Breadcrumb
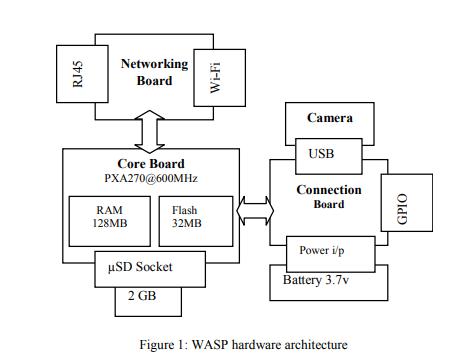
WASP: Wireless autonomous sensor prototype for Visual Sensor Networks
Visual Sensor Networks (VSNs) enable enhanced three-dimensional sensing of spaces and objects, and facilitate collaborative reasoning to open up a new realm of vision-based distributed smart applications including security/surveillance, healthcare delivery, traffic monitoring, just to name a few. However, such applications require sensor nodes that can efficiently process large volumes of visual information in-situ and exhibit intelligent behavior to support autonomous operation, scalability, and energy efficiency. This paper presents WASP, a vision sensor node prototype with high
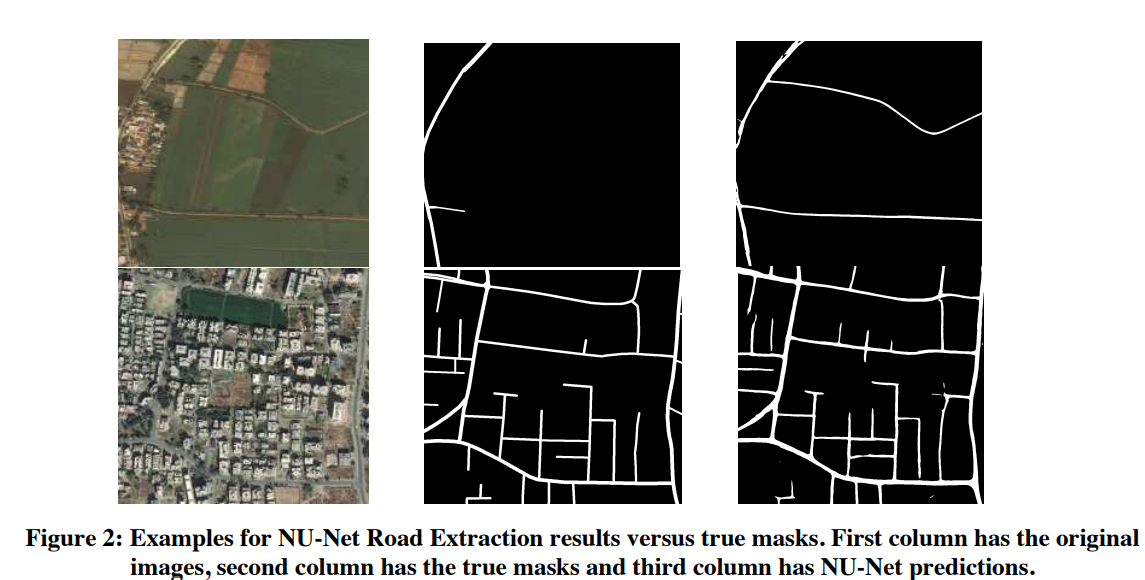
NU-Net: Deep residual wide field of view convolutional neural network for semantic segmentation
Semantic Segmentation of satellite images is one of the most challenging problems in computer vision as it requires a model capable of capturing both local and global information at each pixel. Current state of the art methods are based on Fully Convolutional Neural Networks (FCNN) with mostly two main components: an encoder which is a pretrained classification model that gradually reduces the input spatial size and a decoder that transforms the encoder's feature map into a predicted mask with the original size. We change this conventional architecture to a model that makes use of full
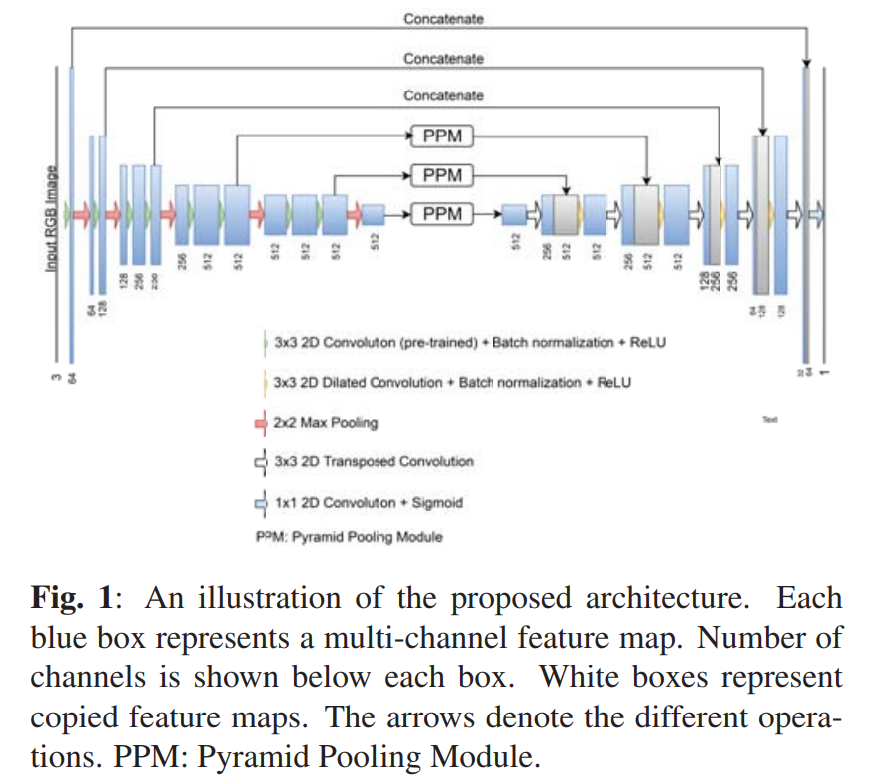
