Breadcrumb
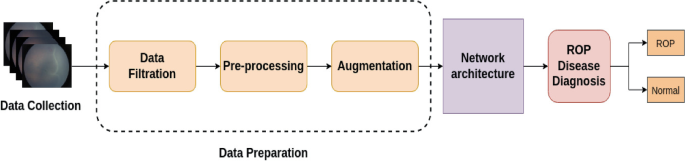
A Robust Deep Learning Detection Approach for Retinopathy of Prematurity
Retinal retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), an abnormal blood vessel formation, can occur in a baby who was born early or with a low birth weight. It is one of the primary causes of newborn blindness globally. Early detection of ROP is critical for slowing and stopping the progression of ROP-related vision impairment which leads to blindness. ROP is a relatively unknown condition, even among medical professionals. Due to this, the dataset for ROP is infrequently accessible and typically extremely unbalanced in terms of the ratio of negative to positive images and the ratio of each stage of it
Light-Weight Food Image Classification For Egyptian Cuisine
Food is an integral aspect of daily life in all cultures. It highly affects people's diets, eating behaviors, and overall health. People with poor eating habits are usually overweight or obese, which leads to chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Today, the classification of food images has several uses in managing medical conditions and dieting. Deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) architectures provide the foundation for the most recent food recognition models. However, DCNNs are computationally expensive due to high computation time and memory requirements. In
Feasibility Study of Using Predictive LTE Connection Selection from Multi-Operator for Teleoperated Vehicles
Service depending on good connection is growing and so its sensitivity, like Advanced Driver-Assistance System (ADAS). ADAS is the most common technological feature in the modern car, and the hope to reach a dependable anonymous car is the ultimate target. We (From end user and manufacture perspectives) are evaluating Teleoperated Driving as the most promising achievable feature to support emerging needs for traffic headache avoidance and health & safety cautions, with human to human sense & interaction proven to be better than Human to Machine in handling (Human driving vs. Machine driving)

DevSecOps: A Security Model for Infrastructure as Code over the Cloud
DevSecOps includes security practice while applying DevOps. DevSecOps help secure the whole DevOps process. This paper aims to define a DevSecOps module to be used by the infrastructure team while applying infrastructure as code. The proposed module solves the problem of security by including security practice with the DevOps cycle to reach DevSecOps. The module was tested to measure time effi-ciency. A small survey was created to test other DevSecOps metrics and enhance future work. © 2022 IEEE.
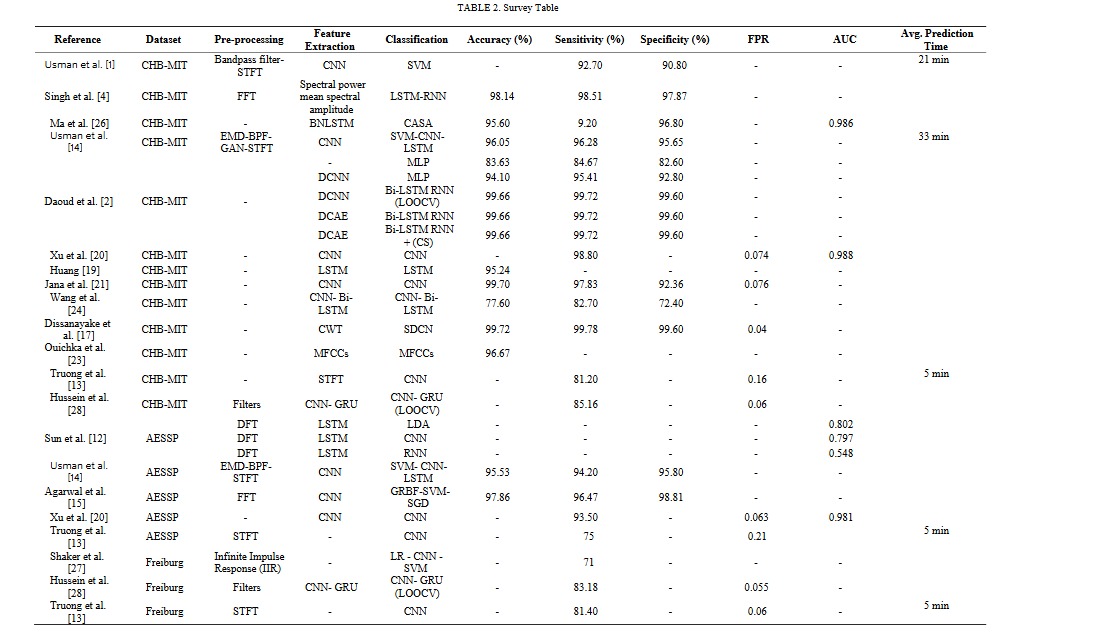
Deep Learning Approaches for Epileptic Seizure Prediction: A Review
Epilepsy is a chronic nervous disorder, which disturbs the normal daily routine of an epileptic patient due to sudden seizure onset that may cause loss of consciousness. Seizures are periods of aberrant brain activity patterns. Early prediction of an epileptic seizure is critical for those who suffer from it as it will give them time to prepare for an incoming seizure and alert anyone in their close circle of contacts to aid them. This has been an active field of study, powered by the decreasing cost of non-invasive electroencephalogram (EEG) collecting equipment and the rapid evolution of
