Breadcrumb
Mobile Application Code Generation Approaches: A Survey
With the extensive usage of mobile applications in daily life, it has become crucial for the companies of software to develop applications for the most popular platforms such as Android and iOS in the shortest possible time and at the lowest possible cost. However, ensuring consistent UIs and functionalities among cross-platform versions can be challenging and costly since different platforms have their own UI controls and programming languages. Also, when cross-platform tools are used, it is always time consuming to learn a new language. Many solutions were proposed to achieve the native
A multi-Kalman filter-based approach for decoding arm kinematics from EMG recordings
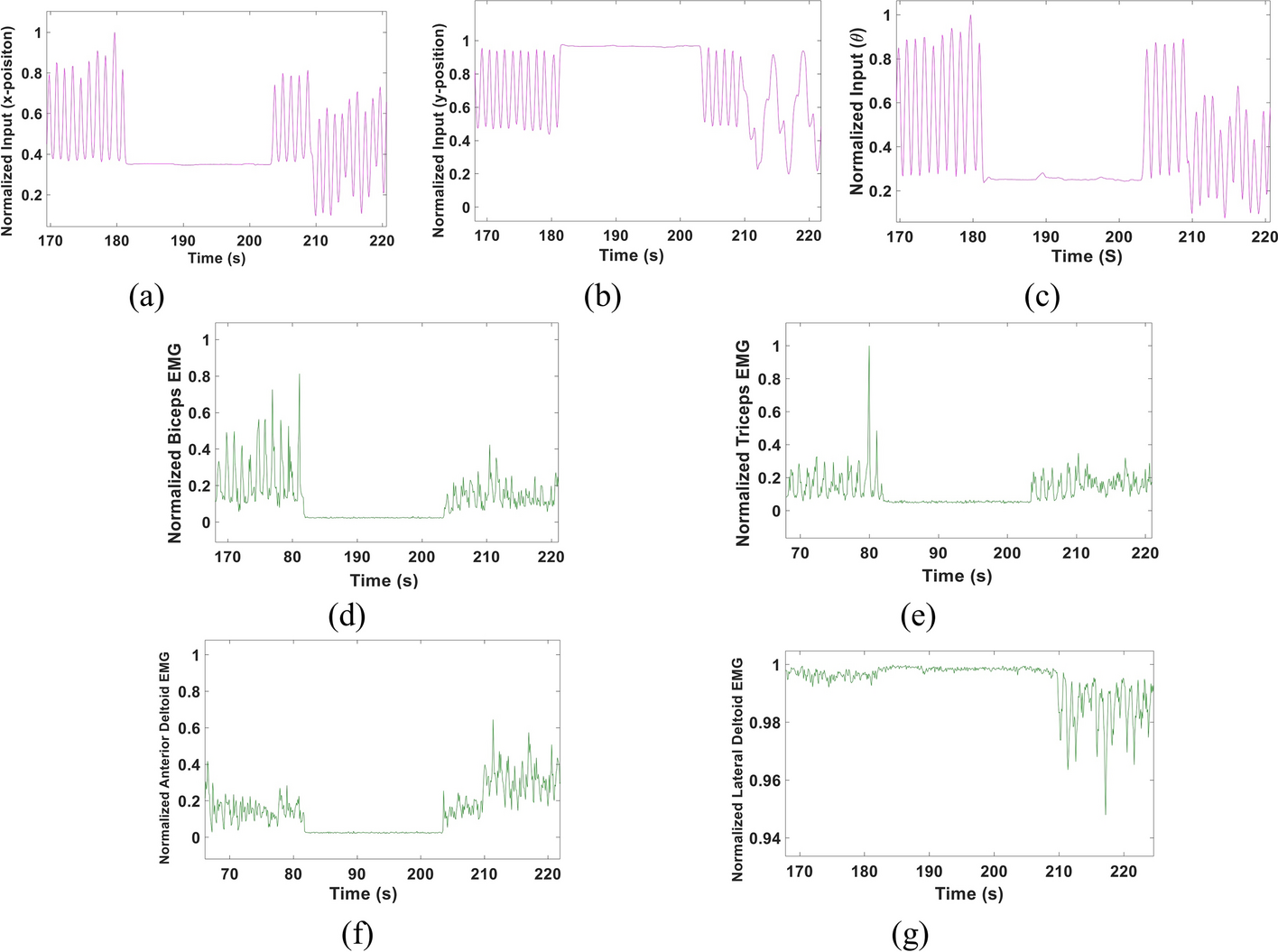
Background: Remarkable work has been recently introduced to enhance the usage of Electromyography (EMG) signals in operating prosthetic arms. Despite the rapid advancements in this field, providing a reliable, naturalistic myoelectric prosthesis remains a significant challenge. Other challenges include the limited number of allowed movements, lack of simultaneous, continuous control and the high computational power that could be needed for accurate decoding. In this study, we propose an EMG-based multi-Kalman filter approach to decode arm kinematics; specifically, the elbow angle (θ), wrist
Topic Modeling on Arabic Language Dataset: Comparative Study
Topic modeling automatically infers the hidden themes in a collection of documents. There are several developed techniques for topic modeling, which are broadly categorized into Algebraic, Probabilistic and Neural. In this paper, we use an Arabic dataset to experiment and compare six models (LDA, NMF, CTM, ETM, and two Bertopic variants). The comparison used evaluation metrics of topic coherence, diversity, and computational cost. The results show that among all the presented models, the neural BERTopic model with Roberta-based sentence transformer achieved the highest coherence score (0.1147)
Immunoinformatics approach of epitope prediction for SARS-CoV-2