Deep convolutional encoder-decoders with aggregated multi-resolution skip connections for skin lesion segmentation
The prevalence of skin melanoma is rapidly increasing as well as the recorded death cases of its patients. Automatic image segmentation tools play an important role in providing standardized computer-assisted analysis for skin melanoma patients. Current state-of-the-art segmentation methods are based on fully convolutional neural networks, which utilize an encoder-decoder approach. However, these methods produce coarse segmentation masks due to the loss of location information during the encoding layers. Inspired by Pyramid Scene Parsing Network (PSP-Net), we propose an encoder-decoder model
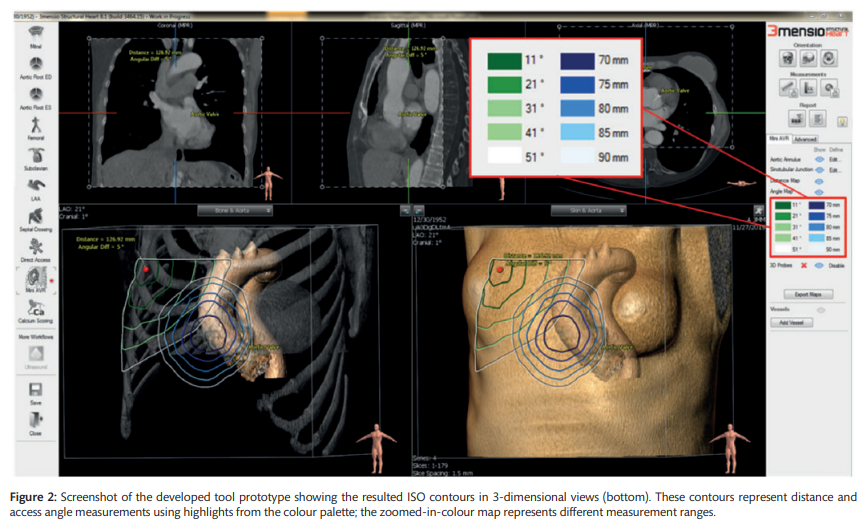
A computed tomography-based planning tool for predicting difficulty of minimally invasive aortic valve replacement
OBJECTIVES Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement has proven its value over the last decade by its significant advancement and reduction in mortality, morbidity and admission time. However, minimally invasive aortic valve replacement is associated with some on-site difficulties such as limited aortic annulus exposure. Currently, computed tomography scans are used to evaluate the anatomical relationship among the intercostal spaces, ascending aorta and aortic valve prior to surgery. We hypothesized that quantitative measurements of access distance and access angle are associated with
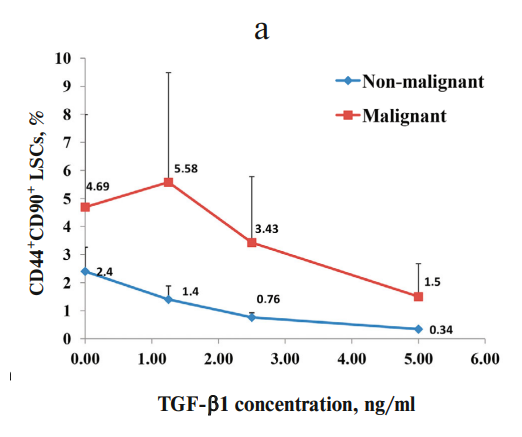