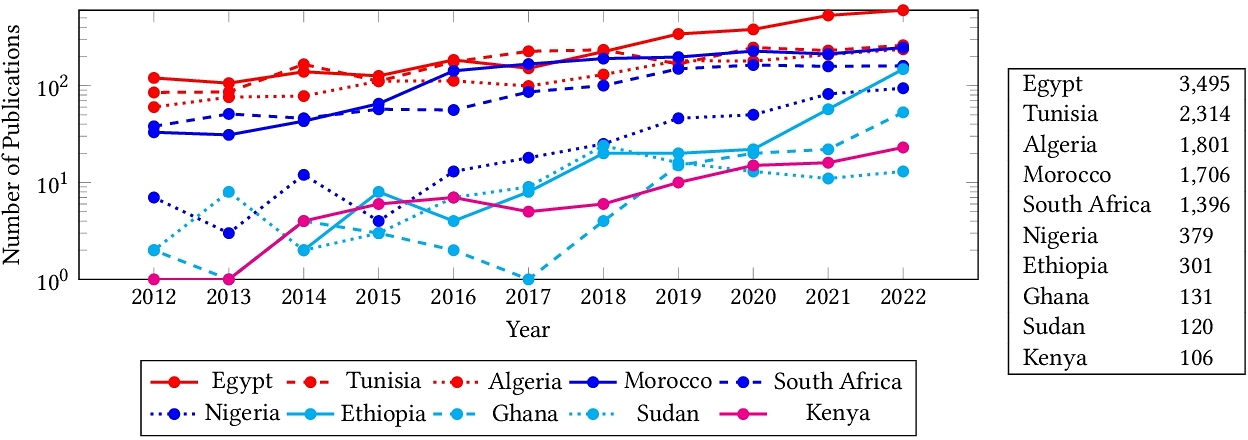
The State of Computer Vision Research in Africa
Despite significant efforts to democratize artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision which is a sub-field of AI, still lags in Africa. A significant factor to this, is the limited access to computing resources, datasets, and collaborations. As a result, Africa's contribution to top-tier publications in this field has only been 0.06% over the past decade. Towards improving the computer vision field and making it more accessible and inclusive, this study analyzes 63,000 Scopus-indexed computer vision publications from Africa. We utilize large language models to automatically parse their
Mobile Application Code Generation Approaches: A Survey
With the extensive usage of mobile applications in daily life, it has become crucial for the companies of software to develop applications for the most popular platforms such as Android and iOS in the shortest possible time and at the lowest possible cost. However, ensuring consistent UIs and functionalities among cross-platform versions can be challenging and costly since different platforms have their own UI controls and programming languages. Also, when cross-platform tools are used, it is always time consuming to learn a new language. Many solutions were proposed to achieve the native
Blockchain in Healthcare for Achieving Patients' Privacy
Heath data are sensitive and valuable for individuals. The patients need to integrate and manage their medical data continuously. Personal Health Record (PHR) is introduced as a solution for managing their health information. It gives patients ownership over their medical data and provides physicians with realignment data. However, it does not achieve reliability, traceability, trust, nor security of patient control. Centralization of any data is vulnerable to the problem of hacking and single failure in addition to control from one organization. So, the centralization of data is the common

Coffee and multiple sclerosis (MS)
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a long-term autoimmune disorder affecting the central nervous system, marked by inflammation, demyelination, and neurodegeneration. While the exact cause of MS remains unknown, recent research indicates that environmental factors, particularly diet, may influence the disease's risk and progression. As a result, the potential neuroprotective effects of coffee, one of the most popular beverages worldwide, have garnered significant attention due to its rich content of bioactive compounds. This chapter explores the impact of coffee consumption on patients with Multiple
Blockchain Application on Big Data Security
In recent years, advances in technology in several industries have resulted in massive data collections on the web. It raises worries about large data security and protection. The advent of Blockchain technology has caused a revolution in the security field for different applications. The distributed ledger is stored on each Blockchain node, which enhances security and data transparency. On the Blockchain network, illegal users are not authorized to undertake any fault transactions. In this article, we will discuss how Blockchain may be employed to secure the big data. We explain the problems
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››
