Breadcrumb
Towards Arabic Image Captioning: A Transformer-Based Approach
The automatic generation of textual descriptions from images, known as image captioning, holds significant importance in various applications. Image captioning applications include accessibility for the visually impaired, social media enhancement, automatic image description for search engines, assistive technology for education, and many more. While extensive research has been conducted in English, exploring this challenge in Arabic remains limited due to its complexity. Arabic is one of the world's most widely spoken languages. Around 420 million native people speak this language. It is also

Sudden Fall Detection and Prediction Using AI Techniques
Fall prediction is a critical process in ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals, particularly the elderly population. This paper focuses on the development of a fall detection and prediction system using wearable sensors and machine learning algorithms. The system issues an alarm upon predicting the occurrence of falling and sends alerts to a monitoring centre for timely assistance. Wearable sensor devices, including Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) equipped with accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers are utilized for data collection. UPFALL, a comprehensive online freely
Clay chips and beads capture in situ barley root microbiota and facilitate in vitro long-term preservation of microbial strains
Capturing the diverse microbiota from healthy and/or stress resilient plants for further preservation and transfer to unproductive and pathogen overloaded soils, might be a tool to restore disturbed plant-microbe interactions. Here, we introduce Aswan Pink Clay as a low-cost technology for capturing and storing the living root microbiota. Clay chips were incorporated into the growth milieu of barley plants and developed under gnotobiotic conditions, to capture and host the rhizospheric microbiota. Afterward, it was tested by both a culture-independent (16S rRNA gene metabarcoding) and

Synthetic to Real Human Avatar Translation via One Shot Pretrained GAN Inversion
