Breadcrumb
A comparative study for nuclei segmentation using latest deep learning optimizers
Nuclei segmentation is a critical task in biological image analysis, with numerous applications in cancer diagnosis, grading, staging, and treatment planning. However, this task is challenging, particularly when dealing with low-resolution and low signal-to-noise ratio microscopy images. Segmentation problems arise, such as touching and missing cells, which make the process even more challenging. Deep learning models, including Attention U-Net and TransUNet, have demonstrated exceptional performance in medical image segmentation. Nonetheless, the choice of optimizer can significantly impact
Automatic Detection of Some Tajweed Rules
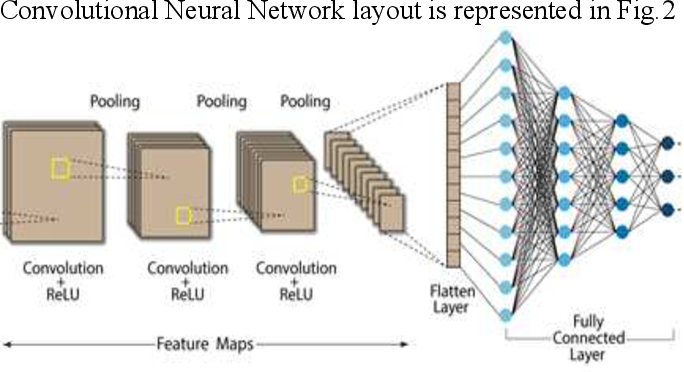
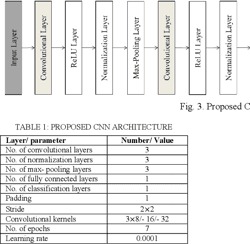
correct understanding of the Holy Quran is an essential duty for all Muslims. Tajweed rules guide the reciter to perform Holy Quran reading exactly as it was uttered by Prophet Muhammad peace be upon him. This work focused on the recognition of one Quranic recitation rule. Qalqalah rule is applied to five letters of the Arabic Alphabet (Baa/Daal/Jeem/Qaaf/Taa) having sukun vowelization. The proposed system used the Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) as the feature extraction technique, and the Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) model was used for recognition. The available dataset
Classification of Autism Spectrum Disorder using Convolutional Neural Networks from Neuroimaging Data
Current Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnosis methods exhibit some limitations as they are based on clinical interviews and observations of behaviors, characteristics, and abilities. Moreover, considering the current challenges in identifying the causes and mechanisms associated with ASD, there is an essential need for automated techniques capable of providing an accurate classification between ASD and typically developed (TD). In this paper, we present a convolutional neural network model that can differentiate ASD from TD. This proposed system is trained and validated on the well-known

Pharmacotherapy of PD and related movements disorders and their limitations
A wide range of neurodegenerative illnesses, including Parkinson's disease (PD) and related movement disorders, greatly impair the quality of life for those who are afflicted. This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of Parkinson's disease (PD), covering everything from the disease's basic definitions, epidemiology, and pathophysiology to the complex issues involved in treating its symptoms with medication and other approaches. It emphasizes the significance of adjunct therapies and a multidisciplinary approach in comprehensive care, as well as the crucial role that personalized medicine

Supervised ML for Identifiying Biomarkers Driving the Response to ICBs in Melanoma patients
The Immune Checkpoint Blockade has transformed cancer treatment. Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Associated Protein 4 (CTLA4), Programmed death-1 (PD-1) are antibodies that block immune checkpoint proteins that have been FDA approved for treating a variety of cancers including melanoma, renal carcinoma, and non-small cell lung cancer. Immunotherapy tend to stimulate the immune system of patients to detect and kill cancer cells while sparing normal cells by using checkpoints such as CTLA-4 and PD-1, which are molecules on immune cells that are turned on or off to allow the immune response to begin

