Breadcrumb
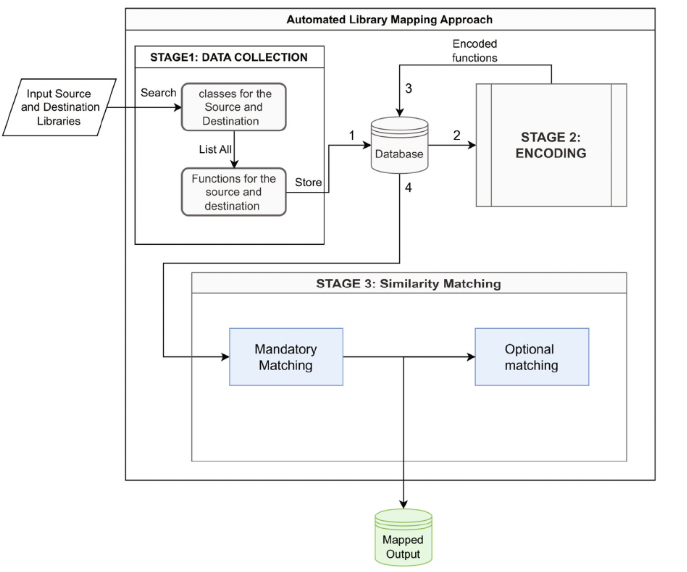
Automated library mapping approach based on cross-platform for mobile development programming languages
Context: The most popular mobile platforms, Android and iOS, are traditionally developed using native programming languages—Java and Kotlin for Android, and Objective-C followed by Swift for iOS, respectively. Due to their popularity, there is always a demand to convert applications written for one of these two platforms to another. Cross-platform mobile development is widely used as a solution where an application is written once and deployed on multiple platforms written in several other programming languages. One common cross-platform approach that has been used recently by some research

A (k,n)-Secret Image Sharing With Steganography Using Generalized Tent Map
Secret Image Sharing (SIS) transfers an image to mutually suspicious receivers as n meaningless shares, where k or more shares must be present to recover the secret. This paper proposes a (k, n)-SIS system for any image type using polynomial interpolation based on Lagrange polynomials, where the generated shares are of size 1/k of the secret image size. A full encryption system, consisting of substitution and permutation stages, is employed by using the generalized Tent map as a source of randomness. In addition to using a long and sensitive system key, steganography using the Least

A distributed real-time recommender system for big data streams
Recommender Systems (RS) play a crucial role in our lives. As users become continuously connected to the internet, they are less tolerant of obsolete recommendations made by an RS. Online RS has to address three requirements: continuous training and recommendation, handling concept drifts, and the ability to scale. Streaming RS proposed in the literature address the first two requirements only. That is because they run the training process on a single machine. To tackle the third challenge, we propose a Splitting and Replication mechanism for distributed streaming RS. Our mechanism is inspired
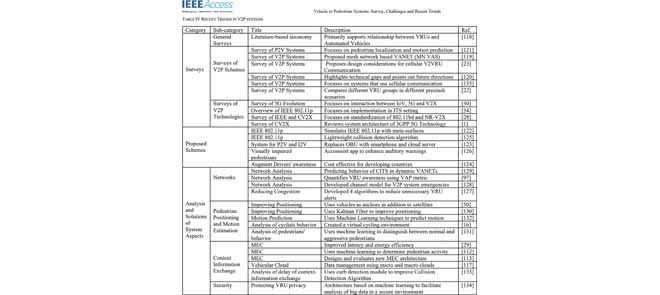
Vehicle to Pedestrian Systems: Survey, Challenges and Recent Trends