Role of TGF-β1 and C-Kit Mutations in the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients: in vitro Study
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) acts as a tumor-suppressing cytokine in healthy tissues and non-malignant tumors. Yet, in malignancy, TGF-β can exert the opposite effects that can promote proliferation of cancer cells. C-Kit plays a prominent role in stem cell activation and liver regeneration after injury. However, little is known about the cross-talk between TGF-β and C-Kit and its role in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we studied the effect of increasing doses of TGF-β1 on CD44+CD90+ liver stem cells (LSCs) and C-Kit gene expression in malignant and
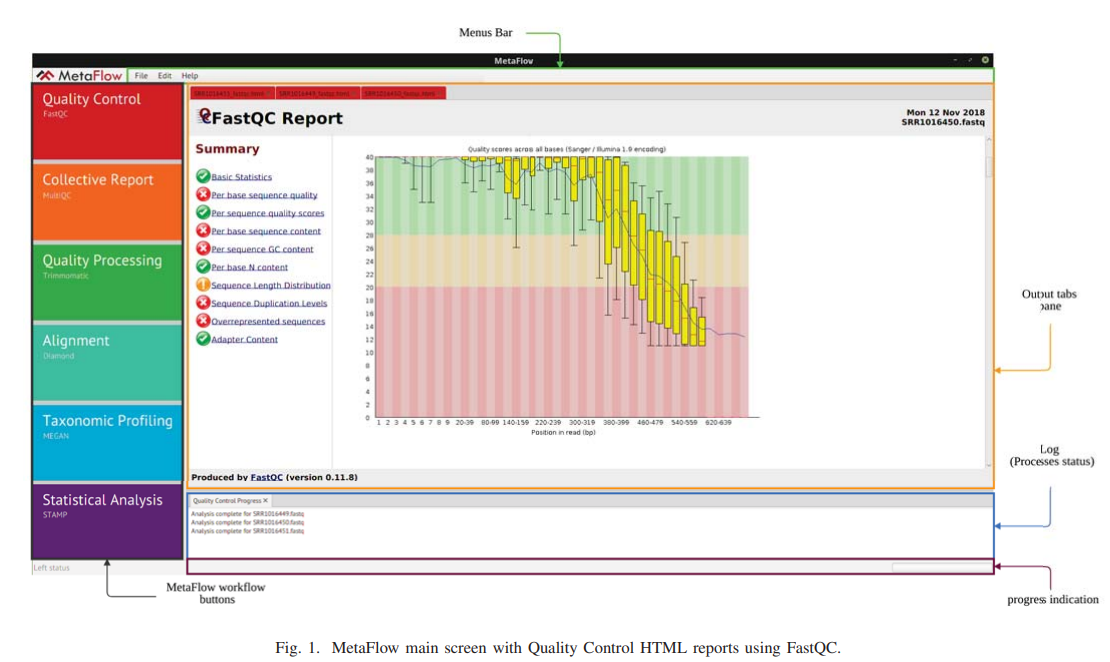
MetaFlow: An interactive user-friendly workflow for automated analysis of whole genome shotgun sequencing metagenomic data
Metagenomics is a rapidly emerging field that is concerned with the study of microbial communities 'microbiomes' on both levels of taxonomic classification and functional annotation. Targeted amplicon (16S rRNA) and whole genome shotgun (WGS) sequencing are the two main sequencing strategies in metagenomics. As amplicon sequencing provides a cheap way to classify the composition of a microbial community, it lacks the ability to identify microbial genes and annotate its corresponding functions. On the other hand, WGS sequencing allows further investigation of the complete genomes with all