Background: The novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) caused lethal infections worldwide during an unprecedented pandemic. Identification of the candidate viral epitopes is the first step in the design of vaccines against the viral infection. Several immunoinformatic approaches were employed to identify the SARS-CoV-2 epitopes that bind specifically with the major histocompatibility molecules class I (MHC-I). We utilized immunoinformatic tools to analyze the whole viral protein sequences, to identify the SARS-CoV-2 epitopes responsible for binding to the most frequent human leukocyte antigen (HLA)

Design and Implementation of a Dockerized, Cross Platform, Multi-Purpose Cryptography as a Service Framework Featuring Scalability, Extendibility and Ease of Integration
Following cybersecurity st and ards nowadays is becoming one of the highest priorities to the digital specialists. Due to the global direction to apply digital transformation, data security is a concern. It becomes crucial to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability whether while transmitting, at rest or even while processing it. The difficulty being faced by organizations, is the challenge of applying the needed security measures. Also, implementing, and maintaining the cryptographic algorithms that ensure the wellness of the data encryption. Having a crypto library or a
Light-Weight Food/Non-Food Classifier for Real-Time Applications
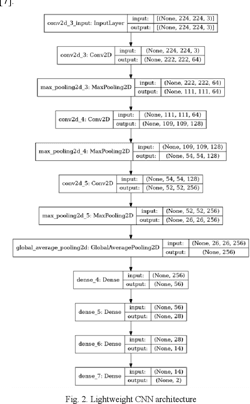
Today, automatic food/non-food classification became extremely important for many real-time applications, specifically since the pandemic of the COVID-19 virus. Such that the 'no food policy' now became applied more than ever to help decrease the spread of the COVID-19 virus. Consequently, many studies used deep neural networks for the food/non-food classification task, yet these deep neural networks were computationally expensive. As a result, in this paper, a lightweight Convolution Neural Network (CNN) is proposed and put into use for classifying foods and non-foods. Compared to prior
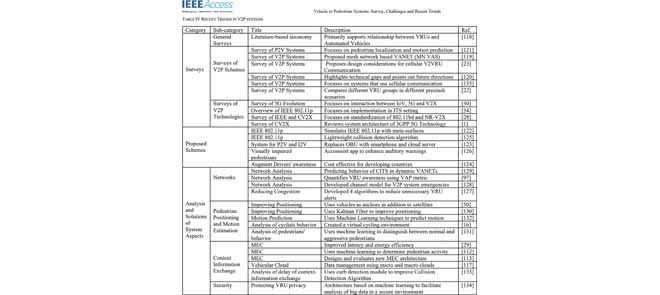
Vehicle to Pedestrian Systems: Survey, Challenges and Recent Trends
The accelerated rise of new technologies has reshaped the manufacturing industry of contemporary vehicles. Numerous technologies and applications have completely revolutionized the driving experience in terms of both safety and convenience. Although vehicles are now connected and equipped with a multitude of sensors and radars for collision avoidance, millions of people suffer serious accidents on the road, and unfortunately, the death rate is still on the rise. Collisions are still a dire reality for vehicles and pedestrians alike, which is why the improvement of collision prevention
