Breadcrumb
In-Silico targeting of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 for drug and natural products repurposing
Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) has a protecting role for SARS-CoV-2 replication by inhibiting the expansion of autophagosomes inside the cell. NSP6 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response by binding to Sigma receptor 1 (SR1). Nevertheless, NSP6 crystal structure is not solved yet. Therefore, NSP6 is considered a challenging target in Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Herein, we utilized the high quality NSP6 model built by AlphaFold in our study. Targeting a putative NSP6 binding site is believed to inhibit the SR1-NSP6 protein-protein interactions. Three databases were
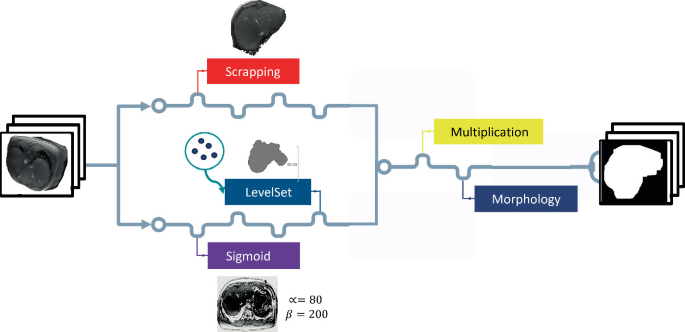
Iterative Refinement Algorithm for Liver Segmentation Ground-Truth Generation Using Fine-Tuning Weak Labels for CT and Structural MRI
Medical image segmentation is indicated in a number of treatments and procedures, such as detecting pathological changes and organ resection. However, it is a time-consuming process when done manually. Automatic segmentation algorithms like deep learning methods overcome this hurdle, but they are data-hungry and require expert ground-truth annotations, which is a limitation, particularly in medical datasets. On the other hand, unannotated medical datasets are easier to come by and can be used in several methods to learn ground-truth masks. In this paper, we aim to utilize across-modalities

ArFakeDetect: A Deep Learning Approach for Detecting Fabricated Arabic Tweets on COVID-19 Vaccines
Social media platforms have emerged as major sources of false information, particularly regarding health topics. like COVID-19 vaccines. This rampant dissemination of inaccurate content contributes significantly to vaccine hesitancy and undermines vaccination campaigns. This research addresses the pressing need for automated methods to distinguish between factual and fabricated Arabic tweets concerning vaccines, aiming to mitigate the spread of misinformation on these platforms. The proposed approach utilizes deep learning techniques, leveraging pre-trained Arabic language models (Arabert)
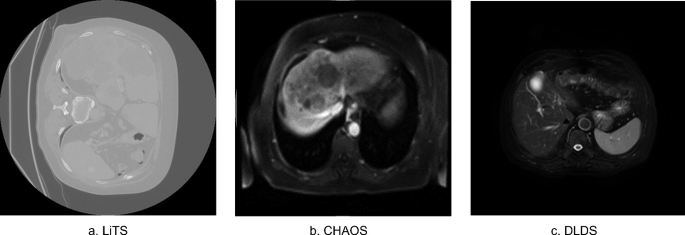
Cross-Modality Deep Transfer Learning: Application to Liver Segmentation in CT and MRI
Liver diseases cause up to two million deaths yearly. Their diagnosis and treatment plans require an accurate assessment of the liver structure and tissue characteristics. Imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic resonance (MR) can be used to assess the liver. CT has better spatial resolution compared to MR, which has better tissue contrast. Each modality has its own applications. However, CT is widely used due its ease of access, lower cost and a shorter examination time. Liver segmentation is an important step that helps to accurately identify and isolate the liver
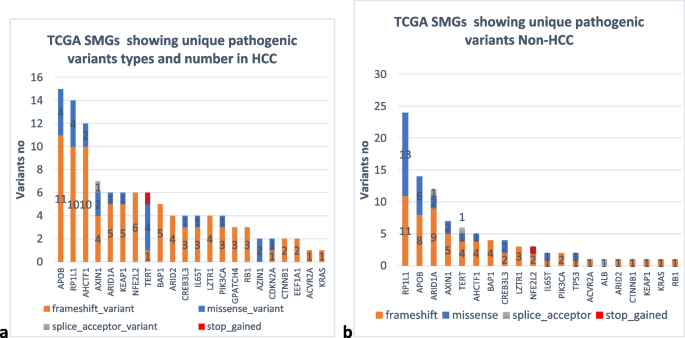
Correction to: Genomic landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients by whole exome sequencing (BMC Medical Genomics, (2024), 17, 1, (202), 10.1186/s12920-024-01965-w)
Tables 2, 3, and 6, as shown in the original publication, were modified to black and white during the typesetting process. Following the publication, the authors requested that the tables be reverted to their original-colored versions, as the colors in the heatmap indicate the number of pathogenic variants present in genes. Green indicates the smallest number, and red indicates the highest number. The colored tables are as follows: Heatmap for pathogenic variants in highly mutated genes in HCC samples Heatmap for pathogenic variants in highly mutated genes in Non-HCC samples Heatmap showing
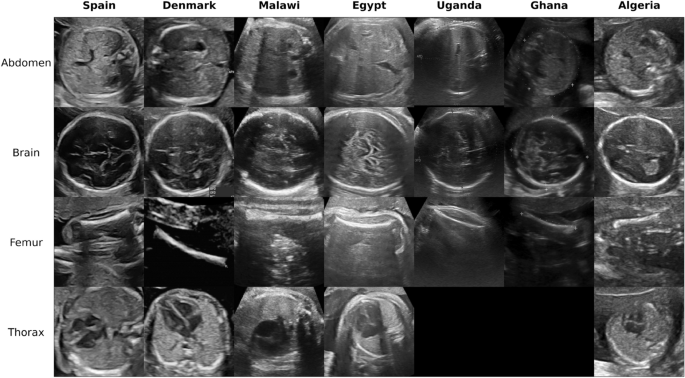
Generalisability of fetal ultrasound deep learning models to low-resource imaging settings in five African countries
Most artificial intelligence (AI) research and innovations have concentrated in high-income countries, where imaging data, IT infrastructures and clinical expertise are plentiful. However, slower progress has been made in limited-resource environments where medical imaging is needed. For example, in Sub-Saharan Africa, the rate of perinatal mortality is very high due to limited access to antenatal screening. In these countries, AI models could be implemented to help clinicians acquire fetal ultrasound planes for the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. So far, deep learning models have been