This paper tackles the problem of generating pho-torealstic images of synthetically rendered human avatar faces from computer graphics engines, our approach leverages the high capabilities of generative models as StyleGAN that can generate high quality human faces that are hard to distinguish from real human faces images. We present a framework that effectively bridges the gap between synthetic and real domain through Single shot GAN inversion that maps the synthetic image into the real latent space of StyleGAN. Benchmarks and Quantitative results show that our method demonstrate significant
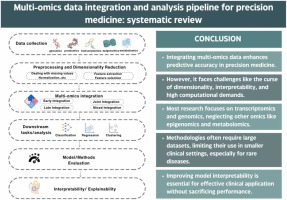
Multi-omics data integration and analysis pipeline for precision medicine: Systematic review
Precision medicine has gained considerable popularity since the “one-size-fits-all” approach did not seem very effective or reflective of the complexity of the human body. Subsequently, since single-omics does not reflect the complexity of the human body's inner workings, it did not result in the expected advancement in the medical field. Therefore, the multi-omics approach has emerged. The multi-omics approach involves integrating data from different omics technologies, such as DNA sequencing, RNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, and others, using computational methods and then analyzing the
New antileishmanial quinoline linked isatin derivatives targeting DHFR-TS and PTR1: Design, synthesis, and molecular modeling studies
In a search for new drug candidates for one of the neglected tropical diseases, leishmaniasis, twenty quinoline-isatin hybrids were synthesized and tested for their in vitro antileishmanial activity against Leishmania major strain. All the synthesized compounds showed promising in vitro activity against the promastigote form in a low micromolar range (IC50 = 0.5084–5.9486 μM) superior to the reference miltefosine (IC50 = 7.8976 μM). All the target compounds were then tested against the intracellular amastigote form and showed promising inhibition effects (IC50 = 0.60442–8.2948 μM versus 8.08
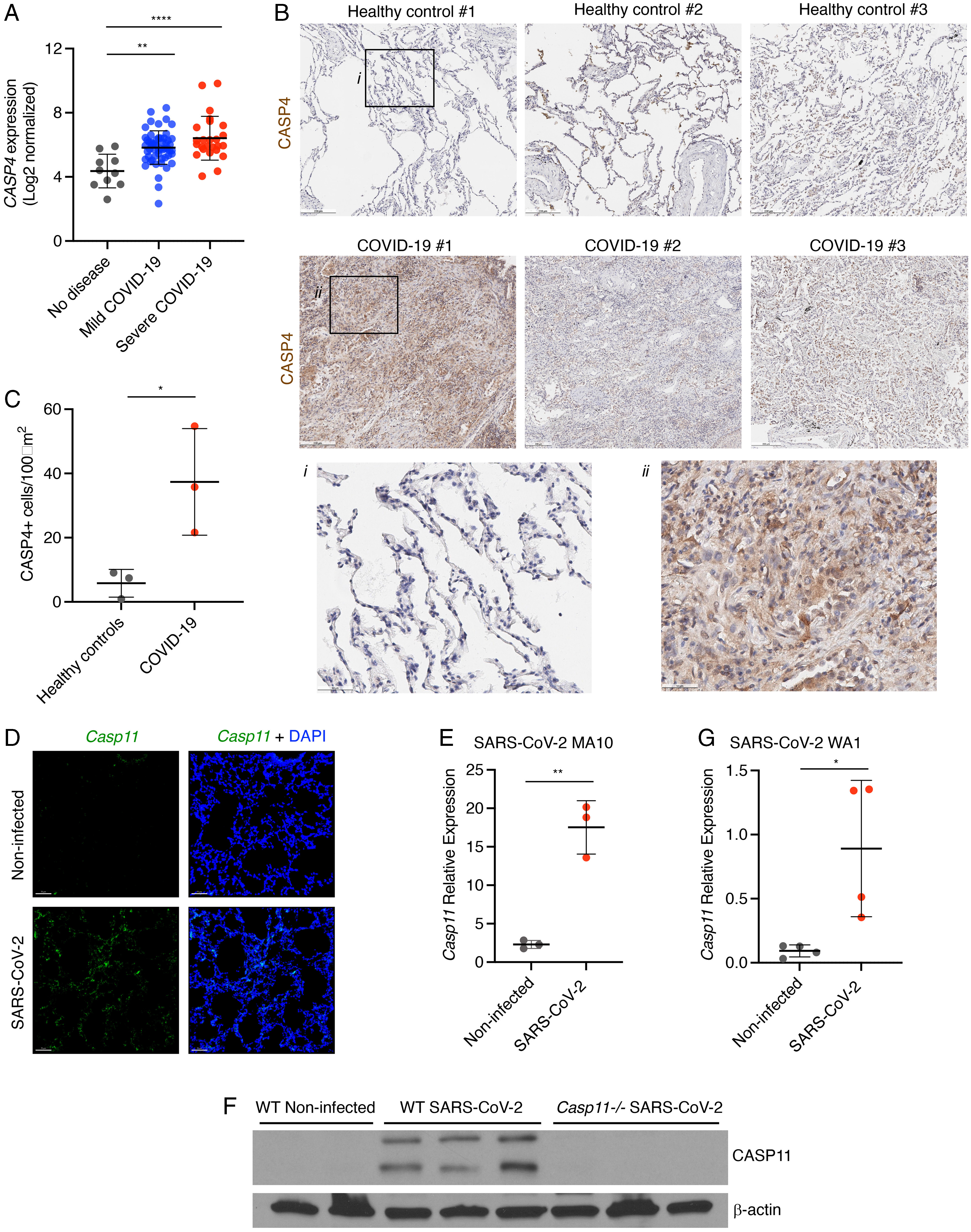
Caspase-4/11 exacerbates disease severity in SARS–CoV-2 infection by promoting inflammation and immunothrombosis
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS–CoV-2) is a worldwide health concern, and new treatment strategies are needed. Targeting inflammatory innate immunity pathways holds therapeutic promise, but effective molecular targets remain elusive. Here, we show that human caspase-4 (CASP4) and its mouse homolog, caspase-11 (CASP11), are up-regulated in SARS–CoV-2 infections and that CASP4 expression correlates with severity of SARS–CoV-2 infection in humans. SARS–CoV-2–infected Casp112/2 mice were protected from severe weight loss and lung pathology, including blood vessel damage