Blockchain in Healthcare for Achieving Patients' Privacy
Heath data are sensitive and valuable for individuals. The patients need to integrate and manage their medical data continuously. Personal Health Record (PHR) is introduced as a solution for managing their health information. It gives patients ownership over their medical data and provides physicians with realignment data. However, it does not achieve reliability, traceability, trust, nor security of patient control. Centralization of any data is vulnerable to the problem of hacking and single failure in addition to control from one organization. So, the centralization of data is the common
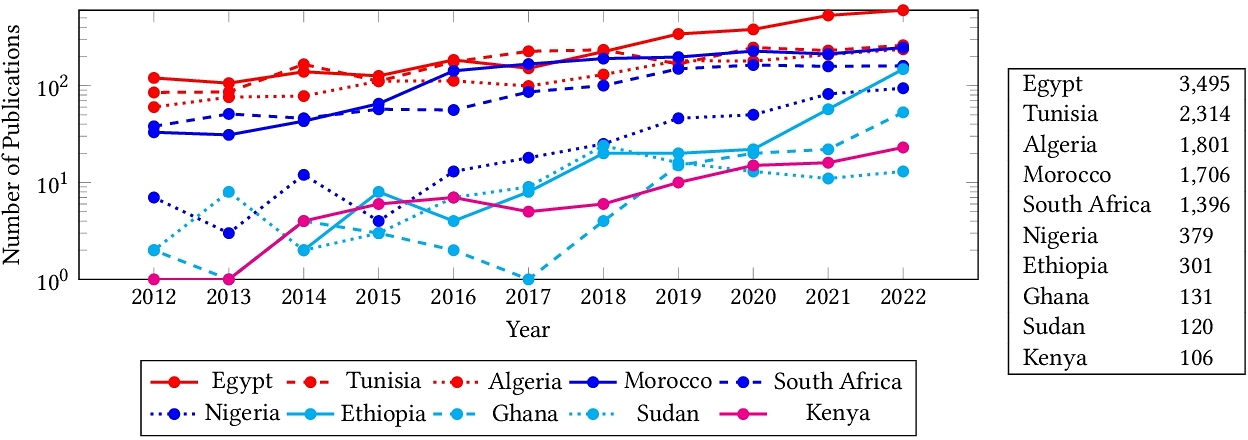
The State of Computer Vision Research in Africa
Despite significant efforts to democratize artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision which is a sub-field of AI, still lags in Africa. A significant factor to this, is the limited access to computing resources, datasets, and collaborations. As a result, Africa's contribution to top-tier publications in this field has only been 0.06% over the past decade. Towards improving the computer vision field and making it more accessible and inclusive, this study analyzes 63,000 Scopus-indexed computer vision publications from Africa. We utilize large language models to automatically parse their
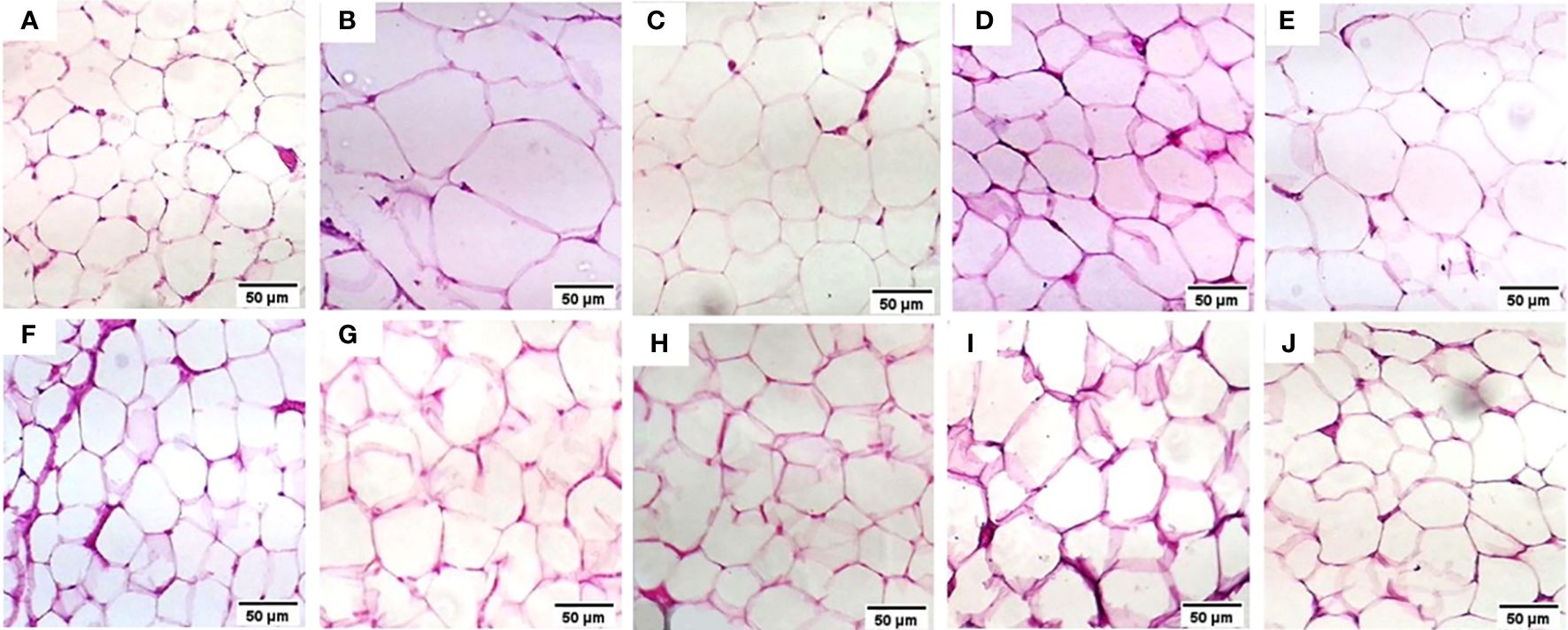
Comprehensive machine learning models for predicting therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes utilizing molecular and biochemical features in rats
Introduction: With the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), there is an urgent need to discover effective therapeutic targets for this complex condition. Coding and non-coding RNAs, with traditional biochemical parameters, have shown promise as viable targets for therapy. Machine learning (ML) techniques have emerged as powerful tools for predicting drug responses. Method: In this study, we developed an ML-based model to identify the most influential features for drug response in the treatment of type 2 diabetes using three medicinal plant-based drugs (Rosavin, Caffeic
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