OMICS and bioinformatics in Parkinson disease and related movements disorders
This chapter explores the integration of omics and bioinformatics for Parkinson's disease (PD) diagnosis and potential cure discovery. It begins with an overview of PD and its prevalence, followed by an examination of key mutations in genes linked to the disease. These mutations lead to dysfunctional proteins, triggering PD progression. The chapter delves into techniques like whole-exome sequencing (WES), genome-wide association sequencing (GWAS), and whole-genome sequencing (WGS). These methods enable the exploration of omics levels such as lipidomics, metabolomics, genomics, and proteomics
Tracking Antibiotic Resistance from the Environment to Human Health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the threats to our world according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Resistance is an evolutionary dynamic process where host-associated microbes have to adapt to their stressful environments. AMR could be classified according to the mechanism of resistance or the biome where resistance takes place. Antibiotics are one of the stresses that lead to resistance through antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). The resistome could be defined as the collection of all ARGs in an organism’s genome or metagenome. Currently, there is a growing body of evidence

Introduction to genomics-based pharmaceutical applications
Biomedical research and pharmaceutical development have been profoundly impacted by genomics in recent years, with researchers gaining new understanding of the genetic pathways underlying disease and opening up new opportunities for the creation of targeted therapeutic interventions. Without a comprehensive grasp of the genetic mechanisms at play, medication discovery approaches in the past often relied on trial and error, targeting particular symptoms or pathways. However, the advent of genomics has changed the game. Scientific advances in high-throughput DNA sequencing have allowed
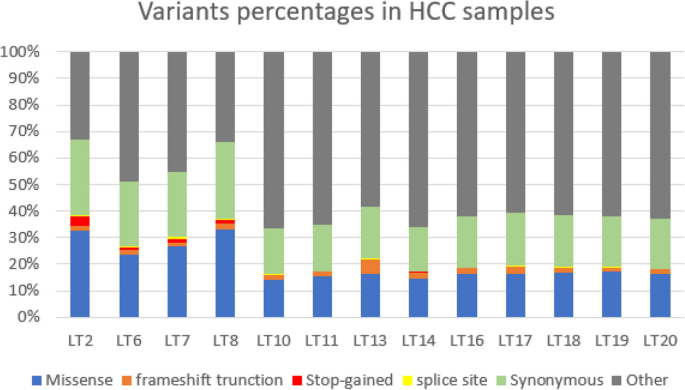
Genomic landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients by whole exome sequencing
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis lead to accumulation of genetic alterations driving HCC pathogenesis. This study is designed to explore genomic landscape of HCC in Egyptian patients by whole exome sequencing. Methods: Whole exome sequencing using Ion Torrent was done on 13 HCC patients, who underwent surgical intervention (7 patients underwent living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) and 6 patients had surgical resection}. Results: Mutational signature was mostly S1, S5, S6, and S12 in HCC. Analysis of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
