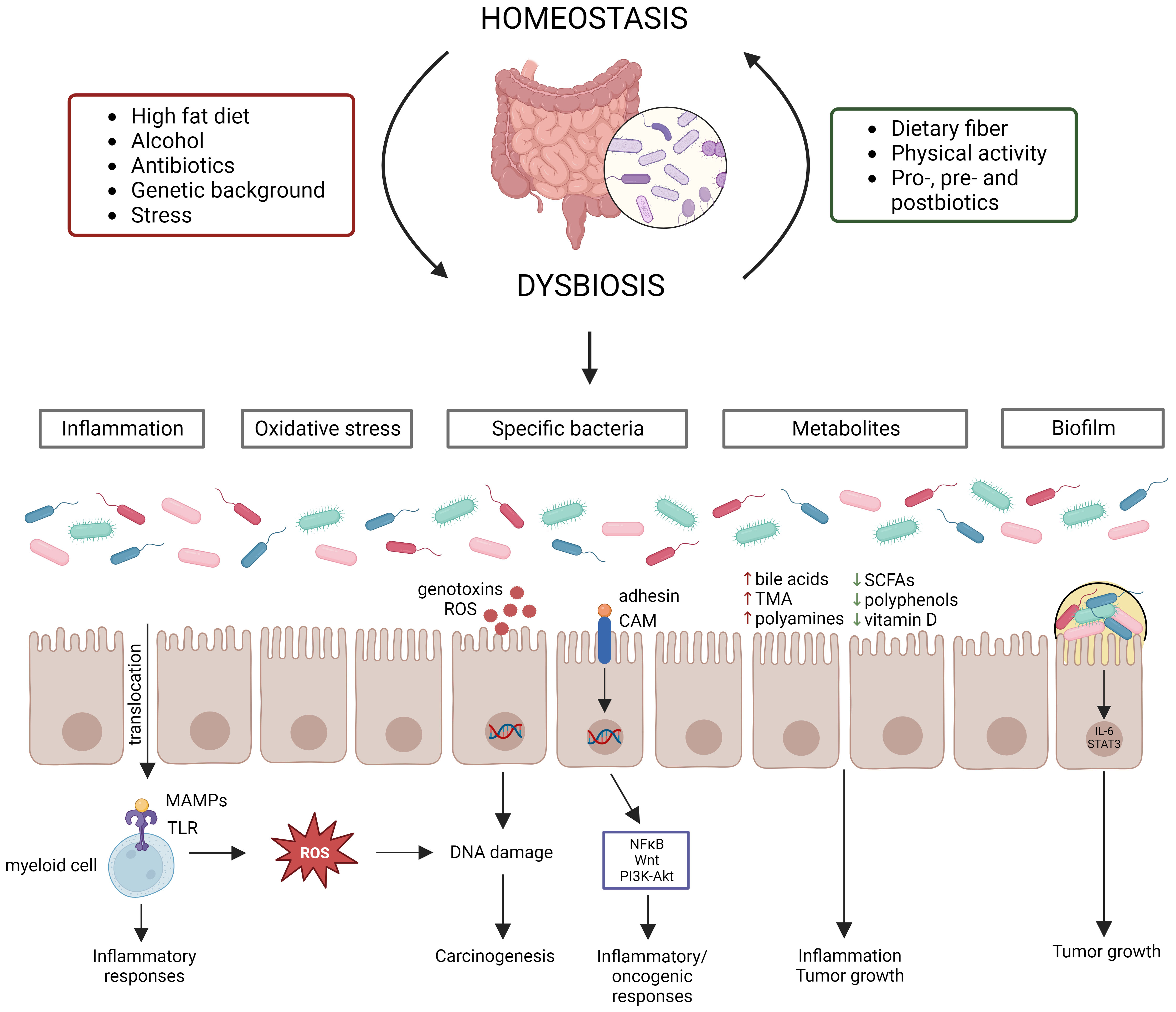
Dissecting the role of the gut microbiome and fecal microbiota transplantation in radio- and immunotherapy treatment of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers and poses a major burden on the human health worldwide. At the moment, treatment of CRC consists of surgery in combination with (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. More recently, immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs) have also been approved for CRC treatment. In addition, recent studies have shown that radiotherapy and ICBs act synergistically, with radiotherapy stimulating the immune system that is activated by ICBs. However, both treatments are also associated with severe toxicity and efficacy issues, which can
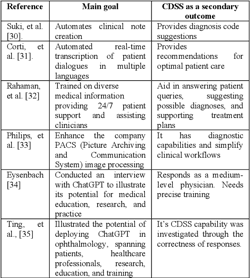
A Review of the Role of ChatGPT for Clinical Decision Support Systems
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) provided powerful assistant tools for humans in various aspects. Healthcare is rapidly evolving, with AI playing a crucial role in improving patient care. The extensive use of AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) enables providing real-time evidence-based recommendations to healthcare professionals at the point of Care. The AI chatbot ChatGPT proved its ability to solve several natural language processing tasks. One notable advancement is the integration of ChatGPT into Clinical Decision Support Systems. ChatGPT, despite not being
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 14
- Next page ››