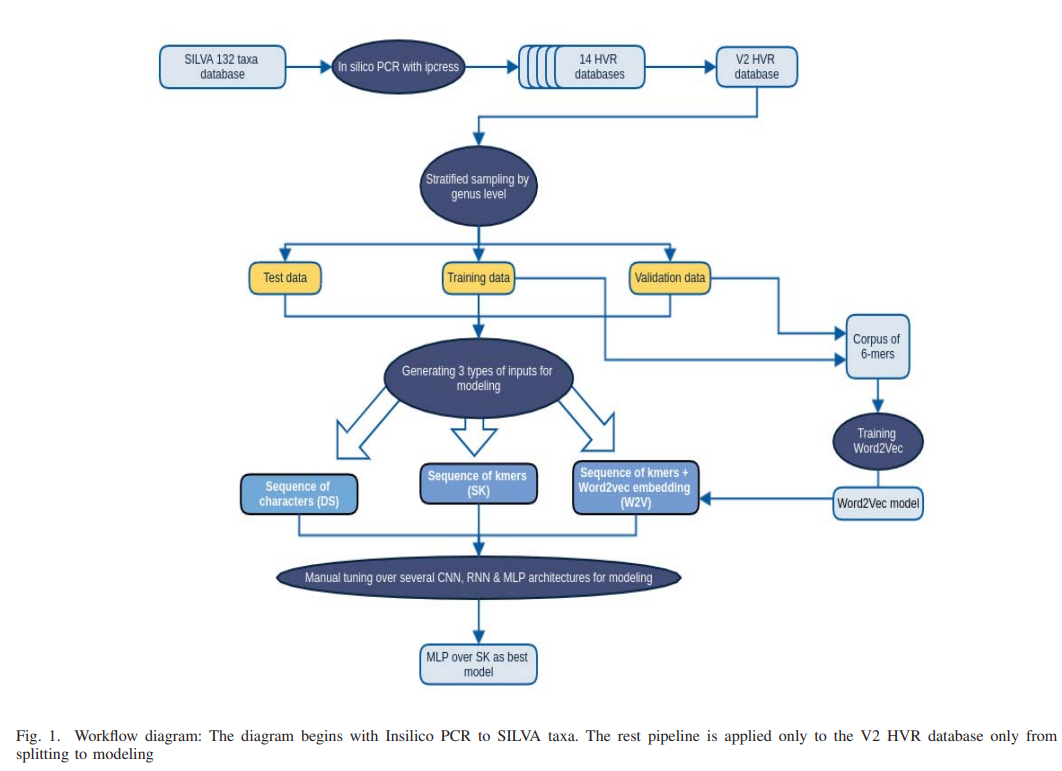
AmpliconNet: Sequence Based Multi-layer Perceptron for Amplicon Read Classification Using Real-time Data Augmentation
Taxonomic assignment is the core of targeted metagenomics approaches that aims to assign sequencing reads to their corresponding taxonomy. Sequence similarity searching and machine learning (ML) are two commonly used approaches for taxonomic assignment based on the 16S rRNA. Similarity based approaches require high computation resources, while ML approaches dont need these resources in prediction. The majority of these ML approaches depend on k-mer frequency rather than direct sequence, which leads to low accuracy on short reads as k-mer frequency doesnt consider k-mer position. Moreover
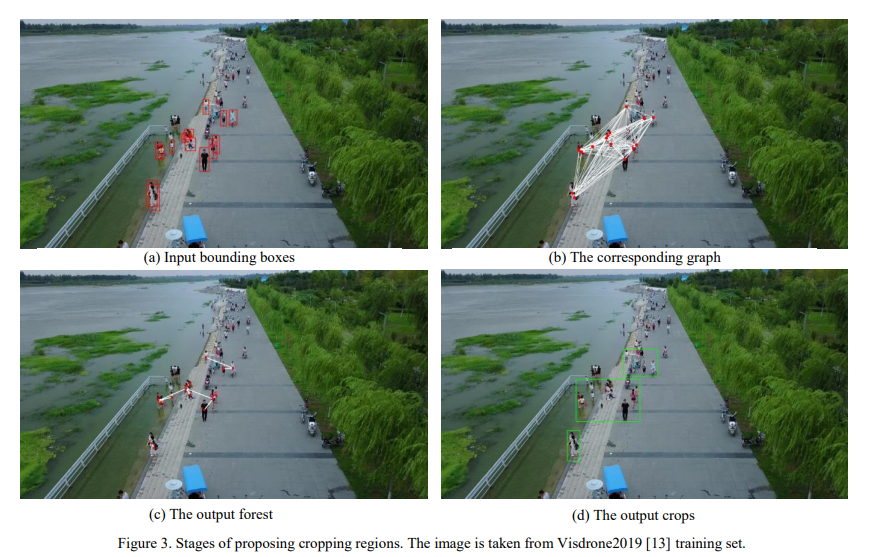
Robust real-time pedestrian detection on embedded devices
Detection of pedestrians on embedded devices, such as those on-board of robots and drones, has many applications including road intersection monitoring, security, crowd monitoring and surveillance, to name a few. However, the problem can be challenging due to continuously-changing camera viewpoint and varying object appearances as well as the need for lightweight algorithms suitable for embedded systems. This paper proposes a robust framework for pedestrian detection in many footages. The framework performs fine and coarse detections on different image regions and exploits temporal and spatial
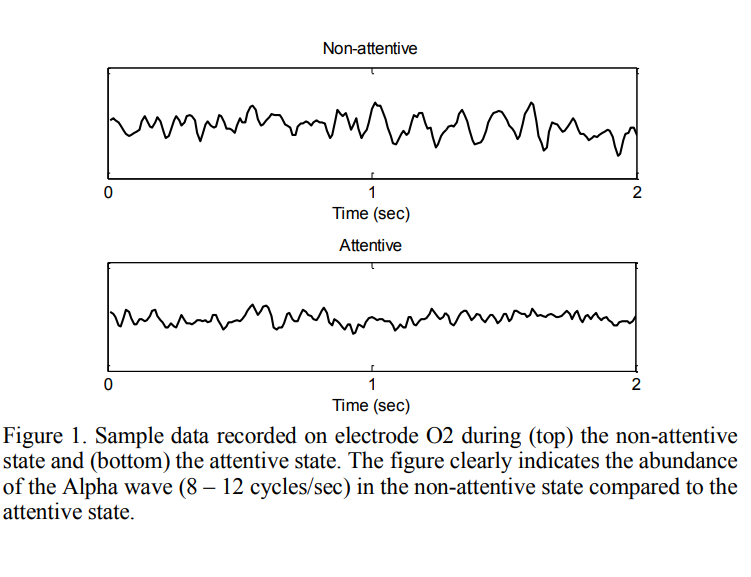
