Breadcrumb

Advanced Phishing Detection in Ethereum Blockchain Transactions Using Machine Learning Models
Deceptive phishing attacks greatly endanger blockchain security, tricking miners into adding harmful blocks to the chain. Current methods of detection and agreement protocols are frequently not enough, especially if authorized miners accidentally include these blocks. Despite the potential for improving detection capabilities, the adoption of zero-trust policies is still restricted. This paper explores different machine learning techniques, like k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN), Decision Trees (DT), Random Forest (RF), and XGBoost, to predict phishing attacks. It also evaluates feature selection
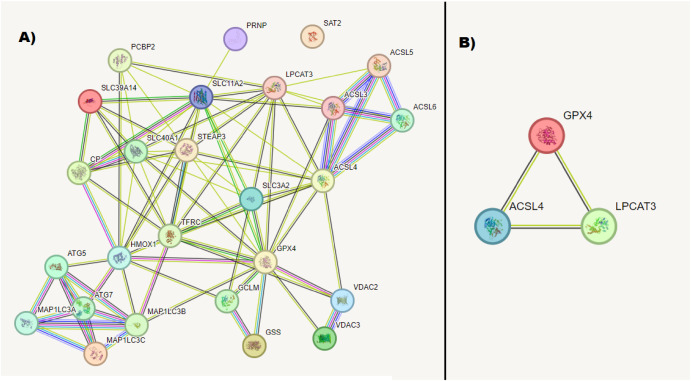
Innovative approaches to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis diagnosis and stratification
The global rise in Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)/Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) highlights the urgent necessity for noninvasive biomarkers to detect these conditions early. To address this, we endeavored to construct a diagnostic model for MASLD/MASH using a combination of bioinformatics, molecular/biochemical data, and machine learning techniques. Initially, bioinformatics analysis was employed to identify RNA molecules associated with MASLD/MASH pathogenesis and enriched in ferroptosis and exophagy. This analysis unveiled specific
Immunoinformatics approach of epitope prediction for SARS-CoV-2
Background: The novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) caused lethal infections worldwide during an unprecedented pandemic. Identification of the candidate viral epitopes is the first step in the design of vaccines against the viral infection. Several immunoinformatic approaches were employed to identify the SARS-CoV-2 epitopes that bind specifically with the major histocompatibility molecules class I (MHC-I). We utilized immunoinformatic tools to analyze the whole viral protein sequences, to identify the SARS-CoV-2 epitopes responsible for binding to the most frequent human leukocyte antigen (HLA)
Semi-Supervised Machine Learning Applications in RAN Design: Towards Data-Driven Next Generation Cellular Networks
The explosive growth of mobile internet services and demand for data connectivity boosts the innovation and development in Radio Access Network (RAN) to define how next generation mobile networks will look like. Continuous improvement in existing RAN is crucial to meet very strict speed and latency requirements by different mobile applications with minimum investments. Exploiting the advancement in Machine Learning and AI-driven algorithms is essential to tackle these challenges in different functions within the RAN domain. In this paper we surveyed how to leverage different clustering

DevSecOps: A Security Model for Infrastructure as Code over the Cloud
DevSecOps includes security practice while applying DevOps. DevSecOps help secure the whole DevOps process. This paper aims to define a DevSecOps module to be used by the infrastructure team while applying infrastructure as code. The proposed module solves the problem of security by including security practice with the DevOps cycle to reach DevSecOps. The module was tested to measure time effi-ciency. A small survey was created to test other DevSecOps metrics and enhance future work. © 2022 IEEE.