The accelerated rise of new technologies has reshaped the manufacturing industry of contemporary vehicles. Numerous technologies and applications have completely revolutionized the driving experience in terms of both safety and convenience. Although vehicles are now connected and equipped with a multitude of sensors and radars for collision avoidance, millions of people suffer serious accidents on the road, and unfortunately, the death rate is still on the rise. Collisions are still a dire reality for vehicles and pedestrians alike, which is why the improvement of collision prevention
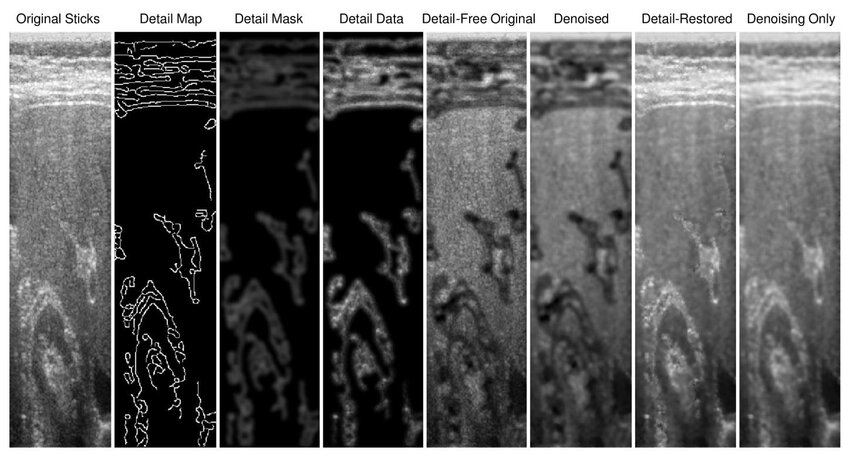
Edge Detail Preservation Technique for Enhancing Speckle Reduction Filtering Performance in Medical Ultrasound Imaging
—Ultrasound imaging is a unique medical imaging modality due to its clinical versatility, manageable biological effects, and low cost. However, a significant limitation of ultrasound imaging is the noisy appearance of its images due to speckle noise, which reduces image quality and hence makes diagnosis more challenging. Consequently, this problem received interest from many research groups and many methods have been proposed for speckle suppression using various filtering techniques. The common problem with such methods is that they tend to distort the edge detail content within the image and

Comparative Analysis of a Generalized Heart Localization Model: Assessing Its Efficacy Against Specialized Models
Heart localization holds significant importance in the process of the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases. Additionally, it plays an important role in planning the cardiac scanning protocol. This research focuses on heart localization by employing the multi-label classification task with the utilization of RES-Net50. The primary objective is to predict the slices containing the heart and determine its endpoint. To ensure high-quality data, we implement filtering techniques and perform up-sampling during the pre-processing stage. Two experiments were conducted to assess different
NGU_CNLP at WANLP 2022 Shared Task: Propaganda Detection in Arabic
This paper presents the system developed by the NGU_CNLP team for addressing the shared task on Propaganda Detection in Arabic at WANLP 2022. The team participated in the shared tasks' two sub-tasks which are: 1) Propaganda technique identification in text and 2) Propaganda technique span identification. In the first sub-task the goal is to detect all employed propaganda techniques in some given piece of text out of a possible 17 different techniques, or to detect that no propaganda technique is being used in that piece of text. As such, this first sub task is a multi-label classification