EEG spectral analysis for attention state assessment: Graphical versus classical classification techniques
Advances in Brain-computer Interface (BCI) technology have opened the door to assisting millions of people worldwide with disabilities. In this work, we focus on assessing brain attention state that could be used to selectively run an application on a hand-held device. We examine different classification techniques to assess brain attention state. Spectral analysis of the recorded EEG activity was performed to compute the Alpha band power for different subjects during attentive and non-attentive tasks. The estimated power values were used to train a number of classical classifiers to
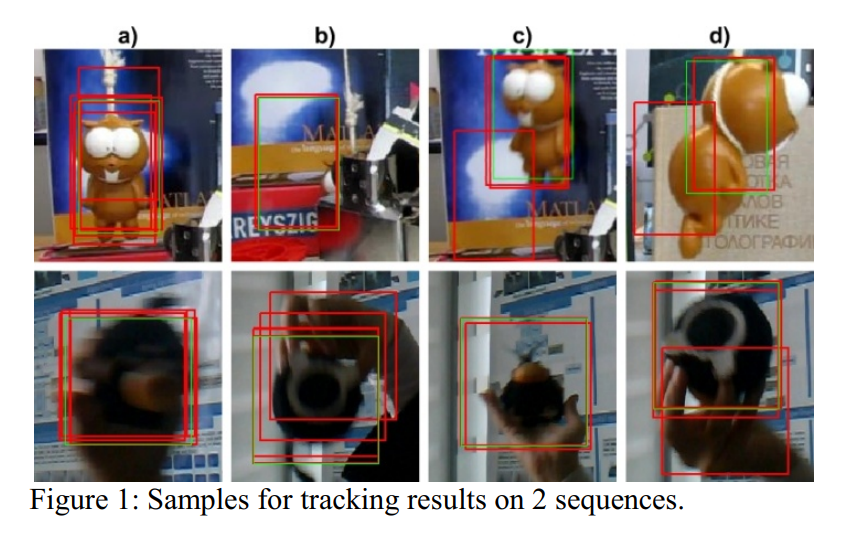

Robust real-time tracking with diverse ensembles and random projections
Tracking by detection techniques have recently been gaining popularity and showing promising results. They use samples classified in previous frames to detect an object in a new frame. However, because they rely on self updating, such techniques are prone to object drift. Multiple classifier systems can be used to improve the detection over that of a single classifier. However, such techniques can be slow as they combine information from different tracking methods. In this paper we propose a novel real-time ensemble approach to tracking by detection. We create a diverse ensemble using random
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 13
- Next page ››