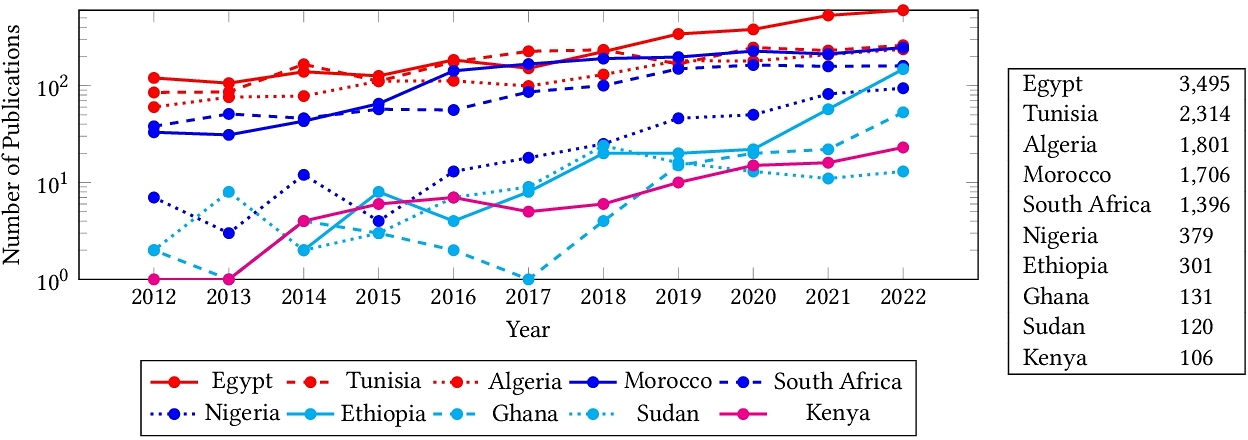
The State of Computer Vision Research in Africa
Despite significant efforts to democratize artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision which is a sub-field of AI, still lags in Africa. A significant factor to this, is the limited access to computing resources, datasets, and collaborations. As a result, Africa's contribution to top-tier publications in this field has only been 0.06% over the past decade. Towards improving the computer vision field and making it more accessible and inclusive, this study analyzes 63,000 Scopus-indexed computer vision publications from Africa. We utilize large language models to automatically parse their
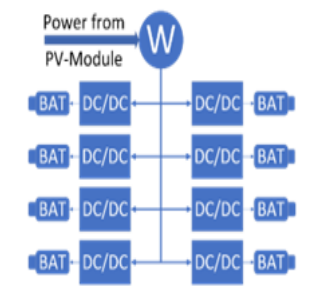
Developing Role Model of PV Powered Battery Swapping Stations for e-scooters in Urban Regions
Electric vehicles (EVs) can only provide lower carbon emissions than conventional, internal combustion-powered vehicles if they are charged using green energy. They also have the drawback of long charging times to 'refuel' them. To combat these two problems, a solar-powered battery charging and swapping station was developed using centered-human design and systems engineering. The design focuses on electric two-wheeled vehicles (e-scooters) due to the easier handling of their light and low-capacity batteries compared to electric cars. These stations are easy to maintain and manage and can be
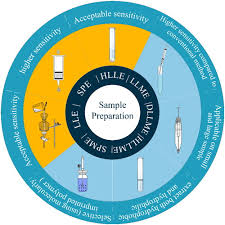
Analytical Methods for the Determination of Quercetin and Quercetin Glycosides in Pharmaceuticals and Biological Samples
Flavonoids are plant-derived compounds that have several health benefits, including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-mutagenic, and anti-carcinogenic effects. Quercetin is a flavonoid that is widely present in various fruits, vegetables, and drinks. Accurate determination of quercetin in different samples is of great importance for its potential health benefits. This review, is an overview of sample preparation and determination methods for quercetin in diverse matrices. Previous research on sample preparation and determination methods for quercetin are summarized, highlighting the
NGU_CNLP at WANLP 2022 Shared Task: Propaganda Detection in Arabic
This paper presents the system developed by the NGU_CNLP team for addressing the shared task on Propaganda Detection in Arabic at WANLP 2022. The team participated in the shared tasks' two sub-tasks which are: 1) Propaganda technique identification in text and 2) Propaganda technique span identification. In the first sub-task the goal is to detect all employed propaganda techniques in some given piece of text out of a possible 17 different techniques, or to detect that no propaganda technique is being used in that piece of text. As such, this first sub task is a multi-label classification
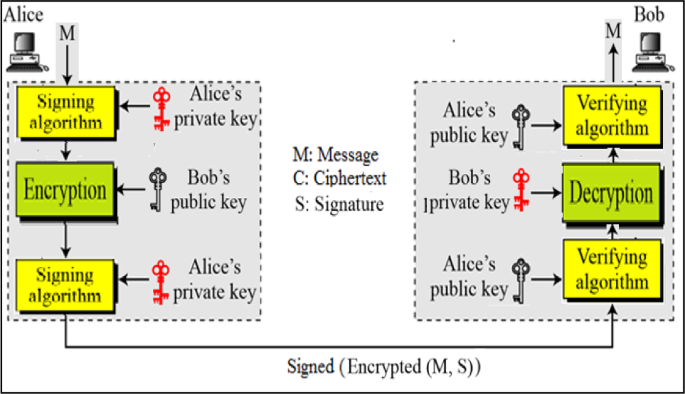
Networking and cryptography library with a non-repudiation flavor for blockchain
Blockchain is currently one of the most widely discussed inventions in the information and communication technology industry. It is a pillar of the fourth industrial revolution and it is a cryptographically demanding technology that is regarded as one of the most influential topics in academia. Many blockchain platforms currently utilize third-party cryptographic libraries that offer many cryptographic primitives in order to ensure users' protection against cyber-attacks. The Networking and Cryptography library (NaCl) is an open-source library for cryptographic primitives. NaCl is known to be
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