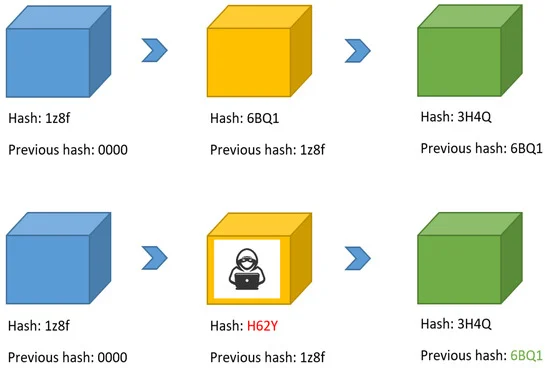
Smart Automotive Diagnostic and Performance Analysis Using Blockchain Technology
The automotive industry currently is seeking to increase remote connectivity to a vehicle, which creates a high demand to implement a secure way of connecting vehicles, as well as verifying and storing their data in a trusted way. Furthermore, much information must be leaked in order to correctly diagnose the vehicle and determine when or how to remotely update it. In this context, we propose a Blockchain-based, fully automated remote vehicle diagnosis system. The proposed system provides a secure and trusted way of storing and verifying vehicle data and analyzing their performance in
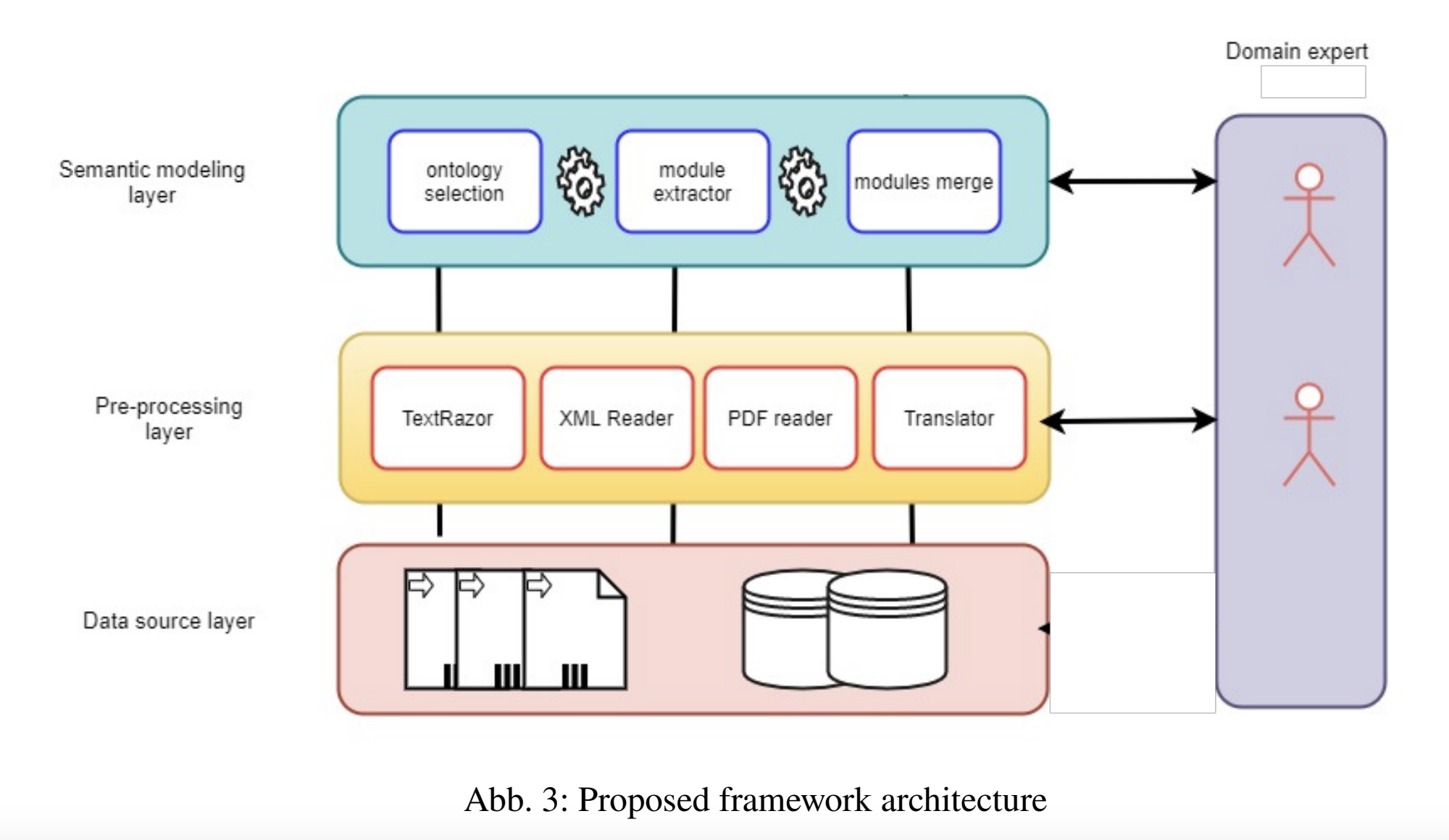
A Core Ontology to Support Agricultural Data Interoperability
The amount and variety of raw data generated in the agriculture sector from numerous sources, including soil sensors and local weather stations, are proliferating. However, these raw data in themselves are meaningless and isolated and, therefore, may offer little value to the farmer. Data usefulness is determined by its context and meaning and by how it is interoperable with data from other sources. Semantic web technology can provide context and meaning to data and its aggregation by providing standard data interchange formats and description languages. In this paper, we introduce the design

Design and Implementation of a Dockerized, Cross Platform, Multi-Purpose Cryptography as a Service Framework Featuring Scalability, Extendibility and Ease of Integration
Following cybersecurity st and ards nowadays is becoming one of the highest priorities to the digital specialists. Due to the global direction to apply digital transformation, data security is a concern. It becomes crucial to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability whether while transmitting, at rest or even while processing it. The difficulty being faced by organizations, is the challenge of applying the needed security measures. Also, implementing, and maintaining the cryptographic algorithms that ensure the wellness of the data encryption. Having a crypto library or a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
