Breadcrumb
Tracking Antibiotic Resistance from the Environment to Human Health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the threats to our world according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Resistance is an evolutionary dynamic process where host-associated microbes have to adapt to their stressful environments. AMR could be classified according to the mechanism of resistance or the biome where resistance takes place. Antibiotics are one of the stresses that lead to resistance through antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). The resistome could be defined as the collection of all ARGs in an organism’s genome or metagenome. Currently, there is a growing body of evidence

Introduction to genomics-based pharmaceutical applications
Biomedical research and pharmaceutical development have been profoundly impacted by genomics in recent years, with researchers gaining new understanding of the genetic pathways underlying disease and opening up new opportunities for the creation of targeted therapeutic interventions. Without a comprehensive grasp of the genetic mechanisms at play, medication discovery approaches in the past often relied on trial and error, targeting particular symptoms or pathways. However, the advent of genomics has changed the game. Scientific advances in high-throughput DNA sequencing have allowed
Author Correction: Generalisability of fetal ultrasound deep learning models to low-resource imaging settings in five African countries (Scientific Reports, (2023), 13, 1, (2728), 10.1038/s41598-023-29490-3)
The Funding section in the original version of this Article was incomplete. “This work received funding from the European Union’s 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 825903 (euCanSHare project), as well as from the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities under grant agreement RTI2018-099898-B-I00. Additionally, the research leading to these results has received funding from Cerebra Foundation for the Brain Injured Child (Carmarthen, Wales, UK).” now reads: “This work received funding from the European Union’s 2020 research and innovation programme
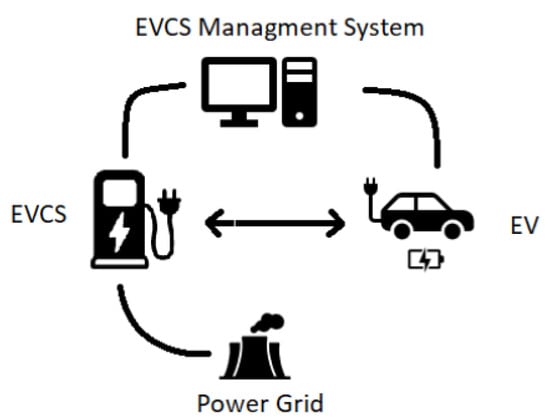
A Machine Learning-Based Intrusion Detection System for IoT Electric Vehicle Charging Stations (EVCSs)
The demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is growing rapidly. This requires an ecosystem that meets the user’s needs while preserving security. The rich data obtained from electric vehicle stations are powered by the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. This is achieved through us of electric vehicle charging station management systems (EVCSMSs). However, the risks associated with cyber-attacks on IoT systems are also increasing at the same pace. To help in finding malicious traffic, intrusion detection systems (IDSs) play a vital role in traditional IT systems. This paper proposes a classifier
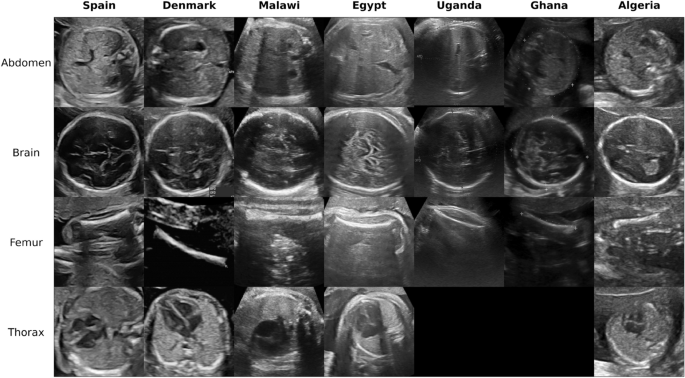
Generalisability of fetal ultrasound deep learning models to low-resource imaging settings in five African countries
Most artificial intelligence (AI) research and innovations have concentrated in high-income countries, where imaging data, IT infrastructures and clinical expertise are plentiful. However, slower progress has been made in limited-resource environments where medical imaging is needed. For example, in Sub-Saharan Africa, the rate of perinatal mortality is very high due to limited access to antenatal screening. In these countries, AI models could be implemented to help clinicians acquire fetal ultrasound planes for the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. So far, deep learning models have been
Dual-Level Sensor Selection with Adaptive Sensor Recovery to Extend WSNs’ Lifetime
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have garnered much attention in the last decades. Nowadays, the network contains sensors that have been expanded into a more extensive network than the internet. Cost is one of the issues of WSNs, and this cost may be in the form of bandwidth, computational cost, deployment cost, or sensors’ battery (sensor life). This paper proposes a dual-level sensor selection (DLSS) model used to reduce the number of sensors forming WSNs. The sensor reduction process is performed at two consecutive levels. First, a combination of the Fisher score method and ANOVA test at the
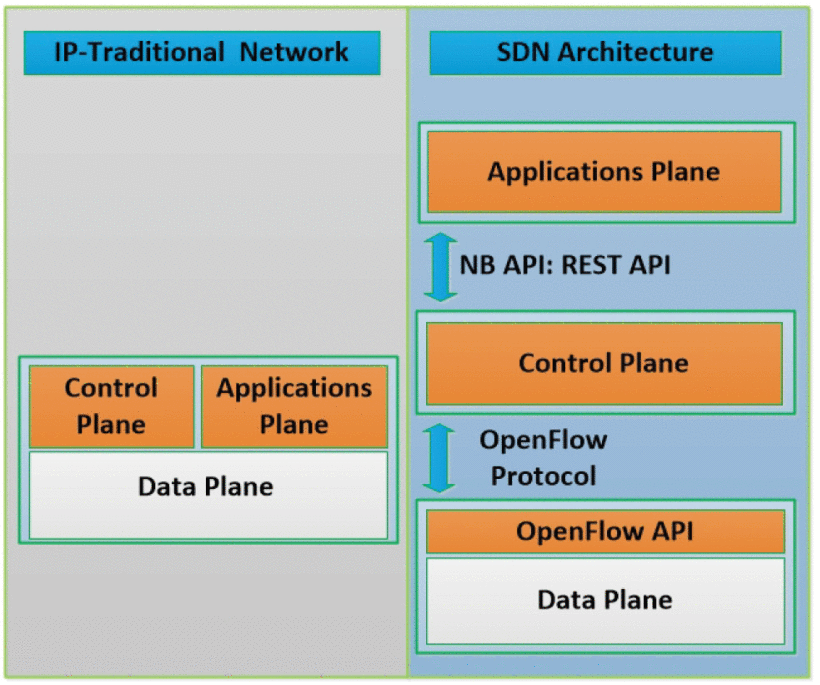
A Flow-Based Anomaly Detection Approach With Feature Selection Method Against DDoS Attacks in SDNs
Software Defined Networking (SDN) is an emerging network platform, which facilitates centralised network management. The SDN enables the network operators to manage the overall network consistently and holistically, regardless the complexity of infrastructure devices. The promising features of the SDN enhance network security and facilitate the implementation of threat detection systems through software applications using open APIs. However, the emerging technology creates new security concerns and new threats that do not exist in the current traditional networks. Distributed Denial of Service