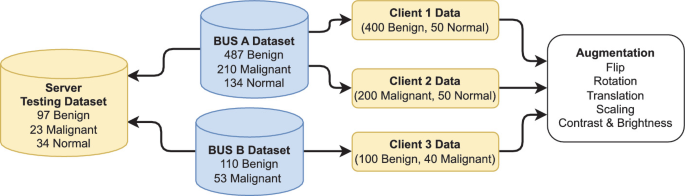
A Novel Approach to Breast Cancer Segmentation Using U-Net Model with Attention Mechanisms and FedProx
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death among women worldwide, emphasizing the need for early detection and accurate diagnosis. As such Ultrasound Imaging, a reliable and cost-effective tool, is used for this purpose, however the sensitive nature of medical data makes it challenging to develop accurate and private artificial intelligence models. A solution is Federated Learning as it is a promising technique for distributed machine learning on sensitive medical data while preserving patient privacy. However, training on non-Independent and non-Identically Distributed (non-IID) local datasets
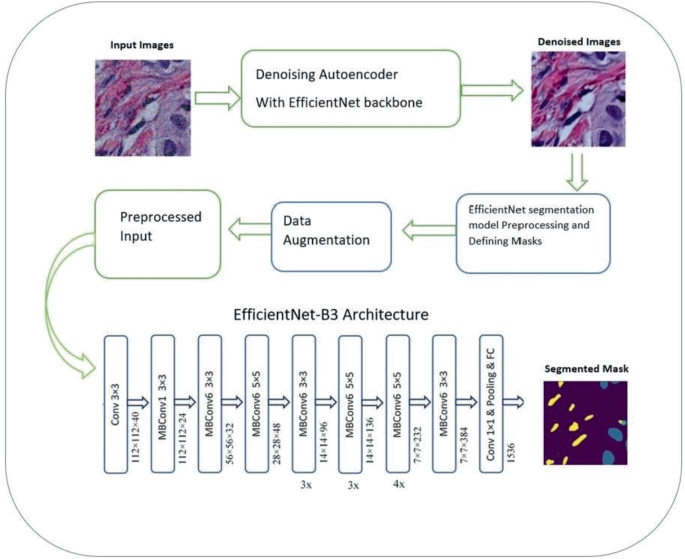
Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis Through Hybrid Self-supervised Deep Learning: EfficientNet with Denoising Autoencoder for Semantic Segmentation of Histopathological Images
Machine Learning technologies are being developed day after day, especially in the medical field. New approaches, algorithms and architectures are implemented to increase the efficiency and accuracy of diagnosis and segmentation. Deep learning approaches have proven their efficiency; these approaches include architectures like EfficientNet and Denoising Autoencoder. Accurate segmentation of nuclei in histopathological images is essential for the diagnosis and prognosis of diseases like cancer. In this paper, we propose a novel method for semantic segmentation of nuclei using EfficientNet and
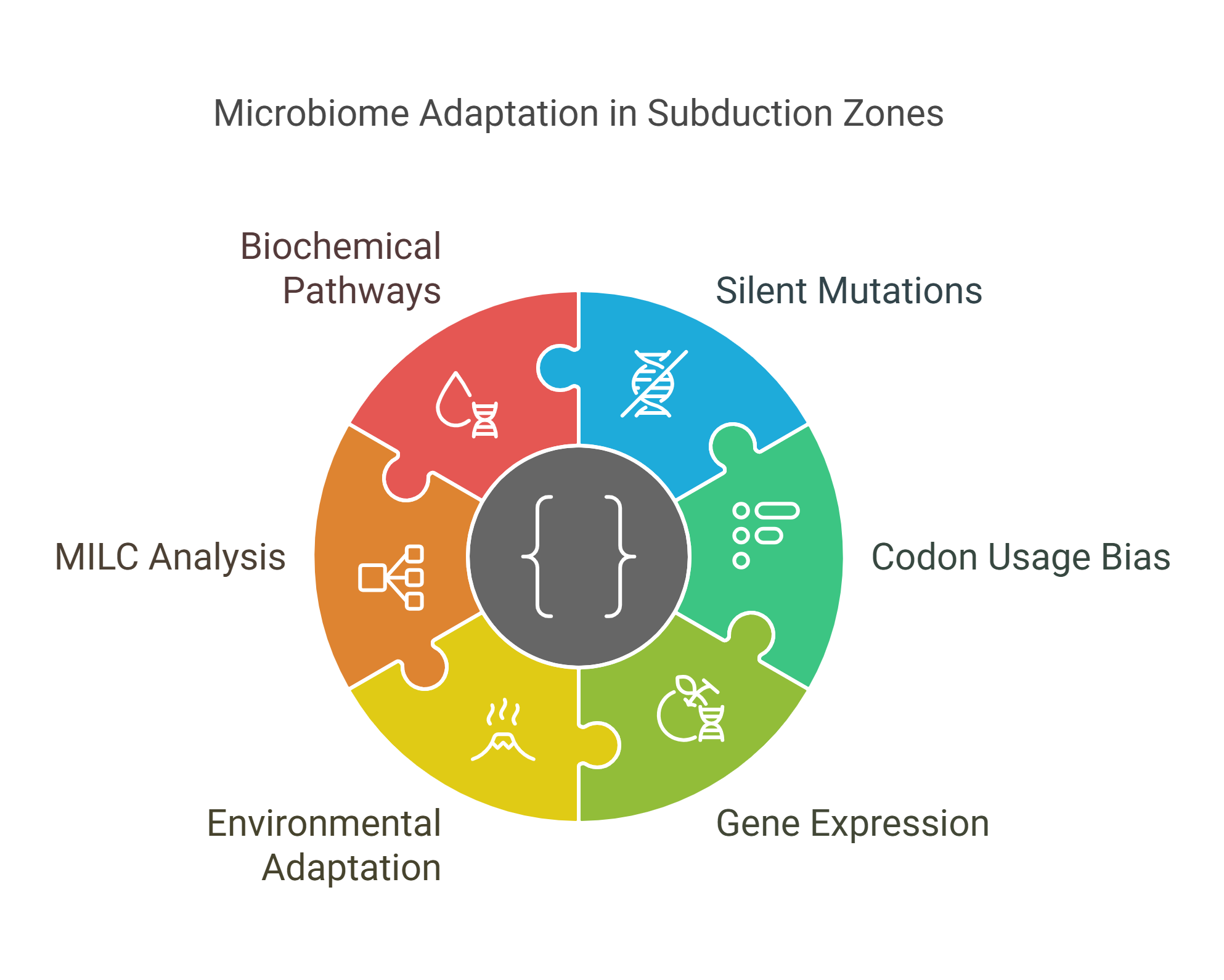
The Melody of Silent Mutations: Microbiome Adaptation Across the Subduction Zone
Silent mutations generate synonymous codons that encode the same amino acid however, they may be silent yet operative. These synonymous codons are used in unequal frequencies resulting in a phenomenon known as codon usage bias (CUB). It drives gene expression towards highly expressed and adaptation genes. In this study we investigated CUB in one of the largest, most dynamic exotic niches, the volcanic subduction zones in Costa Rica. CUB analysis in such challengingly inaccessible sites can help distinguish highly expressed genes under certain environmental factors, elucidating molecular
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