Harris Hawks Feature Optimization for Identifying the Informative Pathogens of Pediatric Sepsis
One of the most fatal potentially life-threatening medical condition that increases the mortality in pediatric populations is pediatric sepsis. Unfortunately, the improper control of such disease can lead to tissue damage and organ dysfunction because of the overwhelming the human body's response to an infection. Therefore, early recognition and intervention can clearly improve outcome for infants and children with conditions that lead to sepsis before the admission to the intensive care unit (ICU). Accordingly, 17 informative differential expressed genes have been selected using a nature
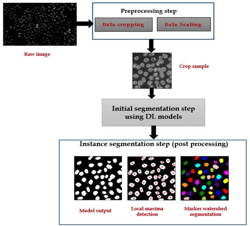
A Multi-scale Self-supervision Method for Improving Cell Nuclei Segmentation in Pathological Tissues
Nuclei detection and segmentation in histopathological images is a prerequisite step for quantitative analysis including morphological shape and size to help in identifying cancer prognosis. Digital pathology field aims to improve the quality of cancer diagnosis and has helped pathologists to reduce their efforts and time. Different deep learning architectures are widely used recently in Digital pathology field, yielding promising results in different problems. However, Deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) need a large subset of labelled data that are not easily available all the time in
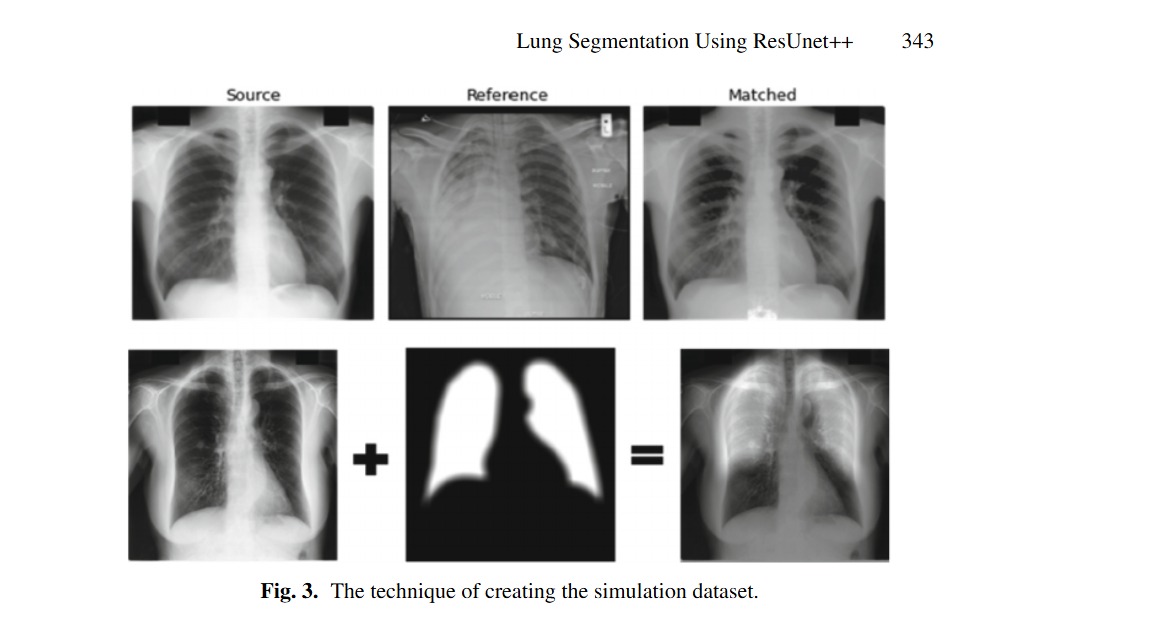
Lung Segmentation Using ResUnet++ Powered by Variational Auto Encoder-Based Enhancement in Chest X-ray Images
X-ray has a huge popularity around the world. This is due to its low cost and easy to access. Most of lung diseases are diagnosed using Chest X-ray (CXR). So, developing computer aided detection (CAD) provided with automatic lung segmentation can improve the efficiency of the detection and support the physicians to make a reliable decision at early stages. But when the input image has image artifacts, then any lung segmentation model will introduce suboptimal lung segmentation results. In this paper, a new approach is proposed to make the lung segmentation model robust and boost the basic
Deep Learning for ECG Image Analysis: A Lightweight Approach for Covid-19 Diagnosis
Since late 2019, Covid-19 has broken out causing immense pressure on healthcare systems worldwide. Fast detection of Covid-19 has become crucial in controlling and slow-pacing the virus outbreak. Innovative methods that are cheap, fast, and accurate for Covid-19 detection are of high importance to aid in the efforts of containment of the disease. In this study a novel method is proposed for Covid-19 detection through analysis of ECG image records. Three models are introduced for three classification schemas, Normal vs Covid-19, Covid-19 vs non Covid-19, Normal vs Covid-19 vs Abnormal HeartBeat
Does Deep Learning Require Image Registration for Early Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease? A Comparative Study Using ADNI Database
Image registration is the process of using a reference image to map the input images to match the corresponding images based on certain features. It has the ability to assist the physicians in the diagnosis and following up on the patient’s condition. One of the main challenges of the registration is that it takes a huge time to be computationally efficient, accurate, and robust as it can be framed as an optimization problem. In this paper, we introduce a comparative study to investigate the influence of the registration step exclusion from the preprocessing pipeline and study the counter
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