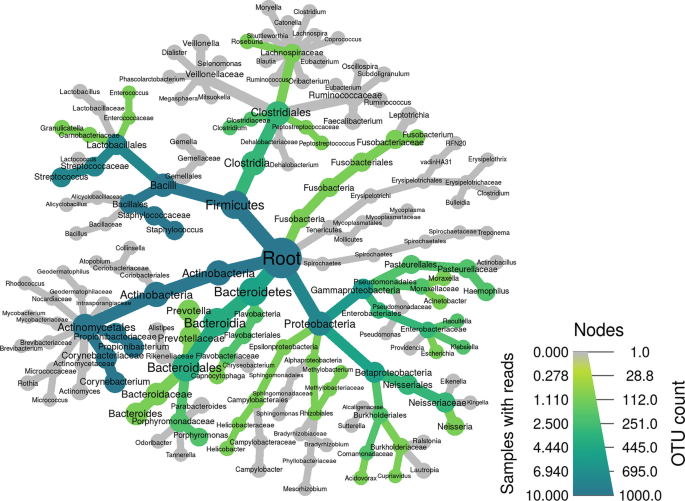
Comprehensive Guideline for Microbiome Analysis Using R
The need for a comprehensive consolidated guide for R packages and tools that are used in microbiome data analysis is significant; thus, we aim to provide a detailed step-by-step dissection of the most used R packages and tools in the field of microbiome data integration and analysis. The guideline aims to be a user-friendly simplification and tutorial on five main packages, namely phyloseq, MegaR, DADA2, Metacoder, and microbiomeExplorer due to their high efficiency and benefit in microbiome data analysis. © 2023, The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
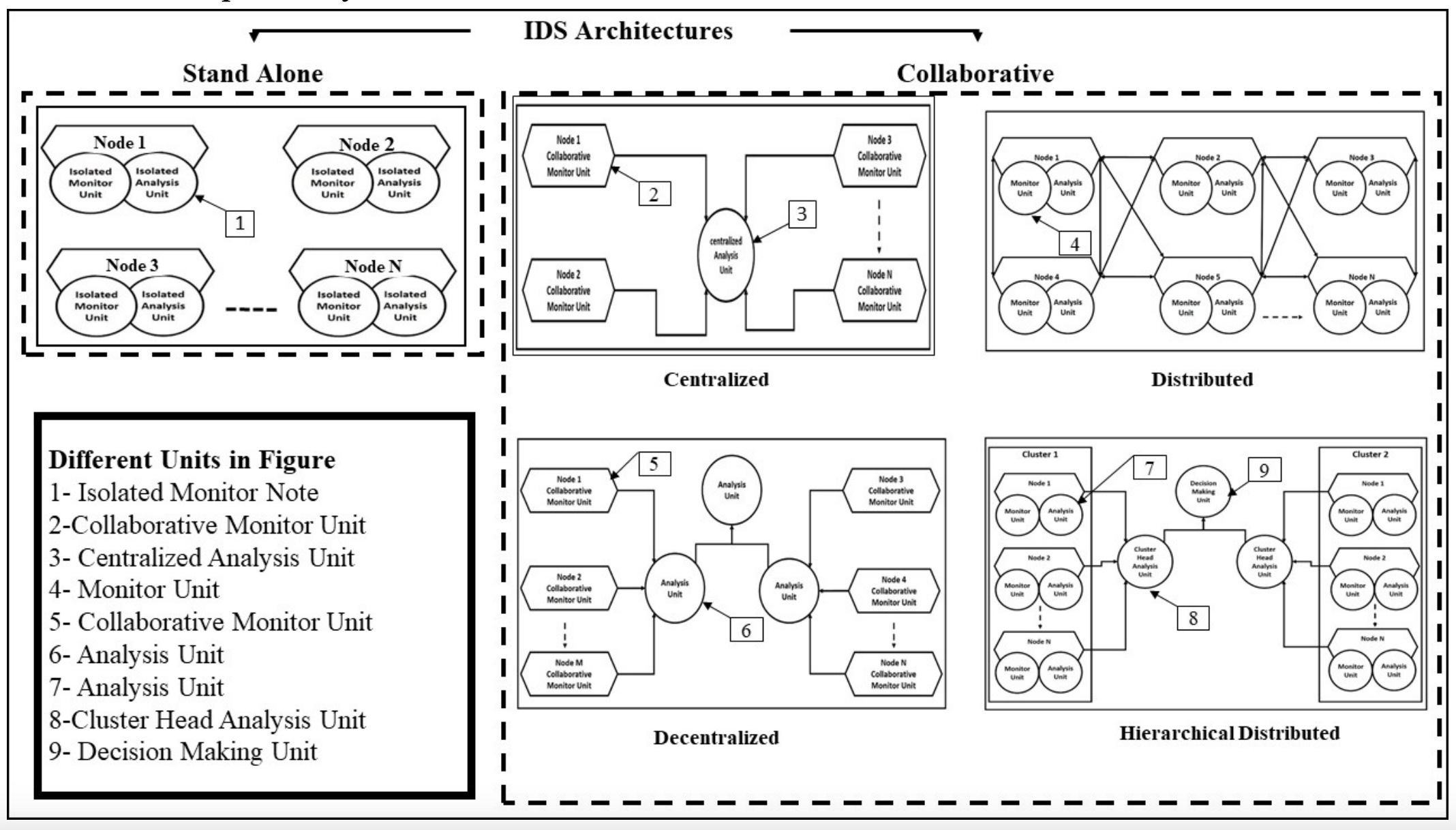
MSDAR: Multi-Stage Dynamic Architecture Intrusion Detection System
Ad hoc networks have been through extensive research in the last decade. Even with their desirable characteristics, major issues related to their security need to be considered. Various security solutions have been proposed to reduce the risks of malicious actions. They mainly focus on key management, authentication, secure localization, and aggregation techniques. These techniques have been proposed to secure wireless communications but they can only deal with external threats. Therefore, they are considered the first line of defense. Intrusion detection systems are always required to
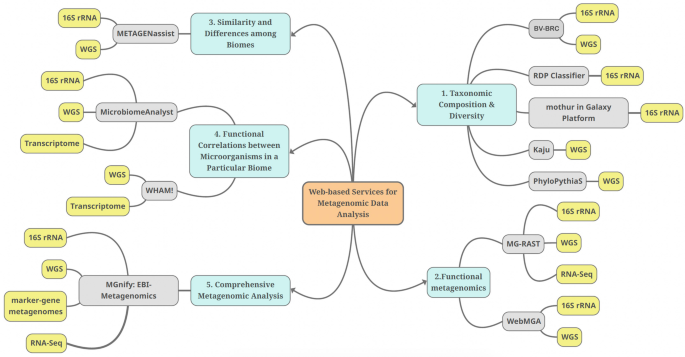
Interactive Web-Based Services for Metagenomic Data Analysis and Comparisons
Recently, sequencing technologies have become readily available, and scientists are more motivated to conduct metagenomic research to unveil the potential of a myriad of ecosystems and biomes. Metagenomics studies the composition and functions of microbial communities and paves the way to multiple applications in medicine, industry, and ecology. Nonetheless, the immense amount of sequencing data of metagenomics research and the few user-friendly analysis tools and pipelines carry a new challenge to the data analysis. Web-based bioinformatics tools are now being developed to facilitate the
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
